Abstract
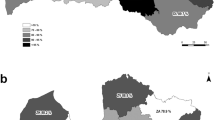
The digenean trematode Alaria alata, an intestinal parasite of wild canids is widely distributed in Europe. The recent finding of the mesocercarial life cycle stage in the paratenic wild boar host suggests that it may potentially infect humans Mohl et al. (Parasitol Res 105:1–15, 2009). Over 500 foxes were examined during a wildlife survey for zoonotic diseases in 2009 and 2010. The prevalence of A. alata ranged from 21% to 26% in 2009 and 2010, and the intensity of infection varied, with the majority of foxes having between one and ten trematodes, but a small number of animals had parasitic burdens greater than 500. The location of foxes was geo-referenced and mapped using a geographic information system. The results of the spatial analysis suggest that A. alata may have a limited distribution being confined mainly to areas of pasture especially in the central plain and north Munster. Hot spot analysis indicated a clustering and that the level of parasitism was greatest in foxes from those areas where the prevalence of infection was highest.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Becart E, Aubry A, Whelan P, Emerson MC (2007) The natterjack toad Bufo calamita in Co. Kerry, Ireland: conservation status, current and foreseeable threats. Ir Natural J 28:477–487
Borgsteede FHM (1984) Helminth parasites of wild foxes (Vulpes vulpes L.) in the Netherlands. Z Parasitenkd 70:281–285
Carpenter TE (2011) The spatial epidemiologic (r)evolution: a look back in time and forward to the future. Spat Spatio-tempor Epidemiol 2:119–124
Charlier J, Bennema SC, Caron Y, Counotte M, Ducheyne E, Hendrickx G, Vercruysse J (2011) Towards assessing fine-scale indicators for the spatial transmission risk of Fasciola hepatica in cattle. Geospat Health 5:239–245
Cleaveland S, Laurenson MK, Taylor LH (2001) Diseases of humans and their domestic mammals: pathogen characteristics, host range and risk of emergence. Phil Trans Royal Soc Lond B 356:991–999
Coman BJ, Robinson J, Beaumont C (1991) Home range, dispersal and density of red foxes (Vulpes vulpes L.) in central Victoria. Wild Res 18:215–223
Craig HL, Craig PS (2005) Helminth parasites of wolves (Canis lupus): a species list and an analysis of published prevalence studies in Neartic and Palaearctic populations. J Helmintol 79:95–103
Criado-Fernelio A, Gutierrez-Garcia L, Rodriguez-Caabeiro F, Reus-Garcia E, Roldan-Soriano MA, Diaz-Sanchez MA (2000) A parasitological survey of wild red foxes (Vulpes vulpes) from the province of Guadalajara, Spain. Vet Parasitol 92:245–251
Dalimi A, Sattari A, Motamedi G (2006) A study on intestinal helminths of dogs, foxes and jackals in the western part of Iran. Vet Parasitol 142:129–133
Eckert J, Deplazes P, Craig PS, Gemmell MA, Gottstein B, Heath D, Jenkins DJ, Kamiya M, Lightowlers M (2001) Echinococcus in animals: clinical aspects, diagnosis and treatment. In: Eckert J, Gemmell MA, Meslin FX, Pawlowski ZS (eds) WHO/OIE manual on echinococcus in humans and animals: a public health problem of global concern. World Organisation for Animal Health, Paris, pp 73–99
EPA (2006) Technical details of CORINE land cover. http://www.epa.ie/whatwedo/assessment/land/corine/tech/. Accessed 28 Jan 2010
EPA (2007) Land cover update for 2006—final report. In EPA Ed. Dublin, ERA-Maptec Ltd. Environment Protection Agency, 2007
ESRI (2010) ArcGIS, version 9.3. Environmental Systems Research Institute, Inc. (ESRI), Redlands, California, USA
Fairley JS (1969) Tagging studies of the red fox Vulpes vulpes in north-east Ireland. J Zool 159:527–532
Freeman RS, Stuart PF, Cullen JB, Ritchie AC, Mildon A, Fernandes BJ, Bonin R (1976) Fatal human infection with mesocercariae of the trematode Alaria americana. Am J Trop Med Hyg 25:803–807
Fried B, Abruzzi A (2010) Food-borne trematode infections of humans in the United States of America. Parasitol Res 106:1263–1280
Gicik Y, Kara M, Sari B, Kilic K, Arslan MO (2009) Intestinal parasites of red foxes (Vulpes vulpes) and their zoonotic importance for humans in Kars province. Kafkas Univ Vet Fak Derg 15:135–140
Greger M (2007) The human/animal interface: emergence and resurgence of zoonotic infectious diseases. Clin Rev Microbiol 33:243–299
Jones KE, Patel NG, Levy MA, Storeygard A, Balk D, Gittleman JL, Daszak P (2008) Global trends in emerging infectious diseases. Nature 451:990–993
