Abstract
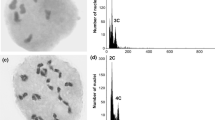
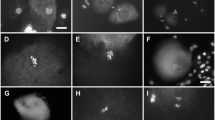
The genus Disporum (Colchicaceae) comprises approximately 20 species distributed throughout Asia, of which four species (Disporum sessile, D. smilacinum, D. uniflorum, and D. viridescens) are currently recognized in Korea. Mixed-ploidy variations, including odd-ploidy levels within the same species, are important in evolution as they enable backcrosses with their parental cytotypes. However, Korean Disporum species have not been examined in detail with regard to ploidy variation and pollen fertility. Therefore, we document the occurrence of diploids and triploids among the Disporum spp. in Korea and report for the first time that D. sessile and D. smilacinum are both diploid (2n = 2x = 16) and triploid (2n = 3x = 24), though they were previously known as diploids from Korean natural populations. The total haploid chromosome length is variable, ranging from 67.32 µm in diploid D. smilacinum to 108.11 µm in triploid D. smilacinum; however, the karyotypes of the investigated species are similar regardless of the ploidy levels. The occurrence of fertile pollen grains from triploid individuals is approximately two-thirds that from diploid species, but triploid plants show no pollen tube germination compared to their diploid counterparts. Overall, this study presents the first comprehensive chromosomal and pollen fertility data for Korean Disporum species, and thus lays the foundation for better understanding the evolution and diversification of morphologically and cytologically variable plant groups.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article [and its supplementary information files].
References
Adams KL, Wendel JF (2005) Polyploidy and genome evolution in plants. Curr Opin Pl Biol 8:135–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2005.01.001
Baeza C, Schrader O, Budahn H (2007) Characterization of geographically isolated accessions in five Alstroemeria L. species (Chile) using FISH of tandemly repeated DNA sequences and RAPD analysis. Pl Syst Evol 269:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00606-007-0591-5
Bennert W, Lubienski M, Körner S, Steinberg M (2005) Triploidy in Equisetum subgenus Hippochaete (Equisetaceae, Pteridodphyta). Ann Bot (Oxford) 95:807–815. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mci084
Chacón J, Cusimano N, Renner SS (2014) The evolution of Colchicaceae, with a focus on chromosome number. Syst Bot 39:415–427. https://doi.org/10.1600/036364414X680852
Chao CY, Chuang TI, Hu WWL (1962) A cytotaxonomic study of the Disporum of Taiwan. Bot Bull Acad Sin 4:80–89
Chao C-T, Tseng Y-H (2019) Taxonomic revision of Disporum Salisb. (Colchicaceae, Uvularioideae) of Taiwan. Phytokeys 119:1–22. https://doi.org/10.3897/phytokeys.119.33516
Chen XQ, Liang SY, Xui JM, Tamura MN (2000) Liliaceae. In: Wu Z-Y, Raven PH (eds) Flora of China. Beijing & Missouri Botanical Garden Press, St. Louis, pp 73–263
Chen LF, Palmer RG (1985) Cytological studies of triploids and their progeny from male-sterile (ms1) soybean. Theor Appl Genet 71:400–407. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00251179
Choi B, Yang S, Song JH, Jang TS (2019) Karyotype and genome size variation in Ajuga L. (Ajugoideae-Lamiaceae). Nordic J Bot 37:e02337. https://doi.org/10.1111/njb.02337
Choi B, Weiss-Schneeweiss H, Temsch EM, So S, Myeong HH, Jang TS (2020) Genome size and chromosome number evolution in Korean Iris L. species (Iridaceae Juss.). Plants 9:1284. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9101284
Erdtman G (1952) On pollen and spore terminology. Stockholm, Sweden, pp 169–176
Ezura H, Kikuta I, Oosawa K (1994) Production of aneuploid melon plants following in vitro culture of seeds from a triploid × diploid cross. Pl Cell Tiss Org Cult 38:61–63. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00034445
