Abstract
The authors describe new bifunctional mesoporous silica nanoparticles (NPs) for specific targeting of tumor cells and for intracellular delivery of the cancer drug doxorubicin (DOX). Mesoporous silica nanoparticles (MSNPs) were coated with blue fluorescent N-graphene quantum dots, loaded with the drug DOX, and finally coated with hyaluronic acid (HA). Cellular uptake of the NPs with an architecture of the type HA-DOX-GQD@MSNPs enabled imaging of human cervical carcinoma (HeLa) cells via fluorescence microscopy. The cytotoxicity of the nanoparticles on HeLa cells was also assessed. The results suggest that the NPs are higher cytotoxicity effect and exert in living cell imaging ability. Compared to the majority of other drug nanocarrier systems, the one described here enables simultaneous DOX release and fluorescent monitoring.

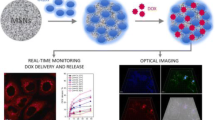
Schematic of the bifunctional mesoporous silica nanoparticles were obtained via the Stöber method, along with the doxorubicin loaded and the hyaluronic acid capped. The sensor shows good specificity and significant cytotoxicity effect on Hela cells. (TEOS: tetraethyl orthosilicate; GQDs: graphene quantum dots; DOX: doxorubicin; HA: Hyaluronic acid).







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hocinea O, Gary-Bobod M, Breveta D, Maynadierd M, Fontaneld S, Raehma L, Richetera S, Loockh B, Couleaudj P, Frochotj C, Charnayb C, Derrienb G, Smaïhic M, Sahmounel A, Morèrek A, Maillardh P, Garciad M, Duranda JO (2010) Silicalites and mesoporous silica nanoparticles for photodynamic therapy. Int J Pharm 402:221–230
Hu JJ, Lei Q, Peng MY, Zheng DW, Chen YX, Zhang XZ (2017) A positive feedback strategy for enhanced chemotherapy based on ROS-triggered self-accelerating drug release nanosystem. Biomaterials 128:136–146
Li XY, Pan LM, Shi JL (2015) Nuclear-targeting MSNs-based drug delivery system: global gene expression analysis on the MDR-overcoming mechanisms. Adv Healthcare Mater 4:2641–2648
Liu YY, Miyoshi H, Nakamurac M (2007) Novel drug delivery system of hollow mesoporous silica nanocapsules with thin shells: preparation and fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) release kinetics. Colloids Surf B: Biointerfaces 58:180–187
Mekaru H, Lu J, Tamanoi F (2015) Development of mesoporous silica-based nanoparticles with controlled release capability for cancer therapy. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 95:40–49
Paulo CSO, Neves RPD, Ferreira LS (2011) Nanoparticles for intracellular-targeted drug delivery. Nanotechnology 22:494002–494012
Shahabi S, Döscher S, Bollhorst T, Treccani L, Maas M, Dringen R, Rezwan K (2015) Enhancing cellular uptake and doxorubicin delivery of mesoporous silica nanoparticles via surface functionalization: effects of serum. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:26880–26891
Xu XB, Lü SY, Gao CM, Wang XG, Bai X, Gao NN, Liu MZ (2015) Facile preparation of pH-sensitive and self-fluorescent mesoporous silica nanoparticles modified with PAMAM dendrimers for label-free imaging and drug delivery. Chem Eng J 266:171–178
Lin VSY, Slowing I, Trewyn BG (2006) Effect of surface functionalization of MCM-41-type mesoporous silica nanoparticles on the endocytosis by human cancer cells. J Am Chem Soc 128:14792–14793
Rosenholm JM, Meinander A, Peuhu E, Niemi R, Eriksson JE, Sahlgren C, Linde’n M (2009) Targeting of porous hybrid silica nanoparticles to cancer cells. ACS Nano 3:197–206
Rosenholm JM, Peuhu E, Eriksson JE, Sahlgren C, Linde’n M (2009) Targeted intracellular delivery of hydrophobic agents using mesoporous hybrid silica nanoparticles as carrier systems. Nano Lett 9:3308–3311
