Abstract
The authors report on the microwave-assisted one-step synthesis of nitrogen-doped carbon dots (N-CDs) having a fluorescence quantum yield of 80% and a fluorescence lifetime of 15.0 ns. Citric acid and ethylenediamine were used as carbon source and as a nitrogen source, respectively. The N-CDs show excellent photostability over a wide range of pH values (4–11), even at high ion strength (2 M KCl) and after 4 h of continuous UV light irradiation. This makes these N-QDs promising candidates for fluorescent probes. Cellular toxicity test showed the N-CDs not to be cytotoxic to human nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells and human embryonic kidney cells even at 400 μg∙mL−1 levels after 48 h incubation. The fluorescence intensity of N-CDs at 445 nm is quenched by Fe(III), Hg(II), and chlorite ions, respectively. The N-CDs are shown to be viable fluorescent probes for the ions Fe(III), Hg(II), and chlorite. Respective detection limits are 12 nM, 0.8 nM, and 35 nM.

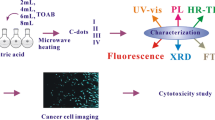
Schematic of the microwave-assisted one-pot synthesis of highly luminescent N-doped carbon dots (N-CDs) by using citric acid (CA) and ethylenediamine (EDA) as carbon and nitrogen sources. The N-CDs were applied to multi-ion [Fe(III); Hg(II) and chlorite] probing and to imaging of human nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells (upper panel) and human embryonic kidney cells (lower panel).







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tan J, Zou R, Zhang J, Li W, Zhang LQ, Yue DM (2016) Large-scale synthesis of N-doped carbon quantum dots and their phosphorescence properties in a polyurethane matrix. Nanoscale 8:4742–4747. doi:10.1039/c5nr08516k
Yang YM, Kong WQ, Li H, Liu J, Yang MM, Huang H, Liu Y, Wang ZY, Wang ZQ, Sham TK, Zhong J, Wang C, Liu Z, Lee ST, Kang ZH (2015) Fluorescent N-doped carbon dots as in vitro and in vivo nanothermometer. ACS Appl mater interfaces 7:27324–27330. doi:10.1021/acsami.5b08782
Zuo PL, Lu XH, Sun ZG, Guo YH, He H (2016) A review on syntheses, properties, characterization and bioanalytical applications of fluorescent carbon dots. Microchim Acta 183:519–542. doi:10.1007/s00604-015-1705-3
Ma Z, Ming H, Huang H, Liu Y, Kang ZH (2012) One-step ultrasonic synthesis of fluorescent N-doped carbon dots from glucose and their visible-light sensitive photocatalytic ability. New J Chem 36:861–864. doi:10.1039/c2nj20942j
Wang Z, Lu YX, Yuan H, Ren ZH, Xu C, Chen J (2015) Microplasma-assisted rapid synthesis of luminescent nitrogen-doped carbon dots and their application in pH sensing and uranium detection. Nanoscale 7:20743–20748. doi:10.1039/c5nr05804j
Xu Y, Wu M, Liu Y, Feng XZ, Yin XB, He XW, Zhang YK (2013) Nitrogen-doped carbon dots: a facile and general preparation method, photoluminescence investigation, and imaging applications. Chem Eur J 19:2276–2283. doi:10.1002/chem.201203641
Qian ZS, Ma JJ, Shan XY, Feng H, Shao LX, Chen JR (2014) Highly luminescent N-doped carbon quantum dots as an effective multifunctional fluorescence sensing platform. Chem Eur J 20:2254–2263. doi:10.1002/chem.201304374
Yang Z, Xu MH, Liu Y, He FJ, Gao F, Su YJ, Wei H, Zhang YF (2014) Nitrogen-doped, carbon-rich, highly photoluminescent carbon dots from ammonium citrate. Nanoscale 6:1890–1895. doi:10.1039/c3nr05380f
