Abstract
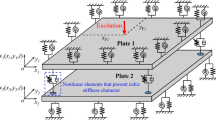
A semi-analytical method is proposed for free and forced vibrations of a thin square binary material configuration plate containing circular plate-type resonators. The resonator embedded in the host plate consists of a rigid mass and a circular plate made of soft material. Based on the classical plate theory, the host plate and the resonator are modelled separately and then coupled by the condition of displacement compatibility. A set of local admissible functions is incorporated into the global admissible functions in the circular plate domain, to describe the non-smoothness and vibration localization of the displacement caused by the material difference between the host plate and the resonator. The resulting global admissible functions promote the capabilities of the Ritz method in predicting accurately the vibration characteristics of the plate with binary material configuration. The Ritz method with the constructed admissible functions is developed to extract frequencies and analytic mode functions of the plate under different boundary conditions. The plate subjected to a transverse harmonic excitation is discretized into a multi-degree-of-freedom system by the Lagrange approach with the analytic mode functions. The effects of boundary conditions, locations of the mass, and material properties on the vibration are explored. It is demonstrated that the mass location in the circular plate only affects the frequencies of the resonator and has almost no effect on the frequencies and the modes of global vibration, and the resonator with the appropriate material parameters reduces significantly the multi-mode plate vibration.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Askari, E., Jeong, K.H., Amabili, M.: A novel mathematical method to analyze the free vibration of eccentric annular plates. J. Sound Vib. 484, 115513 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsv.2020.115513
Chen, Y.X., Li, F.L., Hao, Y.X.: Analysis of vibration and sound insulation characteristics of functionally graded sandwich plates. Compos. Struct. 249, 112515 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2020.112515
Yeh, S.L., Harne, R.L.: Cut-out resonators for tuned vibration suppression of plates. Thin-Walled Struct. 167, 108200 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tws.2021.108200
Lu, S.F., Li, H.J., Zhang, W., Song, X.J.: Vibration reduction of FG-CNTR piezoelectric laminated composite cantilever plate under aerodynamic load using full-dimensional state observer. Eng. Struct. 255, 113942 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engstruct.2022.113942
Richiedei, D., Tamellin, I., Trevisani, A.: Beyond the tuned mass damper: a comparative study of passive approaches to vibration absorption through antiresonance assignment. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 29, 519–544 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11831-021-09583-w
Yang, F., Sedaghati, R., Esmailzadeh, E.: Vibration suppression of structures using tuned mass damper technology: a state-of-the-art review. JVC J. Vib. Control. 28, 812–836 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1177/1077546320984305
Huang, Y., Li, J., Chen, W., Bao, R.: Tunable bandgaps in soft phononic plates with spring-mass-like resonators. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 151, 300–313 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2018.11.029
Gao, P., Climente, A., Sánchez-Dehesa, J., Wu, L.: Single-phase metamaterial plates for broadband vibration suppression at low frequencies. J. Sound Vib. 444, 108–126 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsv.2018.12.022
Yeh, S.L., Harne, R.L.: Structurally-integrated resonators for broadband panel vibration suppression. Smart Mater. Struct. 29, 085010 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-665X/ab9148
Ma, F., Wang, C., Liu, C., Wu, J.H.: Structural designs, principles, and applications of thin-walled membrane and plate-type acoustic/elastic metamaterials. J. Appl. Phys. 129, 231103 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0042132
Liao, G., Luan, C., Wang, Z., Liu, J., Yao, X., Fu, J.: Acoustic metamaterials: a review of theories, structures, fabrication approaches, and applications. Adv. Mater. Technol. 6, 1–29 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1002/admt.202000787
Yang, Z., Mei, J., Yang, M., Chan, N.H., Sheng, P.: Membrane-type acoustic metamaterial with negative dynamic mass. Phys. Rev. Lett. 101, 1–4 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.101.204301
Nouh, M., Aldraihem, O., Baz, A.: Wave propagation in metamaterial plates with periodic local resonances. J. Sound Vib. 341, 53–73 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsv.2014.12.030
Zhou, G., Wu, J.H., Lu, K., Tian, X., Huang, W., Zhu, K.: Broadband low-frequency membrane-type acoustic metamaterials with multi-state anti-resonances. Appl. Acoust. 159, 107078 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apacoust.2019.107078
Naify, C.J., Chang, C.M., McKnight, G., Nutt, S.: Transmission loss and dynamic response of membrane-type locally resonant acoustic metamaterials. J. Appl. Phys. 108, 114905 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3514082
Naify, C.J., Chang, C.M., McKnight, G., Nutt, S.: Transmission loss of membrane-type acoustic metamaterials with coaxial ring masses. J. Appl. Phys. 110, 124903 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3665213
Naify, C.J., Chang, C.M., McKnight, G., Scheulen, F., Nutt, S.: Membrane-type metamaterials: transmission loss of multi-celled arrays. J. Appl. Phys. 109, 104902 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3583656
Gao, C., Halim, D., Yi, X.: Study of bandgap property of a bilayer membrane-type metamaterial applied on a thin plate. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 184, 105708 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2020.105708
Ma, F., Cai, Y., Wu, J.H.: Ultralight plat-type vibration damper with designable working bandwidth and strong multi-peak suppression performance. J. Phys. D. Appl. Phys. 54, 055303 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6463/abc11a
Xiao, W., Zeng, G.W., Cheng, Y.S.: Flexural vibration band gaps in a thin plate containing a periodic array of hemmed discs. Appl. Acoust. 69, 255–261 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apacoust.2006.09.003