Farco GE, Dematteis M (2014) Meiotic behavior and pollen fertility in triploid and tetraploid natural populations of Campuloclinium macrocephalum (Eupatorieae, Asteraceae). Pl Syst Evol 300:1843–1852. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00606-014-1011-2
Felber F (1991) Establishment of a tetraploid cytotype in a diploid population: effect of relative fitness of the cytotypes. J Evol Biol 4:195–207. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1420-9101.1991.4020195.x
Fujishima H, Kurita M (1973) Variation in number, size and location of satellite of Disporum sessile Don. Jap J Genet 48:271–278. https://doi.org/10.1266/jjg.48.271
Giacò A, de Giorgi P, Astuti G, Varaldo L, Sáez L, Carballal R, Serrano M, Casazza G, Caputo P, Bacchetta G, Peruzzi L (2022) Diploids and polyploids in the Santolina chamaecyparissus complex (Asteraceae) show different karyotype asymmetry. Pl Biosyst 156:1237–1246. https://doi.org/10.1080/11263504.2022.2029971
Grubbs KC, Small RL, Schilling EE (2009) Evidence for multiple, autoploid origins of agamospermous populations in Eupatorium sessilifolium (Asteraceae). Pl Syst Evol 279:151–161. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00606-009-0155-y
Guerra M (2008) Chromosome numbers in plant cytotaxonomy: concepts and implications. Cytogenet Genome Res 120:339–350. https://doi.org/10.1159/000121083
Hara H (1988) A revision of the Asiatic species of the genus Disporum (Liliaceae). In: Ōba H, Malla SB (eds) The Himalayan plants. University of Tokyo Press, Tokyo, pp 163–209
Hasegawa N (1932) Comparison of chromosome types in Disporum. Cytologia 3:350–368. https://doi.org/10.1508/cytologia.3.350
Heckenhauer J, Samuel R, Ashton PS, Turner B, Barfuss MHJ, Jang T-S, Temsch EM, McCann J, Salim KA, Attanayake AMAS, Chase MW (2017) Phylogenetic analyses of plastid DNA suggest a different interpretation of morphological evolution than those used as the basis for previous classifications of Dipterocarpaceae (Malvales). Bot J Linn Soc 185:1–26. https://doi.org/10.1093/botlinnean/box044
Hojsgaard D (2018) Transient activation of apomixis in sexual neotriploids may retain genomically altered states and enhance polyploid establishment. Frontiers Pl Sci 9:230. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.00230
Hori Y, Yokoi T, Yokoi Y (1992) Size-structures and reproductive characteristics in diploid and triploid populations of Disporum sessile D. Don (Liliaceae). Pl Species Biol 7:77–85. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1442-1984.1992.tb00221.x
Hori Y, Yokoi T, Yokoi Y (1995) Effects of light intensity on the size structure and establishment of diploid and triploids of Disporum sessile. Pl Species Biol 10:11–16. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1442-1984.1995.tb00116.x
Husband BC (2004) The role of triploid hybrids in the evolutionary dynamics of mixed-ploidy populations. Biol J Linn Soc 82:537–546. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1095-8312.2004.00339.x
Jang T-S, Moon H-K, Hong S-P (2015) Sex expression, population structure, and floral dimorphism in a gynodioecious herb, Agastache rugosa (Lamiaceae) in Korea. Flora 215:23–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.flora.2015.06.004
Kang S, Choi B, Jang T-S (2021) Chromosome evolution in Korean Carduus-Cirsium taxa (Asteraceae). Cytologia 86:375–384. https://doi.org/10.1508/cytologia.86.375
Kim H, Choi B, Lee C, McAdam SAM, Paik J-H, Jang T-S (2021) Micromorphological differentiation of Korean Disporum species using light and scanning electron microscopy. Microsc Res Tech 84:2614–2624. https://doi.org/10.1002/jemt.23812
Kim H, Choi B, Lee C, Paik J-H, Jang C-G, Weiss-Schneeweiss H, Jang T-S (2023) Does the evolution of micromorphology accompany chromosomal changes on dysploidy and polyploid levels in the Barnardia japonica complex (Hyacinthaceae)? BMC Pl Biol 23:485. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-023-04456-9
