Abstract
The authors describe a magnetic metal-organic framework nanocomposite consisting of aminodibenzo-18-crown-6 magnetite nanoparticles and MIL-101(Cr). It was employed to the speciation analysis of Tl(I) and Tl(III) ions. The sorbent is capable of selectively extracting Tl(I) while Tl(III) remains in solution. The total amount of thallium was then determined by reducing Tl(III) to Tl(I) by hydroxylamine hydrochloride and also extracting it. The extraction parameters were optimized by employing design of experiments methodology. Thallium was quantified by ET-AAS. Under optimized conditions, the detection limit is as low as 1.5 ng L−1, the quantification limit is 5.0 ng L−1, the linear range extends from 5 to 400 ng L−1, and the relative standard deviation is <12% (for n = 5 at levels of 5, 50 and 250 ng L−1). The recoveries of real samples analysis were in the range of 90–106%. The method was successfully applied to the analysis of a certified reference material (NIST SRM 1643d water sample) and to various real water samples.

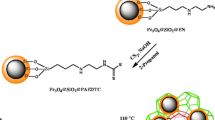
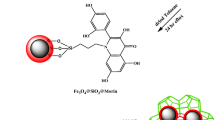
A novel metal-organic framework nanocomposite consisting of aminodibenzo-18-crwon-6 magnetite nanoparticles (Fe3O4@ADB18C6) and MIL-101(Cr) was synthesized, characterized and employed to speciation analysis of Tl(I) and Tl(III).


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shakerian F, Dadfarnia S, Haji Shabani AM, Shiralian Esfahani G (2013) Preconcentration and determination of lead(II) by microextraction based on suspended cadion covered zirconia nano-particles in a surfactant media. Microchim Acta 180:1225–1232
Zeng SL, Gan N, Weideman-Mera R, Cao YT, Li TH, Sang WG (2013) Enrichment of polychlorinated biphenyl 28 from aqueous solutions using Fe3O4 grafted graphene oxide. Chem Eng J 218:108–115
Asgharinezhad AA, Jalilian N, Ebrahimzadeh H, Panjali Z (2015) A simple and fast method based on new magnetic ion imprinted polymer nanoparticles for the selective extraction of Ni(II) ions in different food samples. RSC Adv 5:45510–45519
Jalilian N, Ebrahimzadeh H, Asgharinezhad AA, Molaei K (2017) Extraction and determination of trace amounts of gold(III), palladium(II), platinum(II) and silver(I) with the aid of a magnetic nanosorbent made from Fe3O4-decorated and silica-coated graphene oxide modified with a polypyrrole-polythiophene copolymer. Microchim Acta 184:2191–2200
Tahmasebi E, Yamini Y (2014) Polythiophene-coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles as a selective adsorbent for magnetic solid-phase extraction of silver(I), gold(III), copper(II) and palladium(II). Microchim Acta 181:543–551
Cui Y, Liu S, Wei K, Liu Y, Hu Z (2015) Magnetic solid-phase extraction of trace-level mercury(II) ions using magnetic core-shell nanoparticles modified with thiourea-derived chelating agents. Microchim Acta 182:1337–1344
Mehdinia A, Shoormeij Z, Jabbari A (2017) Trace determination of lead(II) ions by using a magnetic nanocomposite of the type Fe3O4/TiO2/PPy as a sorbent, and FAAS for quantitation. Microchim Acta 184:1529–1537
Li QL, Wang LL, Wang X, Wang ML, Zhao RS (2016) Magnetic metal-organic nanotubes: an adsorbent for magnetic solid-phase extraction of polychlorinated biphenyls from environmental and biological samples. J Chromatogr A 1449:39–47
Yang Y, Ma X, Feng F, Dang X, Huang J, Chen H (2016) Magnetic solid-phase extraction of triclosan using core-shell Fe3O4@MIL-100 magnetic nanoparticles, and its determination by HPLC with UV detection. Microchim Acta 183:2467–2472
Kolaei M, Dashtian K, Rafiee Z, Ghaedi M (2016) Ultrasonic-assisted magnetic solid phase extraction of morphine in urine samples by new imprinted polymer-supported on MWCNT- Fe3O4-NPs: central composite design optimization. Ultrason Sonochem 33:240–248
Liu J, Zhao Z, Shao P, Cui F (2015) Activation of peroxy monosulfate with magnetic Fe3O4-MnO2 core-shell nanocomposites for 4-chlorophenol degradation. Chem Eng J 262:854–861
Rocío-Bautista P, Pacheco-Fernández I, Pasán J, Pino V (2016) Are metal-organic frameworks able to provide a new generation of solid-phase microextraction coatings?-a review. Anal Chim Acta 939:26–41
Maya F, Cabello CP, Frizzarin RM, Estela JM, Palomino GT, Cerdà V (2017) Magnetic solid-phase extraction using metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) and their derived carbons. TrAC, Trends Anal Chem 90:142–152
Leng K, Sun Y, Li X, Sun S, Xu W (2016) Rapid synthesis of metal–organic frameworks MIL-101 (Cr) without the addition of solvent and hydrofluoric acid. Cryst Growth Des 16:1168–1171
Escudero LB, Wuilloud RG, Olsina RA (2013) Sensitive determination of thallium species in drinking and natural water by ionic liquid assisted ion-pairing liquid-liquid microextraction and inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. J Hazard Mater 244-245:380–386
Afshar EA, Taher MA, Fazelirad H (2017) Ultra-trace determination of thallium (I) using a nanocomposite consisting of magnetite, halloysite nanotubes and dibenzo-18-crown-6 for preconcentration prior to its quantitation by ET-AAS. Microchim Acta 184:791–797