Kidawa D, Kowalczyk R (2011) The effects of sex, age, season and habitat on diet of the red fox Vulpes vulpes in north-eastern Poland. Acta Theriolog 56:209–218
Kramer MH, Eberhard ML, Blankenberg TA (1996) Respiratory symptoms and subcutaneous granulomas caused by mesocercariae: a case report. Am J Trop Med Hyg 55:447–448
Lucherini M, Lovari S (1996) Habitat richness affects home range size in the red fox Vulpes vulpes. Behav Proc 36:103–106
MacDonald DW (1983) The ecology of carnivore social behaviour. Nature 301:379–384
Marnell F (1998) Discriminant analysis of the terrestrial and aquatic habitat of the smooth newt (Triturus vulgaris) and the common frog (Rana temporaria). J Zool 244:1–6
McDonald HR, Kazacos KR, Schatz H, Johnson RN (1994) Two cases of intraocular infection with Alaria mesocercaria (Trematoda). Am J Opthalmol 117:447–455
Mohl K, Grosse K, Hamedy A, Wuste T, Kabelitz P, Lucker E (2009) Biology of Alaria spp. and human exposition risk to Alaria mesocercariae—a review. Parasitol Res 105:1–15
Murphy TM, Walochnik J, Hassl A, Moriarty J, Mooney J, Toolan D, Sanchez-Miguel C, O’Loughlin A, McAuliffe A (2007) Study on the prevalence of Toxoplasma gondii and Neospora caninum and molecular evidence of Encephalitozoon cuniculi and Encephalitozoon (Septata) intestinalis infections in red foxes (Vulpes vulpes) in rural Ireland. Vet Parasitol 146:227–234
Musella V, Catelan D, Rinaldi L, Lagazio C, Cringoli G, Biggeri A (2011) Covariate selection and multivariate spatial analysis of ovine parasitic infection. Prev Vet Med 99:69–77
Norstrom M (2001) Geographical information systems (GIS) as a tool in surveillance and monitoring of animal diseases. Acta Vet Scand 42(Suppl 94):79–85
Rafter P, Marucci G, Brangan P, Pozio E (2005) Rediscovery of Trichinella spiralis in red foxes (Vulpes vulpes) in Ireland after 30 years of oblivion. J Infect 50:61–65
Rinaldi L, Musella V, Biggeri A, Cringoli G (2006) New insights into the application of geographical information systems and remote sensing in veterinary parasitology. Geospat Health 1:33–47
Saeed I, Maddox-Hyttel C, Monrad J, Kapel CM (2006) Helminths of red foxes (Vulpes vulpes) in Denmark. Vet Parasitol 139:168–179
Segovia JM, Guerrero R, Torres J, Miquel J, Feliu C (2003) Ecological analyses of the intestinal helminth communities of the wolf, Canis lupus in Spain. Folia Parasitol (Praha) 50:231–236
Shimalov VV, Shimalov VT (2003) Helminth fauna of the red fox (Vulpes vulpes Linnaeus, 1758) in southern Belarus. Parasitol Res 89:77–78
Staubach C, Thulke HH, Tackman K, Hugh-Jones M, Conraths FJ (2001) Geographic information system-aided analysis of factors associated with the spatial distribution of Echinococcus multilocularis infections of foxes. Am J Med Hyg 65:943–948
Teacher AGF, Garner TWJ, Nichols RA (2009) European phylogeography of the common frog (Rana temporaria): routes of postglacial colonisation into the British Isles and evidence for an Irish glacial refugium. Hered 102:490–496
UCD (2010) Urban Institute of Ireland Urbis Database. http://www.ucd.ie/uii/. Accessed on 02 Feb 2010
Wahlström H, Isomursu M, Hallgren G, Christensson D, Cedersmyg M, Wallensten A, Hjertqvist M, Davidson RK, Uhlhorn H, Hopp P (2011) Combining information from surveys of several species to estimate the probability of freedom from Echinococcus multilocularis in Sweden, Finland and mainland Norway. Acta Vet Scand 53:9, http://www.actavetscan.com/contents/53/1/9
Wolfe A, Hogan S, Maguire D, Fitzpatrick C, Vaughan L, Wall D, Hayden TJ, Mulcahy G (2001) Red foxes (Vulpes vulpes) in Ireland as hosts for parasites of potential zoonotic and veterinary significance. Vet Rec 149:759–763
Woolhouse MEJ, Gowtage-Sequeria S (2005) Host range and emerging and re-emerging pathogens. Emerg Infect Dis 11:1842–1847
Acknowledgements
The assistance of the Veterinary Research Officers in the Regional Veterinary Laboratories with the collection of the fox intestines was very much appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Murphy, T.M., O’Connell, J., Berzano, M. et al. The prevalence and distribution of Alaria alata, a potential zoonotic parasite, in foxes in Ireland. Parasitol Res 111, 283–290 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-012-2835-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-012-2835-8