Abstract
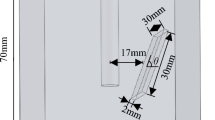
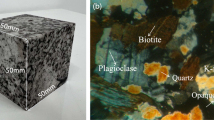
Slate frequently encountered in numerous engineering applications basically exhibits significant anisotropies in terms of physico-mechanical properties due to the presence of well-developed foliation structures. The objective of this study is to investigate the mechanisms of foliation effects on the mechanical and failure characteristics of slate in three-dimensional (3D) space under Brazilian test conditions. A series of laboratory tests are conducted on slate with seven different foliation angles (φ), which are defined as the angle between the foliation plane and end surfaces of the specimen. On the basis of each foliation angle, five different loading angles (θ), which are defined as the projection of the angle between the loading surface and the foliation plane on the front side of the specimen, are selected to ensure that 3D space is involved. The high-speed camera and acoustic emission (AE) system are employed to analyse the failure characteristics of slate during loading process. The testing results indicated that the variations of applied failure force (AFF) with respect to loading angle (θ) significantly differ under varied foliation angles. With increase of foliation angle, the anisotropy ratio of the maximum to minimum AFF shows an increasing trend, suggesting that the anisotropy becomes more notable. The high-speed camera visually recorded the initiation and propagation of cracks. The specimen failure can involve two major processes: the local cracks first occurred on the disc flank, and then the fully connected cracks were formed causing the overall failure. The rupture evolution process inside the specimen was characterised by AE energy and AE hits, which was in good agreement with the high-speed camera observations. When the foliation angle is small, i.e. 0° ≤ φ ≤ 15°, or large, i.e. 75° ≤ φ ≤ 90°, the macro-cracks on both sides (i.e., front and back) show similarity to some certain, and the fracture patterns can be considered as two-dimensional (2D). However, when φ is in the range of 30°–60°, the fractured surfaces have 3D spatial distribution characteristics, and the macro-cracks appearing on both sides exhibit an approximately anti-symmetric relationship. It is also revealed that both φ and θ have significant effects on the AFF and the fracture patterns. The results are likely to provide experimental basis for further improving the theory of tensile properties of anisotropic rocks.














Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
31 March 2021
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-021-02460-9
References
Al-Bazali TM, Zhang JG, Chenevert ME, Sharma MM (2005) Measurement of the sealing capacity of shale caprocks. In: SPE annual technical conference and exhibition, Dallas, Texas. https://doi.org/10.2118/96100-MS
Amann F, Kaiser P, Button EA (2012) Experimental study of brittle behavior of clay shale in rapid triaxial compression. Rock Mech Rock Eng 45(1):21–33. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-011-0195-9
Barla G (1974) Rock anisotropy: theory and laboratory testing. Rock Mech 131–169
Barton N, Quadros E (2015) Anisotropy is everywhere, to see, to measure, and to model. Rock Mech Rock Eng 48(4):1323–1339. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-014-0632-7
Basu A, Mishra DA, Roychowdhury K (2013) Rock failure modes under uniaxial compression, Brazilian, and point load tests. Bull Eng Geol Environ 72:457–475. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-013-0505-4
Bohloli B, Ronge B, Gustafson G (2002) Laboratory examination of anisotropy in the foliation plane of metamorphic rocks. Bull Eng Geol Environ 61:43–47. https://doi.org/10.1007/s100640100110
Cai M, Kaiser PK (2004) Numerical simulation of the Brazilian test and the tensile strength of anisotropic rocks and rocks with pre-existing cracks. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 41(3):450–451. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2003.12.111
Carneiro F, Barcellos A (1953) International association of testing and research laboratories for materials and structures. RILEM Bull 13:99–125
Chen CS, Pan E, Amadei B (1998) Determination of deformability and tensile strength of anisotropic rock using Brazilian tests. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 35(1):43–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0148-9062(97)00329-X
Cho JW, Kim H, Jeon S, Min KB (2012) Deformation and strength anisotropy of Asan gneiss, Boryeong shale, and Yeoncheon schist. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 50:158–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2011.12.004
Claesson J, Bohloli B (2002) Brazilian test: stress field and tensile strength of anisotropic rocks using an analytical solution. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 39(8):991–1004. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1365-1609(02)00099-0
Dan DQ, Konietzky H, Herbst M (2013) Brazilian tensile strength tests on some anisotropic rocks. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 58:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2012.08.010
Debecker B, Vervoort A (2009) Experimental observation of fracture patterns in layered slate. Int J Fract 159(1):51–62. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10704-009-9382-z
Delle Piane C, Almqvist BSG, Macrae CM, Torpy A, Mory AJ, Dewhurst DN (2015) Texture and diagenesis of Ordovician shale from the Canning Basin, Western Australia: implications for elastic anisotropy and geomechanical properties. Mar Pet Geol 59:56–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2014.07.017
