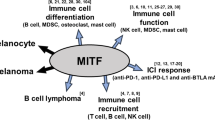
Abstract
The microphthalmia transcription factor (MITF) is discussed as the master gene for melanocytic survival and a key transcription factor regulating the expression of tyrosinase (TYR), tyrosinase-related protein-1 (TRP-1), and tyrosinase-related protein-2 (TRP-2). MITF is influenced in a complex manner by a large number of different extracellular and intracellular proteins. Many transcription factors are able to modulate the expression and/or transcriptional activity of MITF in vivo. In this review, we summarize these transcription factors that regulate MITF and their interactions. The Sry-related HMG box 10 (SOX10) can directly transactivate the MITF gene and cooperate with MITF to activate TRP-2 expression. The Paired box 3 (PAX3) can increase MITF expression by binding to its promoter and simultaneously prevent MITF from activating downstream genes by competition for enhancer occupancy. Activated signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) and protein inhibitor of activated STAT3 (PIAS3) are able to regulate transcriptional activity of MITF through their interaction. Activated cAMP response element binding protein (CREB) can bind the cAMP response element to increase the MITF gene expression. MITF expression can also be initiated by lymphoid-enhancing factor-1 (LEF-1) and be temporally facilitated by the synergy of LEF-1 and MITF. Both immunoglobulin transcription factor-2 (ITF2) and forkhead-box transcription factor D3 (FOXD3) can negatively regulate MITF expression. All the above-mentioned transcription factors constitute a regulatory network that precisely modulates the MITF.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hodgkinson CA, Moore KJ, Nakayama A, Steingrimsson E, Copeland NG, Jenkins NA, Arnheiter H (1993) Mutations at the mouse microphthalmia locus are associated with defects in a gene encoding a novel basic helix-loop-helix zipper protein. Cell 74:395–404
Hughes MJ, Lingrel JB, Krakowsky JM, Anderson KP (1993) A helix-loop-helixtranscription factor-like gene is located at the mi locus. J Biol Chem 268:20687–20690
Goding CR (2000) Mitf from neural crest to melanoma: signal transduction and transcription in the melanocyte lineage. Genes Dev 14:1712–1728
Elworthy S, Lister JA, Carney TJ, Raible DW, Kelsh RN (2003) Transcriptional regulation of mitfa accounts for the sox10 requirement in zebrafish melanophore development. Development 130:2809–2818
Bondurand N, Pingault V, Goerich DE, Lemort N, Sock E, Le Caignec C, Wegner M, Goossens M (2000) Interaction among SOX10, PAX3 and MITF, three genes altered in Waardenburg syndrome. Hum Mol Genet 9:1907–1917
Sonnenblick A, Levy C, Razin E (2004) Interplay between MITF, PIAS3, and STAT3 in mast cells and melanocytes. Mol Cell Biol 24:10584–10592
Bertolotto C, Abbe P, Hemesath TJ, Bille K, Fisher DE, Ortonne JP, Ballotti R (1998) Microphthalmia gene product as a signal transducer in cAMP-induced differentiation of melanocytes. J Cell Biol 142:827–835
Saito H, Yasumoto K, Takeda K, Takahashi K, Fukuzaki A, Orikasa S, Shibahara S (2002) Melanocyte-specific microphthalmia-associated transcription factor isoform activates its own gene promoter through physical interaction with lymphoid-enhancing factor 1. J Biol Chem 277:28787–28794
Potterf SB, Furumura M, Dunn KJ, Arnheiter H, Pavan WJ (2000) Transcription factor hierarchy in Waardenburg syndrome: regulation of MITF expression by SOX10 and PAX3. Hum Genet 107:1–6
Lee M, Goodall J, Verastegui C, Ballotti R, Goding CR (2000) Direct regulation of the microphthalmia promoter by Sox10 links Waardenburg-Shah syndrome (WS4)-associated hypopigmentation and deafness to WS2. J Biol Chem 275:37978–37983
Verastegui C, Bille K, Ortonne JP, Ballotti R (2000) Regulation of the microphthalmia-associated transcription factor gene by the Waardenburg syndrome type 4 gene, SOX10. J Biol Chem 275:30757–33076
