Abstract
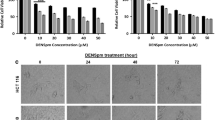
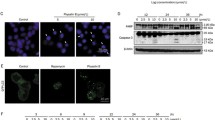
Small molecule inhibitors of cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) show high therapeutic potential in various cancer types which are characterized by the accumulation of transformed cells due to impaired apoptotic machinery. Roscovitine, a CDK inhibitor showed to be a potent apoptotic inducer in several cancer cells. Polyamines, putrescine, spermidine and spermine, are biogenic amines involved in many cellular processes, including apoptosis. In this study, we explored the potential role of polyamines in roscovitine-induced apoptosis in HCT116 colon cancer cells. Roscovitine induced apoptosis by activating mitochondrial pathway caspases and modulating the expression of Bcl-2 family members. Depletion of polyamines by treatment with difluoromethylornithine (DFMO) increased roscovitine-induced apoptosis. Transient silencing of ornithine decarboxylase, polyamine biosynthesis enzyme and special target of DFMO also increased roscovitine-induced apoptosis in HCT116 cells. Interestingly, additional putrescine treatment was found pro-apoptotic due to the presence of non-functional ornithine decarboxylase (ODC). Finally, roscovitine altered polyamine catabolic pathway and led to decrease in putrescine and spermidine levels. Therefore, the metabolic regulation of polyamines may dictate the power of roscovitine induced apoptotic responses in HCT116 colon cancer cells.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- APAO:
-
N1-acetylpolyamine oxidase
- CDKs:
-
Cyclin dependent kinases
- CST:
-
Cell signaling technology
- DFMO:
-
d,l-α-difluoromethylornithine
- DMSO:
-
Dimethyl sulfoxide
- H2-DCFDA:
-
2′-7′ Dichlorofluorescein
- IEC-6:
-
Intestine epithelial cells of rats
- MMP:
-
Mitochondrial membrane potential
- MTT:
-
3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl-tetrazolium bromide
- NAC:
-
N-acetyl cystein
- ODC:
-
Ornithine decarboxylase
- PAs:
-
Polyamines
- PAO:
-
Polyamine oxidase
- POD:
-
Peroxidase
- Put:
-
Putrescine
- SMO:
-
Spermine oxidase
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- RT:
-
Reverse transcriptase
- Spd:
-
Spermidine
- Spm:
-
Spermine
- SSAT:
-
Spermidine/spermine N1-acetyltransferase
- 5-FU:
-
5-Fluorouracil
References
Agostinelli E, Belli F, Molinari A, Condello M, Palmigiani P, Vedova LD, Marra M, Seiler N, Arancia G (2006) Toxicity of enzymatic oxidation products of spermine to human melanoma cells (M14): sensitization by heat and MDL 72527. Biochim Biophys Acta 1763:1040–1050
Agostinelli E, Tempera G, Molinari A, Salvi M, Battaglia V, Toninello A, Arancia G (2007) The physiological role of biogenic amines redox reactions in mitochondria. New perspectives in cancer therapy. Amino acids 33:175–187
Agostinelli E, Tempera G, Viceconte N, Saccoccio S, Battaglia V, Grancara S, Toninello A, Stevanato R (2010) Potential anticancer application of polyamine oxidation products formed by amine oxidase: a new therapeutic approach. Amino acids 38:353–368
Aldoss IT, Tashi T, Ganti AK (2009) Seliciclib in malignancies. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 18:1957–1965
Alvi AJ, Austen B, Weston VJ, Fegan C, MacCallum D, Gianella-Borradori A, Lane DP, Hubank M, Powell JE, Wei W, Taylor AM, Moss PA, Stankovic T (2005) A novel CDK inhibitor, CYC202 (R-roscovitine), overcomes the defect in p53-dependent apoptosis in B-CLL by down-regulation of genes involved in transcription regulation and survival. Blood 105:4484–4491
Andersson G, Heby O (1977) Kinetics of cell proliferation and polyamine synthesis during Ehrlich ascites tumor growth. Cancer Res 37:4361–4366
Appleyard MV, O’Neill MA, Murray KE, Paulin FE, Bray SE, Kernohan NM, Levison DA, Lane DP, Thompson AM (2009) Seliciclib (CYC202, R-roscovitine) enhances the antitumor effect of doxorubicin in vivo in a breast cancer xenograft model. Int J Cancer 124:465–472
Arisan ED, Kutuk O, Tezil T, Bodur C, Telci D, Basaga H (2010) Small inhibitor of Bcl-2, HA14–1, selectively enhanced the apoptotic effect of cisplatin by modulating Bcl-2 family members in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res Treat 119:271–281
Bachrach U (1976) Polyamines as chemical markers of malignancy. The Italian J Biochem 25:77–93
Bragado P, Armesilla A, Silva A, Porras A (2007) Apoptosis by cisplatin requires p53 mediated p38alpha MAPK activation through ROS generation. Apoptosis 12:1733–1742
Burns MR, Graminski GF, Weeks RS, Chen Y, O’Brien TG (2009) Lipophilic lysine-spermine conjugates are potent polyamine transport inhibitors for use in combination with a polyamine biosynthesis inhibitor. J Med Chem 52:1983–1993