Ding CD, Hu DW, Zhou H, Lu JJ, Lv T (2020) Investigations of P-wave velocity, mechanical behavior and thermal properties of anisotropic slate. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 127:104176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2019.104176
Duan K, Kwok CY (2015) Discrete element modeling of anisotropic rock under Brazilian test conditions. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 78:46–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2015.04.023
Everitt RA, Lajtai EZ (2004) The influence of rock fabric on excavation damage in the Lac du Bonnet granite. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 41(8):1277–1303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2004.09.013
Garcia-Fernandez CC, Gonzalez-Nicieza C, Alvarez-Fernandez MI, Gutierrez-Moizant RA (2019) New methodology for estimating the shear strength of layering in slate by using the Brazilian test. Bull Eng Geol Environ 78:2283–2297. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-018-1297-3
Gholami R, Rasouli V (2014) Mechanical and elastic properties of transversely isotropic slate. Rock Mech Rock Eng 47(5):1763–1773. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-013-0488-2
Ho NC, van der Pluijm BA, Peacor DR (2001) Static recrystallization and preferred orientation of phyllosilicates: Michigamme Formation, Northern Michigan, USA. J Struct Geol 23(6):887–893. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0191-8141(00)00162-0
Hu DW, Zhou H, Zhang F, Shao JF, Zhang JF (2013) Modeling of inherent anisotropic behavior of partially saturated clayey rocks. Comput Geotech 48:29–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2012.09.002
Hu SC, Tan YL, Zhou H, Guo WY, Hu DW, Meng FZ, Liu ZG (2017) Impact of bedding planes on mechanical properties of sandstone. Rock Mech Rock Eng 50(8):2243–2251. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-017-1239-6
ISRM (1978) Suggested methods for determining tensile strength of rock materials. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci Geomech Abstr 15(3):99–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/0148-9062(78)90003-7
Jaeger JC, Cook NGW, Zimmerman R (2009) Fundamentals of rock mechanics. Wiley, New York
Kim H, Cho JW, Song I, Min KB (2012) Anisotropy of elastic moduli, P-wave velocities, and thermal conductivities of Asan Gneiss, Boryeong Shale, and Yeoncheon Schist in Korea. Eng Geol 147–148:68–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2012.07.015
Li DY, Wong LNY (2013) The Brazilian disc test for rock mechanics applications: review and new insights. Rock Mech Rock Eng 46(2):269–287. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-012-0257-7
Lisjak A, Tatone BSA, Mahabadi OK et al (2016) Hybrid finite-discrete element simulation of the EDZ formation and mechanical sealing process around a microtunnel in Opalinus Clay. Rock Mech Rock Eng 49(5):1849–1873. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-015-0847-2
Liu ZJ, Zhang CQ, Zhang CS, Gao Y, Zhou H, Chang ZR (2019) Deformation and failure characteristics and fracture evolution of cryptocrystalline basalt. J Rock Mech Geotech Eng 11(5):990–1003. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrmge.2019.04.005
Lockner D (1993) The role of acoustic emission in the study of rock fracture. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci Geomech Abstr 30(7):883–899. https://doi.org/10.1016/0148-9062(93)90041-B
Ma TS, Peng N, Zhu Z, Zhang CB, Yang CH, Zhao J (2018) Brazilian tensile strength of anisotropic rocks: review and new insights. Energies 11(2):304. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11020304
Ma YF, Huang HY (2018) DEM analysis of failure mechanisms in the intact Brazilian test. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 102:109–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2017.11.010
Masri M, Sibai M, Shao JF, Mainguy M (2014) Experimental investigation of the effect of temperature on the mechanical behavior of Tournemire shale. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 70:185–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2014.05.007
Mokhtari M, Tutuncu AN (2016) Impact of laminations and natural fractures on rock failure in Brazilian experiments: a case study on Green River and Niobrara formations. J Nat Gas Sci Eng 36:79–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jngse.2016.10.015
Moradian Z, Einstein HH, Ballivy G (2016) Detection of cracking levels in brittle rocks by parametric analysis of the acoustic emission signals. Rock Mech Rock Eng 49(3):785–800. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-015-0775-1
Park B, Min KB (2015) Bonded-particle discrete element modeling of mechanical behavior of transversely isotropic rock. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 76:243–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2015.03.014
Qiu JD, Li DY, Li XB (2017) Dynamic failure of a phyllite with a low degree of metamorphism under impact Brazilian test. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 94:10–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2017.02.013
Roy DG, Singh TN (2016) Effect of heat treatment and layer orientation on the tensile strength of a crystalline rock under Brazilian test condition. Rock Mech Rock Eng 49(5):1663–1677. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-015-0891-y
Shen WQ, Shao JF (2015) A micromechanical model of inherently anisotropic rocks. Comput Geotech 65:73–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2014.11.016