Tsai CP, Chen CY, Hung Y, Chang FH, Mou CY (2009) Monoclonal antibody-functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles (MSN) for selective targeting breast cancer cells. J Mater Chem 19:5737–5743
Wang LS, Wu LC, Lu SY, Chang LL, Teng IT, Yang CM, Ho JA (2010) Biofunctionalized phospholipid-capped mesoporous silica nanoshuttles for targeted drug delivery: improved water suspensibility and decreased nonspecific protein binding. ACS Nano 4:4371–4379
Huang HD, Liao L, Xu X, Zou MJ, Liu F, Li N (2013) The electron-transfer based interaction between transition metal ions and photoluminescent graphene quantum dots (GQDs): a platform for metal ion sensing. Talanta 117:152–157
Shi JY, Chan CY, Pang Y, Ye WW, Tian F, Lyn J, Zhang Y, Yang M (2015) A fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) biosensor based on graphene quantum dots (GQDs) and gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) for the detection of mecA gene sequence of Staphylococcusaureus. Biosens Bioelectron 67:595–600
Biswal BP, Shinde DB, Pillai VK, Banerjee R (2013) Stabilization of graphene quantum dots (GQDs) by encapsulation inside zeolitic imidazolate framework nanocrystals for photoluminescence tuning. Nano 5:10556–10561
Surgawanshi A, Biswal M, Mhamane D, Gokhale R, Patil S, Guin D, Ogale S (2014) Large scale synthesis of graphene quantum dots (GQDs) from waste biomass and their use as an efficient and selective photoluminescence on–off– on probe for Ag+ ions. Nano 6:11664–11670
Li X, Zhao Z, Pan C (2016) Ionic liquid-assisted electrochemical exfoliation of carbon dots of different size for fluorescent imaging of bacteria by tuning the water fraction in electrolyte. Microchim Acta 183:2525–2532
Xiao Q, Liang Y, Zhu F, Lu S, Huang S (2017) Microwave-assisted one-pot synthesis of highly luminescent N-doped carbon dots for cellular imaging and multi-ion probing. Microchim Acta 184:2429–2438
Li J, Jiao Y, Feng L, Zhong Y, Zuo G, Xie A, Dong W (2017) Highly N,P-doped carbon dots: rational design, photoluminescence and cellular imaging. Microchim Acta 184:2933–2940
Parvin N, Mandal TK (2017) Dually emissive P,N-co-doped carbon dots for fluorescent and photoacoustic tissue imaging in living mice. Microchim Acta 184:1117–1125
Li H, Shao FQ, Zou SY, Yang QJ, Huang H, Feng JJ, Wang AJ (2016) Microwave-assisted synthesis of N,P-doped carbon dots for fluorescent cell imaging. Microchim Acta 183:821–826
Ruiz V, Fernández I, Carrasco P, Cabanero G, Grande HJ, Herrán J (2015) Graphene quantum dots as a novel sensing material for low-cost resistive and fast-response humidity sensors. Sensors Actuators B Chem 218:73–77
Zheng XT, Ananthanarayanan A, Luo KQ, Chen P (2015) Glowing graphene quantum dots and carbon dots: properties, syntheses, and biological applications. Mater Rev 14:1620–1636
Chen T, Yu H, Yang N, Wang M, Ding C, Fu J (2014) Graphene quantum dot-capped mesoporous silica nanoparticles through an acid-cleavable acetal bond for intracellular drug delivery and imaging. J Mater Chem B 2:4979–4982
Yuan H, Yu J, Feng SL, Gong YJ (2016) Highly photoluminescent pH-independent nitrogen-doped carbon dots for sensitive and selective sensing of p-nitrophenol. RSC Adv 6:15192–15200
Li Y, Zhao Y, Cheng HH, Hu Y, Shi GQ, Dai LM, Qu LT (2012) Nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots with oxygen-rich functional groups. J Am Chem Soc 134:15–18
Chen SF, Song Y, Li Y, Liu YL, Su XG, Ma Q (2015) A facile photoluminescence modulated nanosensor based on nitrogen-doped grapheme quantum dots for sulfite detection. New J Chem 39:8114–8120
Tran VT, Trung NB, Kim HR, Chung JS, Choi WM (2014) One-pot synthesis of N-doped grapheme quantum dots as a fluorescent sensing platform for Fe3+ ions detection. Sensors Actuators B Chem 202:568–573