Jiao Z, Mollaaghababa R, Pavan WJ, Antonellis A, Green ED, Hornyak TJ (2004) Direct interaction of Sox10 with the promoter of murine Dopachrome Tautomerase (Dct) and synergistic activation of Dct expression with Mitf. Pigment Cell Res 17:352–362
Yasumoto K, Takeda K, Saito H, Watanabe K, Takahashi K, Shibahara S (2002) Microphthalmia-associated transcription factor interacts with LEF-1, a mediator of Wnt signaling. EMBO J 21:2703–2714
Watanabe A, Takeda K, Ploplis B, Tachibana M (1998) Epistatic relationship between Waardenburg syndrome genes MITF and PAX3. Nat Genet 18:283–286
Lang D, Lu MM, Huang L, Engleka KA, Zhang M, Chu EY, Lipner S, Skoultchi A, Millar SE, Epstein JA (2005) Pax3 functions at a nodal point in melanocyte stem cell differentiation. Nature 433:884–887
Darnell JE Jr, Kerr IM, Stark GR (1994) Jak-STAT pathways and transcriptional activation in response to IFNs and other extracellular signaling proteins. Science 264:1415–1421
Bowman T, Broome MA, Sinibaldi D, Wharton W, Pledger WJ, Sedivy JM, Irby R, Yeatman T, Courtneidge SA, Jove R (2001) Stat3-mediated Myc expression is required for Src transformation and PDGF-induced mitogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:7319–7324
Bromberg JF, Wrzeszczynska MH, Devgan G, Zhao Y, Pestell RG, Albanese C, Darnell JE Jr (1999) Stat3 as an oncogene. Cell 98:295–303
Grandis JR, Drenning SD, Zeng Q, Watkins SC, Melhem MF, Endo S, Johnson DE, Huang L, He Y, Kim JD (2000) Constitutive activation of Stat3 signaling abrogates apoptosis in squamous cell carcinogenesis in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:4227–4232
Sinibaldi D, Wharton W, Turkson J, Bowman T, Pledger WJ, Jove R (2000) Induction of p21WAF1/CIP1 and cyclin D1 expression by the Src oncoprotein in mouse fibroblasts: role of activated STAT3 signaling. Oncogene 19:5419–5427
Dorvault CC, Weilbaecher KN, Yee H, Fisher DE, Chiriboga LA, Xu Y, Chhieng DC (2001) Microphthalmia transcription factor: a sensitive and specific marker for malignant melanoma in cytologic specimens. Cancer 93:337–343
Kamaraju AK, Bertolotto C, Chebath J, Revel M (2002) Pax3 down-regulation and shut-off of melanogenesis in melanoma B16/F10.9 by interleukin-6 receptor signaling. J Biol Chem 277:15132–15141
Boulon S, Dantonel JC, Binet V, Vié A, Blanchard JM, Hipskind RA, Philips A (2002) Oct-1 potentiates CREB-driven cyclin D1promoter activation via a phospho-CREB- and CREB binding protein-independent mechanism. Mol Cell Biol 22:7769–7779
Fentzke RC, Korcarz CE, Lang RM, Lin H, Leiden JM (1998) Dilated cardiomyopathy in transgenic mice expressing a dominant-negative CREB transcription factor in the heart. J Clin Invest 101:2415–2426
Saha B, Singh SK, Sarkar C, Bera R, Ratha J, Tobin DJ, Bhadra R (2006) Activation of the Mitf promoter by lipid-stimulated activation of p38-stress signalling to CREB. Pigment Cell Res 19:595–605
Mansky KC, Sankar U, Han J, Ostrowski MC (2002) Microphthalmia transcription factor is a target of the p38 MAPK pathway in response to receptor activator of NF-kappa B ligand signaling. J Biol Chem 277:11077–11083
Luger TA, Scholzen T, Grabbe S (1997) The role of alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone in cutaneous biology. J Investig Dermatol Symp Proc 2:87–93
Slominski A, Wortsman J, Luger T, Paus R, Solomon S (2000) Corticotropin releasing hormone and proopiomelanocortin involvement in the cutaneous response to stress. Physiol Rev 80:979–1020
Eastman Q, Grosschedl R (1999) Regulation of LEF-1/TCF transcription factors by Wnt and other signals. Curr Opin Cell Biol 11:233–240
Takeda K, Yasumoto K, Takada R, Takada S, Watanabe K, Udono T, Saito H, Takahashi K, Shibahara S (2000) Induction of melanocyte-specific microphthalmia-associated transcription factor by Wnt-3a. J Biol Chem 275:14013–14016
Behrens J, von Kries JP, Kühl M, Bruhn L, Wedlich D, Grosschedl R, Birchmeier W (1996) Functional interaction of beta-catenin with the transcription factor LEF-1. Nature 382:638–642