Hou J, Li HY, Wang L, Zhang P, Zhou TY, Ding H, Ding L (2016) Rapid microwave-assisted synthesis of molecularly imprinted polymers on carbon quantum dots for fluorescent sensing of tetracycline in milk. Talanta 146:34–40. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2015.08.024
Pedro SG, Salinas-Castillo A, Ariza-Avidad M, Lapresta-Fernández A, Sánchez-González C, Martinez-Cisneros CS, Puyol M, Capitan-Vallvey LF, Alonso-Chamarro J (2014) Microsystem-assisted synthesis of carbon dots with fluorescent and colorimetric properties for pH detection. Nanoscale 4:6018–6024. doi:10.1039/c4nr00573b
Xu ZZ, Wang CX, Jiang KL, Lin HH, Huang YJ, Zhang C (2015) Microwave-assisted rapid synthesis of amphibious yellow fluorescent carbon dots as a colorimetric nanosensor for Cr(VI). Part Part Synt Charact 32:1058–1062. doi:10.1002/ppsc.201500172
Zhang CF, Cui YY, Song L, Liu XF, Hu ZB (2016) Microwave assisted one-pot synthesis of graphene quantum dots as highly sensitive fluorescent probes for detection of iron ions and pH value. Talanta 150:54–60. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2015.12.015
Edison TN, Atchudan R, Sethuraman MG, Shim JJ, Lee YR (2016) Microwave assisted green synthesis of fluorescent N-doped carbon dots: cytotoxicity and bio-imaging applications. J Photochem Photobiol B 161:154–161. doi:10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2016.05.017
Jiang YL, Wang YX, Meng FD, Wang BX, Cheng YX, Zhu CJ (2015) N-doped carbon dots synthesized by rapid microwave irradiation as highly fluorescent probes for Pb2+ detection. New J Chem 39:3357–3360. doi:10.1039/c5nj00170f
Xu MH, Xu SS, Yang Z, Shu MJ, He GL, Huang D, Zhang LL, Li L, Cui DX, Zhang YF (2015) Hydrophilic and blue fluorescent N-doped carbon dots from tartaric acid and various alkylol amines under microwave irradiation. Nanoscale 7:15915–15923. doi:10.1039/c5nr04209g
Zhang YQ, Liu XY, Fan Y, Guo XY, Zhou L, Lv Y, Lin J (2016) One-step microwave synthesis of N-doped hydroxyl-functionalized carbon dots with ultra-high fluorescence quantum yields. Nanoscale 8:15281–15287. doi:10.1039/c6nr03125k
Chang MMF, Ginjom IR, Ngu-Schwemlein M, Ng SM (2016) Synthesis of yellow fluorescent carbon dots and their application to the determination of chromium(III) with selectivity improved by pH tuning. Microchim Acta 183:1899–1907. doi:10.1007/s00604-016-1819-2
Huang S, Qiu HN, Zhu FW, Lu SY, Xiao Q (2015) Graphene quantum dots as on-off-on fluorescent probes for chromium(VI) and ascorbic acid. Microchim Acta 182:1723–1731. doi:10.1007/s00604-015-1508-6
Wang FX, Hao QL, Zhang YH, Xu YJ, Lei W (2016) Fluorescence quenchometric method for determination of ferric ion using boron-doped carbon dots. Microchim Acta 183:273–279. doi:10.1007/s00604-015-1650-1
Li LB, Li L, Wang C, Liu KY, Zhu RH, Qiang H, Lin YQ (2015) Synthesis of nitrogen-doped and amino acid-functionalized graphene quantum dots from glycine, and their application to the fluorometric determination of ferric ion. Microchim Acta 182:763–770. doi:10.1007/s00604-014-1383-6
Tang WJ, Wang Y, Wang PP, Di JW, Yang JP, Wu Y (2016) Synthesis of strongly fluorescent carbon quantum dots modified with polyamidoamine and a triethoxysilane as quenchable fluorescent probes for mercury(II). Microchim Acta 183:2571–2578. doi:10.1007/s00604-016-1898-0
