Abstract
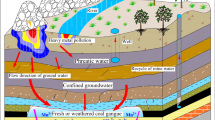
Large quantities of solid wastes, including gangue (waste rock) have been added to the goafs in China’s coal mines as backfill. In this study, the mineral and chemical compositions of gangue from the No. 12 coal mine of the Pingdingshan Coal Group were investigated to determine potential pollution concerns, and the behaviour of contaminants in the gangue, such as salts, alkali metals, and alkaline earth metals, was explored using static immersion tests. COMSOL Multiphysics was used to study contaminant migration. The concentration and diffusion distance of metal ions were found to increase over time; this was negatively correlated with gangue particle size. Acidic environments promoted the dissolution of Ca, Fe, Mn, Na, Zn, Pb, and Be, while in alkaline environments, Se dissolution was accelerated.
Zusammenfassung
Große Mengen an Festabfällen, darunter auch Abraum (Gangart bzw. taubes Gestein), wurden zur Verfüllung ausgekohlter Abbaubereiche in Chinas Kohleminen verwendet. In der vorliegenden Studie wurde die mineralogische und chemische Zusammensetzung von Abraum aus der Kohlemine Nr. 12 der Pingdingshan Coal Group erforscht, um potentielle Risiken im Hinblick auf Umweltverschmutzungen festzustellen. Weiterhin wurde das Verhalten von Schadstoffen wie z.B. Salzen, Alkalimetallen und Erdalkalimetallen im Abraum mittels statischer Immersionsversuche untersucht. Mittels COMSOL Multiphysics wurde die Ausbreitung von Schadstoffen untersucht. Es wurde festgestellt, dass die Konzentration und Ausbreitungsdistanz von Metallionen über die Zeit zunahm, was wiederum negativ mit der Korngröße des Abraums korrelierte. Ein saures Milieu begünstigte die Auflösung von Ca, Fe, Mn, Na, Zn, Pb, and Be, wohingegen im alkalischen Milieu die Auflösung von Se beschleunigt wurde.
Resumen
Se han agregado grandes cantidades de desechos sólidos, incluida ganga (roca de desecho) a los hoyos en las minas de carbón de China como relleno. Se estudiaron las composiciones minerales y químicas de la ganga de la mina de carbón número 12 del Grupo de Carbón Pingdingshan, para determinar posibles problemas de contaminación, y se exploró el comportamiento de los contaminantes en la ganga, como sales, metales alcalinos y metales alcalinotérreos, utilizando pruebas de inmersión estática. COMSOL Multiphysics se usó para estudiar la migración de contaminantes. La concentración y la distancia de difusión de los iones metálicos aumentaron con el tiempo; esto se correlacionó negativamente con el tamaño de partícula de ganga. Los ambientes ácidos promovieron la disolución de Ca, Fe, Mn, Na, Zn, Pb y Be, mientras que en ambientes alcalinos, la disolución de Se se aceleró.
摘要
在中国,大量固体废物(包括矸石)已经被充填到采空区。研究了平顶山矿业集团12矿矸石的矿物和化学成分以识别潜在污染,采用静态浸泡试验分析盐、碱金属、碱土金属等矸石污染物化学行为特征,通过COMSOL Multiphysics预测污染物运移归宿。金属离子的浓度和扩散距离随时间推移而增大,随矸石粒径增大而减小。酸性环境促进钙、铁、锰、钠、锌、铅和铍溶解,而碱性环境加速了硒溶解。










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bian Z, Miao X, Lei S, Chen SE, Wang W, Struthers S (2012) The challenges of reusing mining and mineral-processing wastes. Science 337(6095):702–703. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1224757
Cao YQ, Zhang SS, Liu HH, Wei L (2010) Leaching characteristics of heavy metals in coal gangue in both dynamic leaching and static immersion. J Hebei Univ Eng 27(1):76–80 (in Chinese)
Cheng F, Cheng JP, Sang HC, Yu JL, Xi L, Pi SS (2013) Assessment and correlation analysis of heavy metals pollution in soil of Dajinshan Island. Environ Sci 34(3):1062. https://doi.org/10.13227/j.hjkx.2013.03.033
Dang Z, Wan GJ, LI DR, Watts SF, Haigh M (1996) Kinetics of coal mine spoil—water interaction—II. Mineralogical study on trace metal elements in coal gangue. Sci Chin D 26(1):16–20 (in Chinese)
Dang Z, Liu CQ, Li Z (2001) Experimental simulation of chemical activity of heavy metals in coal gangue. J S Chin Univ Tech Nat Sci 29(12):1–5 (in Chinese)
Faisal AAH, Ali ZTA (2016) Groundwater protection from lead contamination using granular dead anaerobic sludge biosorbent as permeable reactive barrier. Desalin Water Treat 57(9):3891–3903. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2014.990928
General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine (2002) Environmental quality standards for surface water. GB 3838-2002. Standards Press of China, Beijing