Furumura M, Potterf SB, Toyofuku K, Matsunaga J, Muller J, Hearing VJ (2001) Involvement of ITF2 in the transcriptional regulation of melanogenic genes. J Biol Chem 276:28147–28154
Hearing VJ (2000) The melanosome: the perfect model for cellular responses to the environment. Pigment Cell Res 13:23–34
Weigel D, Jäckle H (1990) The fork head domain: a novel DNA binding motif of eukaryotic transcription factors? Cell 63:455–456
Hanna LA, Foreman RK, Tarasenko IA, Kessler DS, Labosky PA (2002) Requirement for Foxd3 in maintaining pluripotent cells of the early mouse embryo. Genes Dev 16:2650–2661
Tompers DM, Foreman RK, Wang Q, Kumanova M, Labosky PA (2005) Foxd3 is required in the trophoblast progenitor cell lineage of the mouse embryo. Dev Biol 285:126–137
Teng L, Mundell NA, Frist AY, Wang Q, Labosky PA (2008) Requirement for Foxd3 in maintenance of neural crest progenitors. Development 135:1615–1624
Thomas AJ, Erickson CA (2009) FOXD3 regulates the lineage switch between neural crest-derived glial cells and pigment cells by repressing MITF through a non-canonical mechanism. Development 136:1849–1858
Ignatius MS, Moose HE, El-Hodiri HM, Henion PD (2008) colgate/hdac1 Repression of foxd3 expression is required to permit mitfa-dependent melanogenesis. Dev Biol 313:568–583
Curran K, Raible DW, Lister JA (2009) Foxd3 controls melanophore specification in the zebrafish neural crest by regulation of Mitf. Dev Biol 332:408–417
Curran K, Lister JA, Kunkel GR, Prendergast A, Parichy DM, Raible DW (2010) Interplay between Foxd3 and Mitf regulates cell fate plasticity in the zebrafish neural crest. Dev Biol 344:107–118
Fujii H, Hamada H (1993) A CNS-specific POU transcription factor, Brn-2, is required for establishing mammalian neural cell lineages. Neuron 11:1197–1206
Schreiber E, Merchant RE, Wiestler OD, Fontana A (1994) Primary brain tumors differ in their expression of octamer deoxyribonucleic acid-binding transcription factors from long-term cultured glioma cell lines. Neurosurgery 34:129–135
Eisen T, Easty DJ, Bennett DC, Goding CR (1995) The POU domain transcription factor Brn-2: elevated expression in malignant melanoma and regulation of melanocyte-specific gene expression. Oncogene 11:2157–2164
Cox PM, Temperley SM, Kumar H, Goding CR (1988) A distinct octamer-binding protein present in malignant melanoma cells. Nucl Acids Res 16:11047–11056
Thomson JA, Parsons PG, Sturm RA (1993) In vivo and in vitro expression of octamer binding proteins in human melanoma metastases, brain tissue, and fibroblasts. Pigment Cell Res 6:13–22
Cook AL, Donatien PD, Smith AG, Murphy M, Jones MK, Herlyn M, Bennett DC, Leonard JH, Sturm RA (2003) Human melanoblasts in culture: expression of BRN2 and synergistic regulation by fibroblast growth factor-2, stem cell factor, and endothelin-3. J Invest Dermatol 121:1150–1159
Wellbrock C, Rana S, Paterson H, Pickersgill H, Brummelkamp T, Marais R (2008) Oncogenic BRAF regulates melanoma proliferation through the lineage specific factor MITF. PLoS One 3:e2734
Kobi D, Steunou AL, Dembélé D, Legras S, Larue L, Nieto L, Davidson I (2010) Genome-wide analysis of POU3F2/BRN2 promoter occupancy in human melanoma cells reveals Kitl as a novel regulated target gene. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res 23:404–418
Miller AJ, Levy C, Davis IJ, Razin E, Fisher DE (2005) Sumoylation of MITF and its related family members TFE3 and TFEB. J Biol Chem 280:146–155
Haflidadóttir BS, Bergsteinsdóttir K, Praetorius C, Steingrímsson E (2010) miR-148 regulates Mitf in melanoma cells. PLoS ONE 5:e11574
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to the two anonymous reviewers for constructive comments on the early version of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wan, P., Hu, Y. & He, L. Regulation of melanocyte pivotal transcription factor MITF by some other transcription factors. Mol Cell Biochem 354, 241–246 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-011-0823-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-011-0823-4