Kolář F, Štech M, Trávníček P, Rauchová J, Urfus T, Vít P, Kubešová M, Suda J (2009) Towards resolving the Knautia arvensis agg. (Dipsacaceae) puzzle: primary and secondary contact zones and ploidy segregation at landscape and microgeographic scales. Ann Bot (Oxford) 103:963–974. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcp016
Kolář F, Čertner M, Suda J, Schönswetter P, Husband BC (2017) Mixed-ploidy species: progress and opportunities in polyploid research. Trends Pl Sci 22:1041–1055. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2017.09.011
Köhler C, Mittelsten Scheid O, Erilova A (2010) The impact of the triploid block on the origin and evolution of polyploid plants. Trends Genet 26:142–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tig.2009.12.006
Kumar P, Rana PK, Singhal VK (2014) Male meiosis, morphometric analysis and natural propagation in the 2x and 3x cytotypes of Tordyliopsis brunonis (Apiaceae) from northwest Himalayas (India). Pl Syst Evol 300:1477–1486. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00606-013-0975-7
Lavia GI, Ortiz AM, Robledo G, Fernández A, Seijo G (2011) Origin of triploid Arachis pintoi (Leguminosae) by autopolyploidy evidenced by FISH and meiotic behaviour. Ann Bot (Oxford) 108:103–111. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcr108
Lee NS (1979) A taxonomic study of the genus Disporum in Korea. Korean J Pl Taxon 9:67–87. https://doi.org/10.11110/kjpt.1979.9.1.067
Lee NS, Yeau SH (1990) A palynological study on Streptopus ovalis (Ohwi) Wang et Y.C. Tang and the relative species (tribe Polygonateae, Liliaceae). Korean J Pl Taxon 20:81–94. https://doi.org/10.11110/kjpt.1990.20.2.081
Lee NS (2007) Disporum Salisb. ex D. Don. In: Park C (ed) The genera of vascular plants of Korea. Academy Publishing Co, Seoul, pp 1309–1310
Lysák MA, Schubert I (2013) Mechanisms of chromosome rearrangements. In: Greilhuber J, Dolezel J, Wendel JF (eds) Plant genome diversity: physical structure, behaviour and evolution of plant genomes. Springer, Wien, pp 137–147
Madlung A (2013) Polyploidy and its effect on evolutionary success: old questions revisited with new tools. Heredity 110:99–104. https://doi.org/10.1038/hdy.2012.79
Marinho RC, Mendes-Rodrigues C, Bonetti AM, Oliveira PE (2014) Pollen and stomata morphometrics and polyploidy in Eriotheca (Malvaceae-Bombacoideae). Pl Biol 16:508–511. https://doi.org/10.1111/plb.12135
Marks GE (1966) The origin and signifcance of intraspecifc polyploidy: experimental evidence from Solanum chacoense. Evolution 20:552–557. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1558-5646.1966.tb03385.x
Mock KE, Callahan CM, Islam-Faridi MN, Shaw JD, Rai HS, Sanderson SC, Rowe CA, Ryel RJ, Madritch MD, Gardner RS, Wolf PG (2012) Widespread triploidy in western north American aspen (Populus tremuloides). PLoS ONE 7:e48406. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0048406
Morgan EJ, Čertner M, Lučanová M, Deniz U, Kubíková K, Venon A, Kovářík O, Placette CL, Kolář F (2021) Disentangling the components of triploid block and its fitness consequences in natural diploid-tetraploid contact zones of Arabidopsis arenosa. New Phytol 232:1449–1462. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.17357
Mráz P, Chrtek J, Šingliarova B (2009) Geographical parthenogenesis, genome size variation and pollen production in the arctic-alpine species Hieracium alpinum. Bot Helv 119:41–51. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00035-009-0055-3
Nishiwaki A, Mizuguti A, Kuwabara S, Toma Y, Ishigaki G, Miyashita T, Tamada T, Matuura H, Yamaguchi S, Rayburn AL, Akashi R, Stewart JR (2011) Discovery of natural Miscanthus (Poaceae) triploid plants in sympatric populations of Miscanthus sacchariflorus and Miscanthus sinensis in southern Japan. Amer J Bot 98:154–159. https://doi.org/10.3732/ajb.1000258
Noyes RD (2000) Diplospory and parthenogenesis in sexual and agamospermous (apomictic) Erigeron (Asteraceae) hybrids. Int J Pl Sci 161:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1086/314238