Casero RA, Pegg AE (2009) Polyamine catabolism and disease. Biochem J 421:323–338
Chen L, Jiang J, Cheng C, Yang A, He Q, Li D, Wang Z (2007) P53 dependent and independent apoptosis induced by lidamycin in human colorectal cancer cells. Cancer Biol Ther 6:965–973
Chen Y, Weeks RS, Burns MR, Boorman DW, Klein-Szanto A, O’Brien TG (2006) Combination therapy with 2-difluoromethylornithine and a polyamine transport inhibitor against murine squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Cancer 118:2344–2349
Cheok CF, Dey A, Lane DP (2007) Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors sensitize tumor cells to nutlin-induced apoptosis: a potent drug combination. Mol Cancer Res 5:1133–1145
Choi SH, Kim SW, Choi DH, Min BH, Chun BG (2000) Polyamine-depletion induces p27Kip1 and enhances dexamethasone-induced G1 arrest and apoptosis in human T lymphoblastic leukemia cells. Leuk Res 24:119–127
Choi W, Gerner EW, Ramdas L, Dupart J, Carew J, Proctor L, Huang P, Zhang W, Hamilton SR (2005) Combination of 5-fluorouracil and N1, N11-diethylnorspermine markedly activates spermidine/spermine N1-acetyltransferase expression, depletes polyamines, and synergistically induces apoptosis in colon carcinoma cells. J Biol Chem 280:3295–3304
David-Pfeuty T (1999) Potent inhibitors of cyclin-dependent kinase 2 induce nuclear accumulation of wild-type p53 and nucleolar fragmentation in human untransformed and tumor-derived cells. Oncogene 18:7409–7422
Evageliou NF, Hogarty MD (2009) Disrupting polyamine homeostasis as a therapeutic strategy for neuroblastoma. Clin Cancer Res 15:5956–5961
Fischer SM, Conti CJ, Viner J, Aldaz CM, Lubet RA (2003) Celecoxib and difluoromethylornithine in combination have strong therapeutic activity against UV-induced skin tumors in mice. Carcinogenesis 24:945–952
Garrofe-Ochoa X, Melero-Fernandez de Mera RM, Fernandez-Gomez FJ, Ribas J, Jordan J, Boix J (2008) BAX and BAK proteins are required for cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitory drugs to cause apoptosis. Mol Cancer Ther 7:3800–3806
Hahntow IN, Schneller F, Oelsner M, Weick K, Ringshausen I, Fend F, Peschel C, Decker T (2004) Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor Roscovitine induces apoptosis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells. Leukemia 18:747–755
Hallaert DY, Spijker R, Jak M, Derks IA, Alves NL, Wensveen FM, de Boer JP, de Jong D, Green SR, van Oers MH, Eldering E (2007) Crosstalk among Bcl-2 family members in B-CLL: seliciclib acts via the Mcl-1/Noxa axis and gradual exhaustion of Bcl-2 protection. Cell Death Differ 14:1958–1967
He J, Fan M, Fang Q (2000) Difluoromethylornithine synergizes with antisense bcl-2 RNA in the induction of apoptosis of HL60 cells. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi 22:105–108
Heby O, Andersson G, Gray JW (1978) Interference with S and G2 phase progression by polyamine synthesis inhibitors. Exp Cell Res 111:461–464
Hudson EA, Howells LM, Gallacher-Horley B, Fox LH, Gescher A, Manson MM (2003) Growth-inhibitory effects of the chemopreventive agent indole-3-carbinol is increased in combination with the polyamine putrescine in the SW480 colon tumour cell line. BMC Cancer 3:2–20
Hui AB, Yue S, Shi W, Alajez NM, Ito E, Green SR, Frame S, O’Sullivan B, Liu FF (2009) Therapeutic efficacy of seliciclib in combination with ionizing radiation for human nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 15:3716–3724
Iseki H, Ko TC, Xue XY, Seapan A, Hellmich MR, Townsend CM Jr (1997) Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors block proliferation of human gastric cancer cells. Surgery 122:187–194 (discussion 194–195)
Kutuk O, Arisan ED, Tezil T, Shoshan MC, Basaga H (2009) Cisplatin overcomes Bcl-2-mediated resistance to apoptosis via preferential engagement of Bak: critical role of Noxa-mediated lipid peroxidation. Carcinogenesis 30:1517–1527
Leitch AE, Riley NA, Sheldrake TA, Festa M, Fox S, Duffin R, Haslett C, Rossi AG (2010) The cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor R-roscovitine down-regulates Mcl-1 to override pro-inflammatory signalling and drive neutrophil apoptosis. Eur J Immunol 40:1127–1138
Marton LJ, Pegg AE (1995) Polyamines as targets for therapeutic intervention. Ann Rev Pharmac Toxicol 35:55–91
Marton LJ, Pegg AE, Morris DR (1991) Directions for polyamine research. J Cell Biochem 45:7–8
Maurer M, Komina O, Wesierska-Gadek J (2009) Roscovitine differentially affects asynchronously growing and synchronized human MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1171:250–256
