Abstract
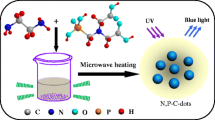
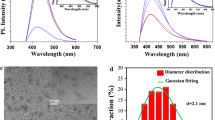
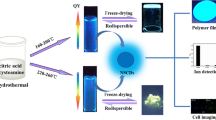
The authors describe the synthesis of carbon dots (CDs) that are highly doped with both nitrogen and phosphorus. Synthesis is accomplished via a hydrothermal reaction starting from diethylenetriaminepenta(methylenephosphonic acid) and m-phenylenediamine as the precursors. The high N,P-doping ratios renders the codoped CDs excellently water soluble, photostable over a wide range of pH values, and photostable in the presence of various metal ions. Ferric ions acts as a strong quencher of fluorescence. Their low cytotoxicity and strong green fluorescence (with excitation/emission peaks at 440/510 nm and a quantum yield of 0.32) make the CDs well suited for purposes of cell imaging, and this is demonstrated by fluorescent bioimaging of human lung carcinoma cells (type A549) and human breast cancer cells (type KB). Furthermore, the CDs were used as an effective probe for monitoring Fe(III) in both aqueous solution and living cells.

A highly N,P-codoped carbon dots (CDs) were synthesized for high-quality cellular Imaging and monitoring Fe3+ in living cells. This water soluble CDs displayed high biocompatibility and emitted strong green fluorescence.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zuo P, Lu X, Sun Z, Guo Y, He H (2016) A review on syntheses, properties, characterization and bioanalytical applications of fluorescent carbon dots. Microchim Acta 183(2):519–542
Zhou J, Zhou H, Tang J, Deng S, Yan F, Li W, Qu M (2017) Carbon dots doped with heteroatoms for fluorescent bioimaging: a review. Microchim Acta 184(2):1–26
Pan L, Sun S, Zhang A, Jiang K, Zhang L, Dong C, Huang Q, Wu A, Lin H (2015) Truly fluorescent excitation-dependent carbon dots and their applications in multicolor cellular imaging and multidimensional sensing. Adv Mater 27(47):7782–7787
Jiang K, Sun S, Zhang L, Wang Y, Cai C, Lin H (2015) Bright-yellow-emissive N-doped carbon dots: preparation, cellular imaging, and bifunctional sensing. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7(41):23231–23238
Huang H, Lv JJ, Zhou DL, Bao N, Xu Y, Wang AJ, Feng JJ (2013) One-pot green synthesis of nitrogen-doped carbon nanoparticles as fluorescent probes for mercury ions. RSC Adv 3(44):21691–21696
Jiang K, Sun S, Zhang L, Lu Y, Wu A, Cai C, Lin H (2015) Red, green, and blue luminescence by carbon dots: full-color emission tuning and multicolor cellular imaging. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 54(18):5360–5363
Li H, Shao FQ, Zou SY, Yang QJ, Huang H, Feng JJ, Wang AJ (2016) Microwave-assisted synthesis of N, P-doped carbon dots for fluorescent cell imaging. Microchim Acta 183(2):821–826
Wang W, Lu YC, Huang H, Feng JJ, Chen JR, Wang AJ (2014) Facile synthesis of water-soluble and biocompatible fluorescent nitrogen-doped carbon dots for cell imaging. Analyst 139(7):1692–1696
Huang H, Lu YC, Wang AJ, Liu JH, Chen JR, Feng JJ (2014) A facile, green, and solvent-free route to nitrogen–sulfur-codoped fluorescent carbon nanoparticles for cellular imaging. RSC Adv 4(23):11872–11875
Lim SY, Shen W, Gao Z (2015) Carbon quantum dots and their applications. Chem Soc Rev 44(1):362–381
Fernando KA, Sahu S, Liu Y, Lewis WK, Guliants EA, Jafariyan A, Wang P, Bunker CE, Sun YP (2015) Carbon quantum dots and applications in photocatalytic energy conversion. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7(16):8363–8376
Ge J, Lan M, Liu W, Jia Q, Guo L, Zhou B, Meng X, Niu G, Wang P (2016) Graphene quantum dots as efficient, metal-free, visible -light-active photocatalysts. Sci China Mater 59(1):12–19
Li H, He X, Kang Z, Huang H, Liu Y, Liu J, Lian S, Tsang CH, Yang X, Lee ST (2010) Water-soluble fluorescent carbon quantum dots and photocatalyst design. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 49(26):4430–4434
