Abstract
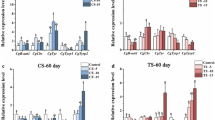
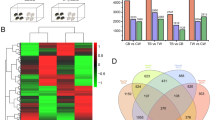
Colorful shells in bivalves are mostly caused by the presence of biological pigments, among which melanin is a key component in the formation of shell colours. Cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) is an important messenger in the regulation of pigmentation in some species. However, the role of cAMP in bivalve melanogenesis has not yet been reported. In this study, we performed in vitro and in vivo experiments to determine the role of cAMP in regulating melanogenesis in Pacific oysters. Besides, the function of cAMP-responsive element modulator (CREM) and the interactions between CREM and melanogenic genes were investigated. Our results showed that a high level of cAMP promotes the expression of melanogenic genes in Pacific oysters. CREM controls the expression of the MITF gene under cAMP regulation. In addition, CREM can regulate melanogenic gene expression, tyrosine metabolism, and melanin synthesis. These results indicate that cAMP plays an important role in the regulation of melanogenesis in Pacific oysters. CREM is a key transcription factor in the oyster melanin synthesis pathway, which plays a crucial role in oyster melanin synthesis through a cAMP-mediated CREM-MITF-TYR axis.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated in the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Arora N, Siddiqui EM, Mehan S (2021) Involvement of adenylate cyclase/cAMP/CREB and SOX9/MITF in melanogenesis to prevent vitiligo. Mol Cell Biochem 476:1401–1409
Bertolotto C, Busca R, Ballotti R, Ortonne JP (2001) Cyclic AMP is a key messenger in the regulation of skin pigmentation. Medecine/Sciences 17:177–185
Boettiger A, Ermentrout B, Oster G (2009) The neural origins of shell structure and pattern in aquatic mollusks. Proc Natl Acad Sci 106:6837–6842
Brake J, Evans F, Langdon C (2003) Is beauty in the eye of the beholder? Development of a simple method to describe desirable shell shape for the Pacific oyster industry. J Shellfish Res 22:767–771
Budd A, McDougall C, Green K, Degnan BM (2014) Control of shell pigmentation by secretory tubules in the abalone mantle. Front Zool 11:1–9
Cal L, Suarez-Bregua P, Cerdá-Reverter JM et al (2017) Fish pigmentation and the melanocortin system. Comp Biochem Physiol Part A Mol Integr Physiol 211:26–33
Chen X, Xiao D, Du X et al (2019a) The role of the dopamine melanin pathway in the ontogeny of elytral melanization in harmonia axyridis. Front Physiol 10:1–8
Chen Y-M, Su W-C, Li C et al (2019b) Anti-melanogenesis of novel kojic acid derivatives in B16F10 cells and zebrafish. Int J Biol Macromol 123:723–731
Chiang H-M, Chien Y-C, Wu C-H et al (2014) Hydroalcoholic extract of Rhodiola rosea L. (Crassulaceae) and its hydrolysate inhibit melanogenesis in B16F0 cells by regulating the CREB/MITF/tyrosinase pathway. Food Chem Toxicol 65:129–139
De Cesare D, Fimia GM, Sassone-Corsi P (1999) Signaling routes to CREM and CREB: plasticity in transcriptional activation. Trends Biochem Sci 24:281–285
Englaro W, Rezzonico R, Durand-Clement M et al (1995) Mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway and AP-1 are activated during cAMP-induced melanogenesis in B-16 melanoma cells. J Biol Chem 270:24315–24320
Ge J, Li Q, Yu H, Kong L (2015) Mendelian inheritance of golden shell color in the Pacific oyster Crassostrea gigas. Aquaculture 441:21–24
Gjertsen B, Mellgren G, Otten A et al (1995) Novel (Rp)-cAMPS Analogs as Tools for Inhibition of cAMP-kinase in Cell Culture. J Biol Chem 270:20599–20607
Gong Z, Matzke NJ, Ermentrout B et al (2012) Evolution of patterns on Conus shells. Proc Natl Acad Sci 109:234–241