Tan X, Konietzky H, Frühwirt T, Dan DQ (2015) Brazilian tests on transversely isotropic rocks: laboratory testing and numerical simulations. Rock Mech Rock Eng 48(4):1341–1351. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-014-0629-2
Tavallali A, Vervoort A (2010a) Effect of layer orientation on the failure of layered sandstone under Brazilian test conditions. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 47(2):313–322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2010.01.001
Tavallali A, Vervoort A (2010b) Failure of layered sandstone under Brazilian test conditions: effect of micro-scale parameters on macro-scale behaviour. Rock Mech Rock Eng 43(5):641–653. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-010-0084-7
Tavallali A, Vervoort A (2013) Behaviour of layered sandstone under Brazilian test conditions: layer orientation and shape effects. J Rock Mech Geotech Eng 5(5):366–377. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrmge.2013.01.004
Tsang CF, Barnichon JD, Birkholzer J, Li XL, Liu HH, Sillen X (2012) Coupled thermo-hydro-mechanical processes in the near field of a high-level radioactive waste repository in clay formations. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 49:31–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2011.09.015
Valente S, Fidelibus C, Loew S, Cravero M, Iabichino G, Barpi F (2012) Analysis of fracture mechanics tests on opalinus clay. Rock Mech Rock Eng 45(5):767–779. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-012-0225-2
Vervoort A, Min KB, Konietzky H et al (2014) Failure of transversely isotropic rock under Brazilian test conditions. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 70:343–352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2014.04.006
Wang J, Xie LZ, Xie HP, Ren L, He B, Li CB, Yang ZP, Gao C (2016) Effect of layer orientation on acoustic emission characteristics of anisotropic shale in Brazilian tests. J Nat Gas Sci Eng 36:1120–1129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jngse.2016.03.046
Wang PT, Cai MF, Ren FH (2018) Anisotropy and directionality of tensile behaviours of a jointed rock mass subjected to numerical Brazilian tests. Tunn Undergr Sp Technol 73:139–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2017.12.018
Winn K, Wong LNY, Alejano LR (2019) Multi-approach stability analyses of large caverns excavated in low-angled bedded sedimentary rock masses in Singapore. Eng Geol 259:105164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2019.105164
Wong LNY, Jong MC (2014) Water saturation effects on the Brazilian tensile strength of gypsum and assessment of cracking processes using high-speed video. Rock Mech Rock Eng 47(4):1103–1115. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-013-0436-1
Xia YJ, Zhou H, Zhang CQ, He SH, Gao Y, Wang P (2019) The evaluation of rock brittleness and its application—a review study. Eur J Environ Civ En. https://doi.org/10.1080/19648189.2019.1655485
Xia YJ, Zhang CQ, Zhou H, Chen JL, Gao Y, Liu N, Chen PZ (2020) Structural characteristics of columnar jointed basalt in drainage tunnel of Baihetan hydropower station and its influence on the behavior of P-wave anisotropy. Eng Geol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2019.105304
Xu GW, He C, Chen ZQ, Su A (2018) Transverse isotropy of phyllite under brazilian tests: laboratory testing and numerical simulations. Rock Mech Rock Eng 51(4):1111–1135. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-017-1393-x
Yang SQ, Yin PF, Huang YH (2019) Experiment and discrete element modelling on strength, deformation and failure behaviour of shale under Brazilian compression. Rock Mech Rock Eng 52:4339–4359. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-019-01847-z
Yin PF, Yang SQ (2018) Experimental investigation of the strength and failure behavior of layered sandstone under uniaxial compression and Brazilian testing. Acta Geophys 66(4):585–605. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11600-018-0152-z
Zhang SW, Shou KJ, Xian XF, Zhou JP, Liu GJ (2018) Fractal characteristics and acoustic emission of anisotropic shale in Brazilian tests. Tunn Undergr Sp Technol 71:298–308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2017.08.031
Zhou H, Liu HT, Hu DW, Yang FJ, Lu JJ, Zhang F (2016) Anisotropies in mechanical behaviour, thermal expansion and P-wave velocity of sandstone with bedding planes. Rock Mech Rock Eng 49(11):4497–4504. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-016-1016-y
Zuo JP, Lu JF, Ghandriz R, Wang JT, Li YH, Zhang XY, Li J, Li HT (2020) Mesoscale fracture behavior of Longmaxi outcrop shale with different bedding angles: experimental and numerical investigations. J Rock Mech Geotech Eng 122(2):297–309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrmge.2019.11.001
Acknowledgements
The financial support of the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant no. 2018YFC0809601), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant no. 51779252), the Major Technological Innovation Projects of Hubei, China (Grant no. 2017AAA128), and the Key Projects of the Yalong River Joint Fund of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant no. U1865203) are gratefully appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest in the present study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix
Appendix
See Table 1.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, C., Zhang, Y., Hu, D. et al. Foliation Effects on Mechanical and Failure Characteristics of Slate in 3D Space Under Brazilian Test Conditions. Rock Mech Rock Eng 53, 3919–3936 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-020-02146-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-020-02146-8