General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine (2007) Identification standards for hazardous wastes—identification for extraction toxicity. In: GB5085.3-2007. Standards Press of China, Beijing
General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine (2017) Standard for groundwater quality. GB/T 14848-2017. Standards Press of China, Beijing
Guo C (2010) Research progress of coal gangue adsorbent. China Sci Technol Expo (34): 378–379 (in Chinese)
He B, Zhang Y, Li XD (2014) Research on experimental dissolution of coal gangue main pollution components. Bull Chin Ceram Soc 33(9):2217–2222 (in Chinese)
Hu J, Hu ND, Lian ML, Miao YJ (2013) Progress of application of coal gangue in the wastewater treatment. Yunnan Chem Technol 40(02):22–25 (in Chinese)
Huang Y, Zhang J, Zhang Q, Nie S (2011a) Backfilling technology of substituting waste and fly ash for coal underground in china coal mining area. Environ Eng Manag J 10(6):769–775
Huang Y, Zhang J, An B, Zhang Q (2011b) Overlying strata movement law in fully mechanized coal mining and backfilling longwall face by similar physical simulation. J Min Sci 47(5):618–627
Ilhan S, Kalpakli AO, Kahruman C, Yusufoglu I (2013) The investigation of dissolution behavior of gangue materials during the dissolution of scheelite concentrate in oxalic acid solution. Hydrometallurgy 136(4):15–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydromet.2013.02.013
Jeng A (1992) Weathering of some Norwegian alum shales II. Laboratory simulations to study the influence of aging, acidification and liming on heavy metal release. Acta Agr Scand B 42(2):76–87. https://doi.org/10.1080/09064719209410203
Ju F, Huang P, Guo S, Xiao M, Lan L (2017) A roof model and its application in solid backfilling mining. Int J Min Sci Technol 27 (1):139-143
Li J (2013) Evolution mechanism and control of water-flowing fracture with gangue backfill under aquifer in coal mine. China University of Mining and Technology, Xuzhou (in Chinese)
Li D, Chen HJ (2012) Study development of wastewater adsorbent prepared by coal gangue. J Luoyang Inst Sci Tech 22(03):6–9, 15 (in Chinese)
Li P, Qian H (2011) Human health risk assessment for chemical pollutants in drinking water source in Shizuishan city, northwest China. Iran J Env Hlth Sci Eng I 8(1):41–48
Li H, Sun H, Tie X, Xiao X (2006) Dissolution properties of calcined gangue. J Univ Sci Tech Beijing Min Metal Mater 13(6):570–576 (in Chinese)
Li P, Wu J, Qian H, Lyu X, Liu H (2014a) Origin and assessment of groundwater pollution and associated health risk: a case study in an industrial park, northwest China. Environ Geochem Health 36(4):693–712. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-013-9590-3
Li P, Qian H, Howard KWF, Wu J, Lyu X (2014b) Anthropogenic pollution and variability of manganese in alluvial sediments of the yellow river, Ningxia, northwest China. Environ Monit Assess 186(3):1385–1398. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-013-3461-3
Li P, Qian H, Howard KWF, Wu J (2015a) Building a new and sustainable “Silk Road economic belt”. Environ Earth Sci 74(10):7267–7270. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-4739-2
Li P, Qian H, Howard KWF, Wu J (2015b) Heavy metal contamination of yellow river alluvial sediments, northwest China. Environ Earth Sci 73(7):3403–3415. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3628-4
Li P, Wu J, Qian H, Zhang Y, Yang N, Jing L, Yu P (2016a) Hydrogeochemical characterization of groundwater in and around a wastewater irrigated forest in the southeastern edge of the Tengger Desert, northwest China. Expos Health 8(3):331–348. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-016-0193-y
Li P, Wu J, Qian H, Zhou W (2016b) Distribution, enrichment and sources of trace metals in the topsoil in the vicinity of a steel wire plant along the Silk Road economic belt, northwest China. Environ Earth Sci 75(10):1–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5719-x
Li P, Qian H, Zhou W (2017) Finding harmony between the environment and humanity: an introduction to the thematic issue of the Silk Road. Environ Earth Sci 76(3):105. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-6428-9
Li P, Tian R, Liu R (2018a) Solute geochemistry and multivariate analysis of water quality in the Guohua phosphorite mine, Guizhou province, China. Expos Health. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-018-0277-y