Wang X, Sun G, Li N, Chen P (2016) Quantum dots derived from two-dimensional materials and their applications for catalysis and energy. Chem Soc Rev 45(8):2239–2262
Gong X, Zhang Q, Gao Y, Shuang S, Choi MM, Dong C (2016) Phosphorus and nitrogen dual-doped hollow carbon dot as a Nanocarrier for doxorubicin delivery and biological imaging. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8(18):11288–11297
Shi B, Su Y, Zhang L, Huang M, Liu R, Zhao S (2016) Nitrogen and phosphorus co-doped carbon Nanodots as a novel fluorescent probe for highly sensitive detection of Fe(3+) in human serum and living cells. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8(17):10717–10725
Sun X, Bruckner C, Lei Y (2015) One-pot and ultrafast synthesis of nitrogen and phosphorus co-doped carbon dots possessing bright dual wavelength fluorescence emission. Nano 7(41):17278–17282
Li W, Zhang Z, Kong B, Feng S, Wang J, Wang L, Yang J, Zhang F, Wu P, Zhao D (2013) Simple and green synthesis of nitrogen-doped photoluminescent carbonaceous nanospheres for bioimaging. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 52(31):8151–8155
Wu ZL, Zhang P, Gao MX, Liu CF, Wang W, Leng F, Huang CZ (2013) One-pot hydrothermal synthesis of highly luminescent nitrogen-doped amphoteric carbon dots for bioimaging from Bombyx mori silk – natural proteins. J Mater Chem B 1(22):2868
Wang L, Zhou HS (2014) Green synthesis of luminescent nitrogen-doped carbon dots from milk and its imaging application. Anal Chem 86(18):8902–8905
Yang Z, Xu M, Liu Y, He F, Gao F, Su Y, Wei H, Zhang Y (2014) Nitrogen-doped, carbon-rich, highly photoluminescent carbon dots from ammonium citrate. Nano 6(3):1890–1895
Bourlinos AB, Stassinopoulos A, Anglos D, Zboril R, Karakassides M, Giannelis EP (2008) Surface functionalized carbogenic quantum dots. Small 4(4):455–458
Peng H, Travas-Sejdic J (2009) Simple aqueous solution route to luminescent Carbogenic dots from carbohydrates. Chem Mater 21(23):5563–5565
Li H, He X, Liu Y, Huang H, Lian S, Lee S-T, Kang Z (2011) One-step ultrasonic synthesis of water-soluble carbon nanoparticles with excellent photoluminescent properties. Carbon 49(2):605–609
Ding H, Yu SB, Wei JS, Xiong HM (2016) Full-color light-emitting carbon dots with a surface-state-controlled luminescence mechanism. ACS Nano 10(1):484–491
Sun D, Ban R, Zhang P-H, Wu G-H, Zhang J-R, Zhu J-J (2013) Hair fiber as a precursor for synthesizing of sulfur- and nitrogen-co-doped carbon dots with tunable luminescence properties. Carbon 64:424–434
Wang L, Yin Y, Jain A, Zhou HS (2014) Aqueous phase synthesis of highly luminescent, nitrogen-doped carbon dots and their application as bioimaging agents. Langmuir 30:14270–14275
Parvin N, Mandal TK (2017) Dually emissive P, N-co-doped carbon dots for fluorescent and photoacoustic tissue imaging in living mice. Microchim Acta 184(4):1117–1125
Xia J, Zhuang YT, Yu YL, Wang JH (2017) Highly fluorescent carbon polymer dots prepared at room temperature, and their application as a fluorescent probe for determination and intracellular imaging of ferric ion. Microchim Acta 184(4):1109–1116
Yan F, Kong D, Luo Y, Ye Q, He J, Guo X, Chen L (2016) Carbon dots serve as an effective probe for the quantitative determination and for intracellular imaging of mercury (II). Microchim Acta 183(5):1611–1618
Li X, Zhao Z, Pan C (2016) Ionic liquid-assisted electrochemical exfoliation of carbon dots of different size for fluorescent imaging of bacteria by tuning the water fraction in electrolyte. Microchim Acta 183(9):2525–2532
Acknowledgements
Financial supports by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (grant number 51573078) are gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 227 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Jiao, Y., Feng, L. et al. Highly N,P-doped carbon dots: Rational design, photoluminescence and cellular imaging. Microchim Acta 184, 2933–2940 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2314-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2314-0