Baxter MJ, Crews HM, Dennis MJ, Goodall I, Anderson D (1997) The determination of the authenticity of wine from its trace element composition. Food Chem 60:443–450
Nazari S, Mehri A, Hassannia AS (2017) Fe3O4-modified graphene oxide as a sorbent for sequential magnetic solid phase extraction and dispersive liquid phase microextraction of thallium. Microchim Acta 184:3239–3246
Medek P, Pavlíčková J, Zbíral J, Čižmárová E, Kubáň V (2001) Inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometric (ICP/MS) determination of thallium in soils and winter rapeseeds. Int J Environ Anal Chem 81:207–219
Maia SM, Vale MG, Welz B, Curtius AJ (2001) Feasibility of isotope dilution calibration for the determination of thallium in sediment using slurry sampling electrothermal vaporization inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Spectrochim Acta B 56:1263–1275
Asami T, Mizui C, Shimada T, Kubota M (1996) Determination of thallium in soils by flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Fresenius J Anal Chem 356:348–351
Dadfarnia S, Assadollahi T, Shabani AH (2007) Speciation and determination of thallium by on-line microcolumn separation/preconcentration by flow injection–flame atomic absorption spectrometry using immobilized oxine as sorbent. J Hazard Mater 148:446–452
Silva AF, Borges DL, Welz B, Vale MG, Silva MM, Klassen A, Heitmann U (2004) Method development for the determination of thallium in coal using solid sampling graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry with continuum source, high-resolution monochromator and CCD array detector. Spectrochim Acta B 59:841–850
Horiguchi R, Nukatsuka I, Shimizu Y, Sekikawa S, Ohzeki K (2002) Determination of thallium in water by electrothermal AAS with the direct injection of a cellulose nitrate resin suspension used for solid-phase extraction. Bunseki Kagaku 51:675–1679
Hoeflich LK, Gale RJ, Good ML (1983) Differential pulse polarography and differential pulse anodic stripping voltammetry for determination of trace levels of thallium. Anal Chem 55:1591–1595
Kalantari H, Manoochehri M (2018) A nanocomposite consisting of MIL-101 (Cr) and functionalized magnetite nanoparticles for extraction and determination of selenium (IV) and selenium (VI). Microchim Acta 185:196
Wang Y, Chen H, Tang J, Ye G, Ge H, Hu X (2015) Preparation of magnetic metal organic frameworks adsorbent modified with mercapto groups for the extraction and analysis of lead in food samples by flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Food Chem 181:191–197
Asgharinezhad AA, Ebrahimzadeh H (2016) Poly (2-aminobenzothiazole)-coated graphene oxide/magnetite nanoparticles composite as an efficient sorbent for determination of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in urine sample. J Chromatogr A 1435:18–29
Darroudi A, Arbab Zavar MH, Chamsaz M, Zohuri G, Ashraf N (2012) Ion-imprinted polymer mini-column for on-line preconcentration of thallium(III) and its determination by flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Anal Methods 4:3798–3803
Gil RA, Pacheco PH, Smichowski P, Olsina RA, Martinez LD (2009) Speciation analysis of thallium using electrothermal AAS following on-line pre-concentration in a microcolumn filled with multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Microchim Acta 167:187–193
Chamsaz M, Arbab-Zavar MH, Darroudi A, Salehi T (2009) Preconcentration of thallium(I) by single drop microextraction with electrothermal atomic absorption spectroscopy detection using dicyclohexano-18-crown-6 as extractant system. J Hazard Mater 167:597–601
Arbab-Zavar MH, Chamsaz M, Zohuri G, Darroudi A (2011) Synthesis and characterization of nano-pore thallium(III) ion imprinted polymer as a new sorbent for separation and preconcentration of thallium. J Hazard Mater 185:38–43
Asadpour S, Chamsaz M, Entezari MH, Haron MJ, Ghows N (2016) On-line preconcentration of ultra-trace thallium(I) in water samples with titanium dioxide nanoparticles and determination by graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry. Arab J Chem 9:S1833–S1839
Karatepe A, Soylak M, Elçi L (2011) Selective preconcentration of thallium species as chloro and iodo complexes on Chromosorb 105 resin prior to electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry. Talanta 85:1974–1979
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge Iran National Science Foundation for their help in funding the project (Project No. 97000284).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 864 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rezabeyk, S., Manoochehri, M. Speciation analysis of Tl(I) and Tl(III) after magnetic solid phase extraction using a magnetite nanoparticle composite modified with aminodibenzo-18-crown-6 functionalized MIL-101(Cr). Microchim Acta 185, 365 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2881-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2881-8