Osuji J, Vuylsteke D, Ortiz R (1997) Ploidy variation in hybrids from interploid 3x × 2x crosses in Musa. Tropicultura 15:37–39
Otto SP, Whitton J (2000) Polyploid incidence and evolution. Annual Rev Genet 34:401–437. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.genet.34.1.401
Peskoller A, Silbernagl L, Hülber K, Sonnleitner M, Schönswetter P (2021) Do pentaploid hybrids mediate gene flow between tetraploid Senecio disjunctus and hexaploid S. carniolicus s.str. (S. carniolicus aggregate, Asteraceae)? Alpine Bot 131:151–160. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00035-021-00254-x
Punt W, Hoen PP, Blackmore S, Nilsson S, Le Thomas A (2007) Glossary of pollen and spore terminology. Rev Palaeobot Palynol 143:1–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.revpalbo.2006.06.008
Ramanna MS, Jacobsen E (2003) Relevance of sexual polyploidization for crop improvement: a review. Euphytica 133:3–18. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1025600824483
Ramsey J, Schemske DW (1998) Pathways, mechanisms and rates of polyploid formation in flowering plants. Annual Rev Ecol Syst 29:467–501. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.ecolsys.29.1.467
Rice A, Glick L, Abadi S, Einhorn M, Kopelman NM, Mayzel J, Chay O, Mayrose I (2015) The chromosome counts database (CCDB): a community resource of plant chromosome numbers. New Phytol 206:19–26. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.13191
Rotreklová O, Krahulcová A (2016) Estimating paternal efficiency in an agamic polyploid complex: pollen stainability and variation in pollen size related to reproduction mode, ploidy level and hybridogenous origin in Pilosella (Asteraceae). Folia Geobot 51:175–186. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12224-016-9240-5
Sabara HA, Kron P, Husband BC (2013) Cytotype coexistence leads to triploid hybrid production in a diploid-tetraploid contact zone of Chamerion angustifolium (Onagraceae). Amer J Bot 100:962–970. https://doi.org/10.3732/ajb.1200583
Saensouk P, Senavongse R, Saensouk S (2023) Cytogenetics of four rare species of the genus Alocasia in Thailand. Cytologia 88:21–25. https://doi.org/10.1508/cytologia.88.21
Saito Y, Iwashina T, Peng C-I, Kokubugata G (2009) Taxonomic reconsideration of Disporum luzoniense (Liliaceae s.l.) using flavonoid characters. Blumea 54:59–62. https://doi.org/10.3767/000651909X474096
Schinkel CCF, Kirchheimer B, Dullinger S, Geelen D, Storme ND, Hörandl E (2017) Pathways to polyploidy: indications of a female triploid bridge in the alpine species Ranunculus kuepferi (Ranunculaceae). Pl Syst Evol 303:1093–1108. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00606-017-1435-6
Shinwari ZK, Terauchi R, Kawano S (1994) Molecular systematics of Liliaceae-Asparagoideae-Polygonatae. I. RFLP Analysis of cpDNA in several Asiatic Disporum species. Pl Spec Biol 9:11–18. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1442-1984.1994.tb00076.x
Singh RN (1992) Chromosomal abnormalities and fertility in induced autotetraploid Helianthus annuus in the C1 and C2 generations. Cytologia 57:277–281
Soltis DE, Albert VA, Leebens-Mack J, Bell CD, Paterson AH, Zheng C, Sankoff D, de Pamphilis CW, Wall PK, Soltis PS (2009) Polyploidy and angiosperm diversification. Am J Bot 96:336–348. https://doi.org/10.3732/ajb.0800079
Stebbins GL (1971) Chromosomal evolution in higher plants. Addison-Wesley, London
Tamura MN, Utech FH, Kawano S (1992) Biosystematic studies in Disporum (Liliaceae-Polygonateae) IV. Karyotype analysis of some Asiatic and North American taxa with special reference to their systematic status. Plant Species Biol 7:103–120. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1442-1984.1992.tb00224.x
Tamura MN, Yamada M, Fuse S, Hotta M (2013) Molecular phylogeny and taxonomy of the genus Disporum (Colchicaceae). Acta Phytotax Geobot 64:137–147. https://doi.org/10.18942/apg.KJ00008918923