Han Z, Li Q (2020) Mendelian inheritance of orange shell color in the Pacific oyster Crassostrea gigas. Aquaculture 516:734616. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2019.734616
Han Z, Li Q (2021) Relationship Between Shell Color and Growth and Survival Traits in the Pacific Oyster Crassostrea gigas. J Ocean Univ China 20:985–991
Jian D, Jiang D, Su J et al (2011) Diethylstilbestrol enhances melanogenesis via cAMP-PKA-mediating up-regulation of tyrosinase and MITF in mouse B16 melanoma cells. Steroids 76:1297–1304
Jiang K, Chen C, Jiang G et al (2024a) Genetic improvement of oysters: current status, challenges, and prospects. Rev Aquac 16:796–817
Jiang K, Xu C, Yu H et al (2024b) Transcriptomic and physiological analysis reveal melanin synthesis-related genes and pathways in Pacific oysters (Crassostrea gigas). Mar Biotechnol (published on line). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10126-024-10302-2
Jiang K, Jiang L, Nie H et al (2020) Molecular cloning and expression analysis of tyrosinases (tyr) in four shell-color strains of Manila clam Ruditapes philippinarum. PeerJ 2020:e8641. https://doi.org/10.7717/PEERJ.8641/SUPP-2
Li H-L, Li M-J, Xiong G-Q et al (2023a) Silver Carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) Scale Collagen Peptides-1 (SCPs1) Inhibit Melanogenesis through Downregulation of the cAMP-CREB Signaling Pathway. Nutrients 15:2449. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15112449
Li Z, Hu B, Du L et al (2023b) Involvement of B-aat1 and Cbs in regulating mantle pigmentation in the Pacific oyster (Crassostrea gigas). Mol Biol Rep 50:377–387
Li Z, Li Q, Liu S et al (2021) Integrated Analysis of Coding Genes and Non-coding RNAs Associated with Shell Color in the Pacific Oyster (Crassostrea gigas). Mar Biotechnol 23:417–429
Li Z, Li Q, Xu C, Yu H (2022) Molecular characterization of Pax7 and its role in melanin synthesis in Crassostrea gigas. Comp Biochem Physiol Part B Biochem Mol Biol 260:110720. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpb.2022.110720
Li Z, Li Q, Xu C, Yu H (2023c) Histological, elemental, and ultrastructural analysis of melanin in mantle of Pacific oyster (Crassostrea gigas). Microsc Res Tech 86:283–293
Li Z, Xu C, Yu H et al (2023d) Effects of Dietary Cystine and Tyrosine Supplementation on Melanin Synthesis in the Pacific Oyster (Crassostrea gigas). Mar Biotechnol 25:537–547
Li Z, Xu C, Yu H et al (2023e) Transcription factor CgPOU3F4-like regulates expression of pheomelanin synthesis related gene CgB-aat1 in the Pacific oyster (Crassostrea gigas). Gene 861:147258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2023.147258
Liang Y, Xu C, Li Q (2023) Growth, survival and color segregation of F2 hybrids between selected “Haida no.1” and Orange-shell lines of the Pacific oyster. Aquaculture 574:739626. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2023.739626
Liu X, Wu F, Zhao H et al (2009) A novel shell color variant of the Pacific abalone Haliotis Discus Hannai INO subject to genetic control and dietary influence. J Shellfish Res 28:419–424
Liu Y, Zhu Q, Li L et al (2020) Identification of HSF1 Target Genes Involved in Thermal Stress in the Pacific Oyster Crassostrea gigas by ChIP-seq. Mar Biotechnol 22:167–179
Luo M, Lu G, Yin H et al (2021) Fish pigmentation and coloration: molecular mechanisms and aquaculture perspectives. Rev Aquac 13:2395–2412
Mao J, Zhang W, Wang X et al (2019a) Histological and Expression Differences Among Different Mantle Regions of the Yesso Scallop (Patinopecten yessoensis) Provide Insights into the Molecular Mechanisms of Biomineralization and Pigmentation. Mar Biotechnol 21:683–696