Li Z, Ni YN, Kokot S (2015) A new fluorescent nitrogen-doped carbon dot system modified by the fluorophore-labeledss DNA for the analysis of 6-mercaptopurine and Hg (II). Biosens Bioelectron 74:91–97
Ju J, Zhang RZ, He SJ, Chen W (2014) Nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots-based fluorescent probe for the sensitive turn-on detection of glutathione and its cellular imaging. RSC Adv 4:52583–52589
Park JH, Cho HJ, Yoon HY, Yoon IS, Ko SH, Shim JS (2014) Hyaluronic acid derivative-coated nanohybrid liposomes for cancer imaging and drug delivery. J Control Release 174:98–108
Zhao QF, Geng HJ, Wang Y, Gao YK, Huang JH, Wang Y, Zhang JH, Wang SL (2014) Hyaluronic acid oligosaccharide modified redox-responsive mesoporous silica nanoparticles for targeted drug delivery. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6:20290–20299
Stöber W, Fink A, Bohn E (1968) Controlled growth of monodisperse silica spheres in the micron size range. J Colloid Interface Sci 26:62–69
Li T, Chen XF, Liu YJ, Fan LL, Lin LQ, Xu Y, Chen SJ, Shao JW (2017) pH-sensitive mesoporous silica nanoparticles anticancer prodrugs for sustained release of ursolic acid and the enhanced anti-cancer efficacy for hepatocellular carcinoma cancer. Eur J Pharm Sci 96:456–463
Lai JP, Shah BP, Garfunkel E, Lee K-B (2014) Versatile FRET-based mesoporous silica nanoparticles for RealTime monitoring of drug release. ACS Nano 7:2741–2750
Tang J, Kong B, Wu H, Xu M, Wang YC, Wang YL, Zhao DY, Zheng CF (2013) Carbon Nanodots featuring efficient FRET for real-time monitoring of drug delivery and two-photon imaging. Adv Mater 25:6569–6574
Rajesh BS, Ammasi P (2003) Fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) microscopy imaging of live cell protein localizations. J Cell Biol 160:629–633
Chen H, Wang ZY, Zong SF, Chen P, Zhu D, Wu L, Cui YP (2015) A graphene quantum dot-based FRET system for nuclear-targeted and real-time monitoring of drug delivery. Nano 7:15477–15486
Liu X, Wei S, Diao Q, Ma P, Xu L, Xu S, Wang X (2017) Hydrothermal synthesis of N-doped carbon dots for selective fluorescent sensing and cellular imaging of cobalt(II). Microchim Acta 184:3825–3831
Xia J, Zhuang YT, Yu YL, Wang JH (2017) Highly fluorescent carbon polymer dots prepared at room temperature, and their application as a fluorescent probe for determination and intracellular imaging of ferric ion. Microchim Acta 184:1109–1116
Yang M, Kong W, Li H, Liu J, Huang H, Liu Y, Kang Z (2015) Fluorescent carbon dots for sensitive determination and intracellular imaging of zinc(II) ion. Microchim Acta 182:2443–2450
Duan HW, Nie SM (2007) Cell-penetrating quantum dots based on multivalent and endosome-disrupting surface coatings. J Am Chem Soc 129:3333–3338
Yao XX, Niu XX, Ma KX, Huang P, Grothe J, Kaskel S, Zhu YF (2017) Graphene quantum dot-capped magnetic mesoporous silica nanoparticles as a multifunctional platform for controlled drug delivery, magnetic hyperthermia, and photothermal therapy. Adv Sci News 13:1602225–1602235
Hao WJ, Shen YX, Liu DY, Shang YZ, Zhang JQ, SH X, Liu HL (2017) Dual-PH-sensitivity and tumour targeting core-shell particles for intracellular drug delivery. RSC Adv 7:851–860
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21075050, No.21005029).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 652 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gui, W., Zhang, J., Chen, X. et al. N-Doped graphene quantum dot@mesoporous silica nanoparticles modified with hyaluronic acid for fluorescent imaging of tumor cells and drug delivery. Microchim Acta 185, 66 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2598-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2598-0