Meijer L, Borgne A, Mulner O, Chong JP, Blow JJ, Inagaki N, Inagaki M, Delcros JG, Moulinoux JP (1997) Biochemical and cellular effects of roscovitine, a potent and selective inhibitor of the cyclin-dependent kinases cdc2, cdk2 and cdk5. Eur J Biochem 243:527–536
Mohapatra S, Chu B, Zhao X, Djeu J, Cheng JQ, Pledger WJ (2009) Apoptosis of metastatic prostate cancer cells by a combination of cyclin-dependent kinase and AKT inhibitors. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 41:595–602
Monti MG, Pernecco L, Manfredini R, Frassineti C, Barbieri D, Marverti G, Ghiaroni S (1996) Inhibition of cell growth by accumulated spermine is associated with a transient alteration of cell cycle progression. Life Sci 58:2065–2072
Odenlund M, Holmqvist B, Baldetorp B, Hellstrand P, Nilsson BO (2009) Polyamine synthesis inhibition induces S phase cell cycle arrest in vascular smooth muscle cells. Amino Acids 36:273–282
Ortiz-Ferron G, Yerbes R, Eramo A, Lopez-Perez AI, De Maria R, Lopez-Rivas A (2008) Roscovitine sensitizes breast cancer cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis through a pleiotropic mechanism. Cell Res 18:664–676
Paprskarova M, Krystof V, Jorda R, Dzubak P, Hajduch M, Wesierska-Gadek J, Strnad M (2009) Functional p53 in cells contributes to the anticancer effect of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor roscovitine. J Cell Biochem 107:428–437
Schutte B, Nieland L, van Engeland M, Henfling ME, Meijer L, Ramaekers FC (1997) The effect of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor olomoucine on cell cycle kinetics. Exp Cell Res 236:4–15
Stanic I, Facchini A, Borzi RM, Vitellozzi R, Stefanelli C, Goldring MB, Guarnieri C, Flamigni F (2006) Polyamine depletion inhibits apoptosis following blocking of survival pathways in human chondrocytes stimulated by tumor necrosis factor-alpha. J Cell Physiol 206:138–146
Wang X, Feith DJ, Welsh P, Coleman CS, Lopez C, Woster PM, O’Brien TG, Pegg AE (2007) Studies of the mechanism by which increased spermidine/spermine N1-acetyltransferase activity increases susceptibility to skin carcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis 28:2404–2411
Wang Y, Casero RA Jr (2006) Mammalian polyamine catabolism: a therapeutic target, a pathological problem, or both? J Biochem 139:17–25
Wesierska-Gadek J, Borza A, Komina O, Maurer M (2009) Impact of roscovitine, a selective CDK inhibitor, on cancer cells: bi-functionality increases its therapeutic potential. Acta Biochim Pol 56:495–501
Wesierska-Gadek J, Hajek SB, Sarg B, Wandl S, Walzi E, Lindner H (2008a) Pleiotropic effects of selective CDK inhibitors on human normal and cancer cells. Biochem Pharmacol 76:1503–1514
Wesierska-Gadek J, Kramer MP, Maurer M (2008b) Resveratrol modulates roscovitine-mediated cell cycle arrest of human MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Food Chem Toxicol 46:1327–1333
Xie SQ, Liu GC, Ma YF, Cheng PF, Wu YL, Wang MW, Ji BS, Zhao J, Wang CJ (2008) Synergistic antitumor effects of anthracenylmethyl homospermidine and alpha-difluoromethylornithine on promyelocytic leukemia HL60 cells. Toxicol In Vitro 22:352–358. doi:S0887-2333(07)00261-5
Yuan Q, Ray RM, Johnson LR (2002) Polyamine depletion prevents camptothecin-induced apoptosis by inhibiting the release of Cytochrome c. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 282:C1290–C1297
Zhang F, Zhang T, Gu ZP, Zhou YA, Han Y, Li XF, Wang XP, Cheng QS, Mei QB (2008) Enhancement of radiosensitivity by roscovitine pretreatment in human non-small cell lung cancer A549 cells. J Radiat Res (Tokyo) 49:541–548
Zhang F, Zhang T, Jiang T, Zhang R, Teng ZH, Li C, Gu ZP, Mei Q (2009) Wortmannin potentiates roscovitine-induced growth inhibition in human solid tumor cells by repressing PI3K/Akt pathway. Cancer Lett 286:232–239
Zolnierczyk JD, Blonski JZ, Robak T, Kilianska ZM, Wesierska-Gadek J (2009) Roscovitine triggers apoptosis in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells with similar efficiency as combinations of conventional purine analogs with cyclophosphamide. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1171:124–131
Acknowledgments
This work was partially supported by Turkish Scientific and Technical Research Council Project, TUBITAK-TBAG 108T630 and Istanbul Kultur University Scientific Projects Support Center.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arısan, E.D., Çoker, A. & Palavan-Ünsal, N. Polyamine depletion enhances the roscovitine-induced apoptosis through the activation of mitochondria in HCT116 colon carcinoma cells. Amino Acids 42, 655–665 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-011-1040-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-011-1040-x