Mao J, Zhang X, Zhang W et al (2019b) Genome-wide identification, characterization and expression analysis of the MITF gene in Yesso scallops (Patinopecten yessoensis) with different shell colors. Gene 688:155–162
Mizutani Y, Hayashi N, Kawashima M, Imokawa G (2010) A single UVB exposure increases the expression of functional KIT in human melanocytes by up-regulating MITF expression through the phosphorylation of p38/CREB. Arch Dermatol Res 302:283–294
Muchardt C, Li C, Kornuc M, Gaynor R (1990) CREB regulation of cellular cyclic AMP-responsive and adenovirus early promoters. J Virol 64:4296–4305
Ostojić J, Yoon Y-S, Sonntag T et al (2021) Transcriptional co-activator regulates melanocyte differentiation and oncogenesis by integrating cAMP and MAPK/ERK pathways. Cell Rep 35:109136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109136
Park HY, Wu C, Yonemoto L et al (2006) MITF mediates cAMP-induced protein kinase C-β expression in human melanocytes. Biochem J 395:571–578
Rodriguez G, Ross JA, Nagy ZS, Kirken RA (2013) Forskolin-inducible cAMP Pathway Negatively Regulates T-cell Proliferation by Uncoupling the Interleukin-2 Receptor Complex. J Biol Chem 288:7137–7146
Saenko SV, Schilthuizen M (2021) Evo-devo of shell colour in gastropods and bivalves. Curr Opin Genet Dev 69:1–5
Schmidt M, Dekker FJ, Maarsingh H (2013) Exchange Protein Directly Activated by cAMP (epac): a Multidomain cAMP Mediator in the Regulation of Diverse Biological Functions. Pharmacol Rev 65:670–709
Slominski A, Tobin DJ, Shibahara S, Wortsman J (2004) Melanin Pigmentation in Mammalian Skin and Its Hormonal Regulation. Physiol Rev 84:1155–1228
Slominski A, Zmijewski MA, Pawelek J (2012) L-tyrosine and L-dihydroxyphenylalanine as hormone-like regulators of melanocyte functions. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res 25:14–27
Stenger P, Ky C, Reisser C, et al (2021) Molecular Pathways and Pigments Underlying the Colors of the Pearl Oyster Pinctada margaritifera var. cumingii (Linnaeus 1758). Genes (Basel) 12:421. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12030421
True JR, Edwards KA, Yamamoto D, Carroll SB (1999) Drosophila wing melanin patterns form by vein-dependent elaboration of enzymatic prepatterns. Curr Biol 9:1382–1391
Wan P, Hu Y, He L (2011) Regulation of melanocyte pivotal transcription factor MITF by some other transcription factors. Mol Cell Biochem 354:241–246
Wang H, Xu J, Lazarovici P et al (2018) cAMP Response Element-Binding Protein (CREB): a Possible Signaling Molecule Link in the Pathophysiology of Schizophrenia. Front Mol Neurosci 11:1–14
Wang X, Ding S, Yin D et al (2020) Response to selection for growth in the second generation of two shell color lines of the bay scallop Argopecten irradians. Aquaculture 528:735536. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2020.735536
Williams ST (2017) Molluscan shell colour. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc 92:1039–1058
Wolf Horrell EM, Jarrett SG, Carter KM, D’Orazio JA (2017) Divergence of cAMP signalling pathways mediating augmented nucleotide excision repair and pigment induction in melanocytes. Exp Dermatol 26:577–584
Xing D, Li Q, Kong L, Yu H (2018) Heritability estimate for mantle edge pigmentation and correlation with shell pigmentation in the white-shell strain of Pacific oyster, Crassostrea gigas. Aquaculture 482:73–77
Xu C, Li Q, Chong J et al (2019a) Mass Selection for Growth Improvement in Black Shell Line of Pacific Oyster Crassostrea gigas. J Ocean Univ China 18:1411–1416
