Abstract
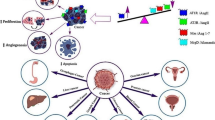
Cancer is a major public health problem, currently affecting hundreds of millions of people worldwide, and its clinical results are unpredictable, partly due to the lack of reliable biomarkers of cancer progression. Recently, it has been reported that (pro)renin receptor (PRR), as a new biomarker, plays an important role in different types of cancer, such as colorectal cancer, breast cancer, glioma, aldosterone-producing adenoma, endometrial cancer, urothelial cancer, and pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. In order to comprehensively and systematically understand the relationship and role of PRR with various cancers, this review will summarize the current research on targeting PRR in cancer from signaling to pathophysiological effects, including the correlation between PRR/sPRR expression level and different cancers, potential mechanisms regulated by PRR in the progress of cancers, and PRR in cancer treatment. PRR can be a novel and promising biomarker and potential therapeutic target for diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis in cancer, which is worthy of extensive development and application in clinics.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data sharing is not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
Abbreviations
- ACE:
-
Angiotensin-converting enzyme
- AGT:
-
Angiotensinogen
- Ang I:
-
Angiotensin I
- Ang II:
-
Angiotensin II
- APA:
-
Aldosterone-producing adenoma
- AT1R:
-
Type 1 Ang II receptor
- AT2R:
-
Type 2 Ang II receptor
- ATP6AP2:
-
Adenosine triphosphatase H+ transporting accessory protein 2
- BC:
-
Breast cancer
- CRC:
-
Colorectal cancer
- ELISA:
-
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
- EOC:
-
Epithelial ovarian cancer
- ERK:
-
Extracellular signal-regulated kinase
- GBM:
-
Glioblastoma multiforme
- HRP:
-
Handle region peptide
- IDH1R132H :
-
Isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 with mutations involving arginine 132
- IH:
-
Infantile hemangioma
- LA:
-
Lung adenocarcinoma
- LRP6:
-
Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 6
- mAbs:
-
Monoclonal antibodies
- MAPK:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase
- mTOR:
-
Mammalian target of rapamycin
- PanIN:
-
Premalignant pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia
- PDAC:
-
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
- PI3K:
-
Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase
- PRR:
-
(Pro)renin receptor
- RAS:
-
Renin–angiotensin system
- RCC:
-
Renal cell carcinoma
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- RT-qPCR:
-
Reverse transcription quantitative polymerase chain reaction
- SPECT:
-
Single-photon emission computed tomography
- sPRR:
-
Soluble (pro)renin receptor
- TGF β-1:
-
Transforming growth factor beta-1
- UC:
-
Urothelial cancer
- V-ATPase:
-
Vacuolar H+-adenosine triphosphatase
- VEGF:
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor
- WST-1:
-
Water-soluble tetrazolium salt-1
- YAP:
-
Yes-associated protein
References
Afsar B, Afsar RE, Ertuglu LA et al (2021) Renin-angiotensin system and cancer: epidemiology, cell signaling, genetics and epigenetics. Clin Transl Oncol 23:682–696. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-020-02488-3
Alzahrani AS (2019) PI3K/Akt/mTOR inhibitors in cancer: At the bench and bedside. Semin Cancer Biol 59:125–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcancer.2019.07.009
Arthur G, Osborn JL, Yiannikouris FB (2021) (Pro)renin receptor in the kidney: function and significance. Am J Physiol Integr Comp Physiol 320:R377–R383. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.00259.2020
Arundhathi A, Chuang WH, Chen JK et al (2016) Prorenin receptor acts as a potential molecular target for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma diagnosis. Oncotarget 7:55437–55448. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.10583
Beitia M, Solano-Iturri JD, Errarte P et al (2019) (Pro)renin receptor expression increases throughout the colorectal adenoma-adenocarcinoma sequence and it is associated with worse colorectal cancer prognosis. Cancers (basel) 11:881. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11060881