Hsu, J.C., Wu, T.T.: Lamb waves in binary locally resonant phononic plates with two-dimensional lattices. Appl. Phys. Lett. 90, 201904 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2739369
Dal Poggetto, V.F., Serpa, A.L.: Flexural wave band gaps in a ternary periodic metamaterial plate using the plane wave expansion method. J. Sound Vib. 495, 115909 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsv.2020.115909
Langfeldt, F., Gleine, W., Von Estorff, O.: Analytical model for low-frequency transmission loss calculation of membranes loaded with arbitrarily shaped masses. J. Sound Vib. 349, 315–329 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsv.2015.03.037
Li, J., Shi, Y., Jiang, R., Zhang, Z., Huang, Q.: Acoustic insulation mechanism of membrane-type acoustic metamaterials loaded with arbitrarily shaped mass blocks of variable surface density. Materials (Basel) 15, 1556 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15041556
Cheng, C.Z., Yao, S.L., Han, Z.L., Recho, N., Niu, Z.R.: Evaluation of the singularity exponents and characteristic angular functions for piezoelectric V-notches under in plane and out of plane conditions. Theor. Appl. Fract. Mech. 76, 50–59 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tafmec.2015.01.001
Cheng, C.Z., Yao, S.L., Sun, J.L., Niu, Z.R.: Singularity characteristic analysis for a V-notch in angularly heterogeneous moderately thick plate. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 115–116, 215–225 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2016.07.001
Moreno-García, P., dos Santos, J.V.A., Lopes, H.: A review and study on ritz method admissible functions with emphasis on buckling and free vibration of isotropic and anisotropic beams and plates. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 25, 785–815 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11831-017-9214-7
Kumar, Y.: The Rayleigh–Ritz method for linear dynamic, static and buckling behavior of beams, shells and plates: a literature review. JVC J. Vib. Control 24, 1205–1227 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1177/1077546317694724
Gozum, M.M., Serhat, G., Basdogan, I.: A semi-analytical model for dynamic analysis of non-uniform plates. Appl. Math. Model. 76, 883–899 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2019.07.013
Gozum, M.M., Aghakhani, A., Serhat, G., Basdogan, I.: Electroelastic modeling of thin-laminated composite plates with surface-bonded piezo-patches using Rayleigh–Ritz method. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 29, 2192–2205 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1177/1045389X18758189
Gao, C., Pang, F., Li, H., Jia, D., Tang, Y.: Steady and transient vibration analysis of uniform and stepped annular/circular plates based on FSDT. Acta Mech. 233, 1061–1082 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-022-03157-y
Chan, Y.J., Tai, C.Y.: Free vibration of stepped rectangular Mindlin plates with non-Lévy boundary conditions. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 144, 668–678 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2018.05.052
Deng, J., Guasch, O., Zheng, L., Song, T., Cao, Y.: Semi-analytical model of an acoustic black hole piezoelectric bimorph cantilever for energy harvesting. J. Sound Vib. 494, 115790 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsv.2020.115790
Blesa Gracia, J., Rammerstorfer, F.G.: Increase in buckling loads of plates by introduction of cutouts. Acta Mech. 230, 2873–2889 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-019-02435-6
Yang, Y., Cheng, C., Niu, Z., Hu, Z.: Free vibration analysis for V-notched Mindlin plates with free or clamped radial edges. Acta Mech. 233, 2271–2285 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-022-03211-9
Xue, J., Wang, Y.: Free vibration analysis of a flat stiffened plate with side crack through the Ritz method. Arch. Appl. Mech. 89, 2089–2102 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00419-019-01565-6
Xue, J., Wang, Y., Chen, L.: Buckling and free vibration of a side-cracked Mindlin plate under axial in-plane load. Arch. Appl. Mech. 90, 1811–1827 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00419-020-01698-z
Milazzo, A.: Free vibrations analysis of cracked variable stiffness composite plates by the eXtended Ritz method. Mech. Adv. Mater. Struct. 0, 1–17 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1080/15376494.2022.2038742
Song, Y., Xue, K., Li, Q.: A solution method for free vibration of intact and cracked polygonal thin plates using the Ritz method and Jacobi polynomials. J. Sound Vib. 519, 116578 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsv.2021.116578
Huang, C.S., Lee, H.T., Li, P.Y., Chang, M.J.: Three-dimensional free vibration analyses of preloaded cracked plates of functionally graded materials via the mls-ritz method. Materials 14, 7712 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14247712
Liew, K.M., Hung, K.C., Lim, M.K.: A solution method for analysis of cracked plates under vibration. Eng. Fract. Mech. 48, 393–404 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1016/0013-7944(94)90130-9
Kharazi, M., Ovesy, H.R., Taghizadeh, M.: Buckling of the composite laminates containing through-the-width delaminations using different plate theories. Compos. Struct. 92, 1176–1183 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2009.10.019
Cheng, C.Z., Zhou, W., Niu, Z.R., Recho, N.: Stress singularity analysis for orthotropic V-notches in the generalised plane strain state. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 38, 881–896 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1111/ffe.12282
Zhou, D., Cheung, Y.K., Au, F.T.K., Lo, S.H.: Three-dimensional vibration analysis of thick rectangular plates using Chebyshev polynomial and Ritz method. Int. J. Solids Struct. 39, 6339–6353 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0020-7683(02)00460-2
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Project No. 11872159, 12132002, and 62188101).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this manuscript. This manuscript has not been published previously and not under consideration for publication elsewhere, in whole or in part.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xue, J., Chen, LQ. A semi-analytical model for dynamic analysis of thin plates with plate-type resonators. Acta Mech 234, 2315–2329 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-023-03496-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-023-03496-4