Xu C, Li Q, Yu H et al (2019b) Inheritance of shell pigmentation in Pacific oyster Crassostrea gigas. Aquaculture 512:734249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2019.734249
Yan X, Nie H, Huo Z et al (2019) Clam Genome Sequence Clarifies the Molecular Basis of Its Benthic Adaptation and Extraordinary Shell Color Diversity. iScience 19:1225–1237
Yarra T, Blaxter M, Clark MS (2021) A Bivalve Biomineralization Toolbox. Mol Biol Evol 38:4043–4055
Yu F, Lu Y, Zhong Z et al (2021) Mitf Involved in Innate Immunity by Activating Tyrosinase-Mediated Melanin Synthesis in Pteria penguin. Front Immunol 12:1–15
Yu F, Pan Z, Qu B et al (2018) Identification of a tyrosinase gene and its functional analysis in melanin synthesis of Pteria penguin. Gene 656:1–8
Yu F, Tang X, Qu B et al (2020) Kojic acid inhibited melanin synthesis by tyrosinase pathway in Pteria penguin. Aquac Res 51:1584–1591
Yu F, Zhong Z, Zhang J et al (2022) Light stress affected body color by tyrosinase-mediated melanin synthesis pathway in hybrid grouper. Aquac Reports 23:101027. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aqrep.2022.101027
Yue X, Nie Q, Xiao G, Liu B (2015) Transcriptome Analysis of Shell Color-Related Genes in the Clam Meretrix meretrix. Mar Biotechnol 17:364–374
Zhang S, Wang H, Yu J et al (2018) Identification of a gene encoding microphthalmia-associated transcription factor and its association with shell color in the clam Meretrix petechialis. Comp Biochem Physiol Part B Biochem Mol Biol 225:75–83
Zhou D, Ota K, Nardin C et al (2018) Mammalian pigmentation is regulated by a distinct cAMP-dependent mechanism that controls melanosome pH. Sci Signal 11:aau7987. https://doi.org/10.1126/scisignal.aau7987
Zhu Y, Li Q, Yu H et al (2022) Expression of tyrosinase-like protein genes and their functional analysis in melanin synthesis of Pacific oyster (Crassostrea gigas). Gene 840:146742. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2022.146742
Acknowledgements
We thank the grants from the National Key R&D Program of China (2022YFD2400305), Earmarked Fund for Agriculture Seed Improvement Project of Shandong Province (2022LZGCQY010, 2022TZXD002 and 2021ZLGX03), and China Agriculture Research System Project (CARS-49).
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the National Key R&D Program of China (2022YFD2400305), Earmarked Fund for Agriculture Seed Improvement Project of Shandong Province (2022LZGCQY010, 2022TZXD002 and 2021ZLGX03), and China Agriculture Research System Project (CARS-49).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Kunyin Jiang: Completion of the experiment, data analysis, and Writing—original draft. Qi Li: Experimental design and coordination, funding acquisition, and Writing—review & editing. Hong Yu: Resources. Lingfeng Kong: Resources. Shikai Liu: Investigation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests or conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
10126_2024_10309_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Fig S1. Flowchart of RNAi experiment. The BRLZ DNA binding domain was selected as the target for this experiment (~500 bp). Double-stranded RNA (dsRNA of CREM) was synthesized by in vitro transcription and verified through 1% agarose gel electrophoresis. Forty oysters were injected with 60 μg dsRNA (40 μL) each time. A total of seven injections were performed at an interval of 48 h. (PDF 3783 KB)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, K., Yu, H., Kong, L. et al. cAMP-Mediated CREM-MITF-TYR Axis Regulates Melanin Synthesis in Pacific Oysters. Mar Biotechnol (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10126-024-10309-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10126-024-10309-9