Utech FH, Kawano S (1977) Biosystematic studies in Disporum (Liliaceae-Polygonatae) II. Pollen fertility, meiosis and chiasma frequency in D. smilacinum A. Gray. Cytologia 42:101–109
van Dijk PJ (2003) Ecological and evolutionary opportunities of apomixis: insights from Taraxacum and Chondrilla. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 358:1113–1121. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2003.1302
Wang J, Huo B, Liu W, Li D, Liao L (2017) Abnormal meiosis in an intersectional allotriploid of Populus L. and segregation of ploidy levels in 2x × 3x progeny. PLoS ONE 12:e0181767. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0181767
Wang L, Gu L, Zhao C, Liu J (2018) Pollen morphology of Polygonatae and its systematic significance. Palynology 42:255–272. https://doi.org/10.1080/01916122.2017.1339217
Weiss-Schneeweiss H, Schneeweiss GM (2013) Karyotype diversity and evolutionary trends in angiosperms. In: Leitch IJ, Greilhuber J, Doležel J, Wendel JF (eds) Plant genome diversity: physical structure, behavior and evolution of plant genomes. Springer Verlag, Vienna, pp 209–230. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-7091-1160-4_13
Weiss-Schneeweiss H, Stuessy TF, Siljak-Yakovlev S, Baeza CM, Parker J (2003) Karyotype evolution in South American species of Hypochaeris (Asteraceae, Lactuceae). Pl Syst Evol 241:171–184. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00606-003-0026-x
Wizenberg SB, Dang M, Campbell LG (2022) Methods for characterizing pollen fitness in Cannabis sativa L. PLoS ONE 17:e0270799. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0270799
Wood TE, Takebayashi N, Barker MS, Mayrose I, Greenspoon PB, Rieseberg LH (2009) The frequency of polyploid speciation in vascular plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:13875–13879. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0811575106
Zhang C, Park S (2009) Aneuploid production from crosses with diploid and triploid in apple tree. Hort Environm Biotechnol 50:203–207
Acknowledgements
The authors appreciate the critical and valuable review of the manuscript provided by anonymous reviewers. The authors thank Mr. Yong-Soon Lee (Kongju National University) and CNUK lab members for their help with field work.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Korea government (NRF-2021R1I1A2045820) to T.-S. Jang.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HK: plant collection, laboratory procedures, and writing—original draft. BC: conceptualization, plant collection, and review & editing. SS: plant collection, manuscript revision. HHM: plant collection, manuscript revision. TSJ: conceptualization, funding acquisition, project administration, supervision, plant collection, writing—original draft, review & editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Handling Editor: Karol Marhold.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
606_2024_1894_MOESM4_ESM.pdf
Independent samples t-tests between diploids and triploids in Disporum. smilacinum with t-value (T), degrees of freedom (df) and p-value (P) for every parameter
Information on Electronic Supplementary Material
Information on Electronic Supplementary Material
Online Resource 1. Previously reported chromosome numbers in the genus Disporum.
Online Resource 2. Pollen viability between diploids and triploids in Disporum smilacinum.
Online Resource 3. Pollen size measurements between diploids and triploids in Disporum smilacinum.
Online Resource 4. Independent samples t-tests between diploids and triploids in Disporum smilacinum with t-value (T), degrees of freedom (df) and p-value (P) for every parameter.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, H., Choi, B., So, S. et al. Cytological and pollen fertility analysis of diploids and triploids in Korean Disporum species. Plant Syst Evol 310, 11 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00606-024-01894-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00606-024-01894-2