Li P, Wu J, Tian R, He S, He X, Xue C (2018b) Geochemistry, hydraulic connectivity and quality appraisal of multilayered groundwater in the Hongdunzi coal mine, northwest China. Mine Water Environ 37(2):222–237. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10230-017-0507-8
Liu D (2006) Research on environmental effect and comprehensive utilization of coal-waste rocks. J Meteorol Environ 3:60–62 (in Chinese)
Ma D, Bai H, Chen Z, Pu H (2015) Effect of particle mixture on seepage properties of crushed mudstones. Transp Porous Med 108(2):257–277. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-015-0473-1
Miao XX (2012) Progress of fully mechanized mining with solid backfilling technology. J Chin Coal Soc 37(8):1247–1255 (in Chinese)
Miao X, Zhang J, Guo G (2010) Method and technology of fully-mechanized coal mining with solid waste filling. China University of Mining and Technology Press, Xuzhou (in Chinese)
Nardi A, Idiart A, Trinchero P, Vries LMD, Molinero J (2014) Interface COMSOL-PHREEQC (ICP), an efficient numerical framework for the solution of coupled multiphysics and geochemistry. Comput Geosci 69(4):10–21
Perry DL (1995) Handbook of inorganic compounds. World Publishing, New York City
Qiao W, Li W, Zhang X (2014) Characteristic of water chemistry and hydrodynamics of deep karst and its influence on deep coal mining. Arab J Geosci 7(4):1261–1275. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-013-0899-0
Qiao W, Li W, Li T, Chang J, Wang Q (2016) Effects of coal mining on shallow water resources in semiarid regions: a case study in the Shennan mining area, Shaanxi, China. Mine Water Environ 36(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10230-016-0414-4
Sasaki K, Haga T, Hirajima T, Kurosawa K, Tsunekawa M (2002) Distribution and transition of heavy metals in mine tailing dumps. Mater Trans 43(11):2778–2783
Wang D, Li Q (2014) Research progress in coal gangue modification. Mod Chem Ind 34(8):50–52 (in Chinese)
Xiao LP (2007) Study on pollution laws of coal gangue leaching solution to groundwater system. Liaoning Eng Tech C (in Chinese)
Xiao LP, Liang B, Lu H, Bi Y, Zhang CC, Di J (2006) Releasement of contaminants within coal gangue based on soaking experiment—a case study of coal gangue in Xinqiu coal mine, Fuxin. Chin J Geol Haz Contr 17(2):151–150 (in Chinese)
Yang Y, Ji H (2016) A study on chemical forms and leaching characteristics of trace elements in coal gangue from xinhua coal mine in Guizhou province, China. Earth Environ 44(1):36–46 (in Chinese)
Yang J, Tang Y, Yang K, Rouff AA, Elzinga EJ, Huang JH (2014) Leaching characteristics of vanadium in mine tailings and soils near a vanadium titanomagnetite mining site. J Hazard Mater 264(2):498–504. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.09.063
Ye JW, Shen GD, Lu L (2010) Hazards and comprehensive utilization of coal gangue. Chin Resour Comp Utiliz 28(05):32–34 (in Chinese)
Yeboah S, Akiti TT, Fletcher JJ (2014) Numerical modeling of radionuclide migration through a borehole disposal site. Springerplus 3(1):155. https://doi.org/10.1186/2193-1801-3-155
Zha J (2011) Theory and application of subsidence control for solid backfilling mining. China University of Mining and Technology Press, Xuzhou (in Chinese)
Zhang ML (2011) Utilization of fly ash for remediation of heavy metals from acid coal waste leachate. J Chin Coal Soc 36(4):654–658 (in Chinese)
Zhang Q, Zhang J, Tai Y, Fang K, Yin Y (2015) Horizontal roof gap of backfill hydraulic support. J Centr South Univ 22(9):3544–3555. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-015-2894-y
Zhu K (2011) Environmental hazards and comprehensive utilization of coal gangue in sustainable development. Arch Mikrobiol 60(2):1–4. https://doi.org/10.1109/icbbe.2011.5781478
Acknowledgements
Financial support for this work was provided by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2017XKZD13).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qi, W., Huang, Y., He, H. et al. Potential Pollution of Groundwater by Dissolution and Release of Contaminants due to Using Gangue for Backfilling. Mine Water Environ 38, 281–293 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10230-018-00585-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10230-018-00585-y