Yan FY, Kong DP, Luo YM, Ye QH, He JJ, Guo XF, Chen L (2016) Carbon dots serve as an effective probe for the quantitative determination and for intracellular imaging of mercury(II). Microchim Acta 183:1611–1618. doi:10.1007/s00604-016-1788-5
Lin YP, Yao BX, Huang TT, Zhang SC, Cao XT, Weng W (2016) Selective determination of free dissolved chlorine using nitrogen-doped carbon dots as a fluorescent probe. Microchim Acta 183:2221–2227. doi:10.1007/s00604-016-1855-y
Simões EF, Leitão JM, da Silva JCE (2016) Carbon dots prepared from citric acid and urea as fluorescent probes for hypochlorite and peroxynitrite. Microchim Acta 183:1769–1777. doi:10.1007/s00604-016-1807-6
Sun J, Yang SW, Wang ZY, Shen H, Xu T, Sun LT, Li H, Chen WW, Jiang XY, Ding GQ, Kang ZH, Xie XM, Jiang MH (2015) Ultra-high quantum yield of graphene quantum dots: aromatic-nitrogen doping and photoluminescence mechanism. Part Part Syst Charact 32:434–440. doi:10.1002/ppsc.201400189
Zhu SJ, Meng QN, Wang L, Zhang JH, Song YB, Jin H, Zhang K, Sun HC, Wang HY, Yang B (2013) Highly photoluminescent carbon dots for multicolor patterning, sensors, and bioimaging. Angew Chem Int Ed 52:3953–3957. doi:10.1002/anie.201300519
Liu Y, Xiao N, Gong NQ, Wang H, Shi X, Gu W, Ye L (2014) One-step microwave-assisted polyol synthesis of green luminescent carbon dots as optical nanoprobes. Carbon 68:258–264. doi:10.1016/j.carbon.2013.10.086
Zhuo Y, Miao H, Zhong D, Zhu SS, Yang XM (2015) One-step synthesis of high quantum-yield and excitation-independent emission carbon dots for cell imaging. Mater Lett 139:197–200. doi:10.1016/j.matlet.2014.10.048
Zou Y, Yan FY, Dai LF, Luo YM, Fu Y, Yang N, Wu JY, Chen L (2014) High photoluminescent carbon nanodots and quercetin-Al3+ construct a ratiometric fluorescent sensing system. Carbon 77:1148–1156. doi:10.1016/j.carbon.2014.06.056
Wang CX, Xu ZZ, Cheng H, Lin HH, Humphrey MG, Zhang C (2015) A hydrothermal route to water-stable luminescent carbon dots as nanosensors for pH and temperature. Carbon 82:87–95. doi:10.1016/j.carbon.2014.10.035
Wolfbeis OS (2015) An overview of nanoparticles commonly used in fluorescent bioimaging. Chem Soc rev 44:4743–4768. doi:10.1039/c4cs00392f
Orte A, Alvarez-Pez JM, Ruedas-Rama MJ (2013) Fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy for the detection of intracellular pH with quantum dot nanosensors. ACS Nano 7:6378–6395. doi:10.1021/nn402581q
Lakowicz JR (2006) Principles of fluorescence spectroscopy, 3rd edn. Plenum Press, New York
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (21563006, 21403039), Natural Science Foundation of Guangxi Province (2015GXNSFAA139033, 2016GXNSFBA380118), BAGUI Scholar Program of Guangxi Province of China, and Guangxi Colleges and Universities Key Laboratory of Synthetic and Natural Functional Molecular Chemistry, Guangxi Teachers Education University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 1112 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, Q., Liang, Y., Zhu, F. et al. Microwave-assisted one-pot synthesis of highly luminescent N-doped carbon dots for cellular imaging and multi-ion probing. Microchim Acta 184, 2429–2438 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2242-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2242-z