Bernhard SM, Seidel K, Schmitz J et al (2012) The (pro)renin receptor ((P)RR) can act as a repressor of Wnt signalling. Biochem Pharmacol 84:1643–1650. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2012.09.020
Bian J, Dannappel M, Wan C, Firestein R (2020) Transcriptional regulation of Wnt/β-Catenin pathway in colorectal cancer. Cells 9:2125. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9092125
Bradshaw AR, Wickremesekera AC, Brasch HD et al (2016) Glioblastoma multiforme cancer stem cells express components of the renin-angiotensin system. Front Surg 3:51. https://doi.org/10.3389/fsurg.2016.00051
Bray F, Laversanne M, Weiderpass E, Soerjomataram I (2021) The ever-increasing importance of cancer as a leading cause of premature death worldwide. Cancer 127:3029–3030. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.33587
Cotter K, Liberman R, Sun-Wada G et al (2016) The a3 isoform of subunit a of the vacuolar ATPase localizes to the plasma membrane of invasive breast tumor cells and is overexpressed in human breast cancer. Oncotarget 7:46142–46157. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.10063
Cousin C, Bracquart D, Contrepas A et al (2009) Soluble form of the (pro)renin receptor generated by intracellular cleavage by furin is secreted in plasma. Hypertension 53:1077–1082. https://doi.org/10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.108.127258
Cruciat CM, Ohkawara B, Acebron SP et al (2010) Requirement of prorenin receptor and vacuolar H+-ATPase-mediated acidification for Wnt signaling. Science 327:459–463. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1179802
Delforce SJ, Lumbers ER, de Meaultsart CC et al (2017) Expression of renin-angiotensin system (RAS) components in endometrial cancer. Endocr Connect 6:9–19. https://doi.org/10.1530/EC-16-0082
Downward J (2003) Targeting RAS signalling pathways in cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer 3:11–22. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc969
Folkman J (2002) Role of angiogenesis in tumor growth and metastasis. Semin Oncol. https://doi.org/10.1053/sonc.2002.37263
George AJ, Thomas WG, Hannan RD (2010) The renin–angiotensin system and cancer: old dog, new tricks. Nat Rev Cancer 10:745–759. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc2945
Goldstein B, Trivedi M, Speth RC (2017) Alterations in gene expression of components of the renin-angiotensin system and its related enzymes in lung cancer. Lung Cancer Int 2017:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/6914976
Guo L, Teng L (2015) YAP/TAZ for cancer therapy: opportunities and challenges (review). Int J Oncol 46:1444–1452. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2015.2877
Huang J, Siragy HM (2009) Glucose promotes the production of interleukine-1beta and cyclooxygenase-2 in mesangial cells via enhanced (Pro)renin receptor expression. Endocrinology 150:5557–5565. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2009-0442
Huang Z, Wang R, Wei G et al (2017) RAS protein activator-like 1 is functionally involved in hypoxia resistance in breast cancer cells by targeting hypoxia inducible factor-1α. Oncol Lett 14:3839–3845. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2017.6648
Ichihara A, Sakoda M, Kurauchimito A et al (2009) Renin, prorenin and the kidney: a new chapter in an old saga. J Nephrol 22:306–311
Ichihara A, Yatabe MS (2019) The (pro)renin receptor in health and disease. Nat Rev Nephrol 15:693–712. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41581-019-0160-5
Kashio-Yokota Y, Sato S, Hirose T et al (2021) Elevated (Pro)renin receptor expression by anti-cancer drugs, carboplatin and paclitaxel, in cultured cancer cells: possible involvement of apoptosis and autophagy. Tohoku J Exp Med 255:91–104. https://doi.org/10.1620/tjem.255.91
Kinouchi K (2011) Functional characterization of (pro)renin receptor in association with V-ATPase. Front Biosci 16:3216. https://doi.org/10.2741/3907
Kinouchi K, Ichihara A, Sano M et al (2010) The (pro)renin receptor/ATP6AP2 is essential for vacuolar H+-ATPase assembly in murine cardiomyocytes. Circ Res 107:30–34. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.110.224667
Kouchi M, Shibayama Y, Ogawa D et al (2017) (Pro)renin receptor is crucial for glioma development via the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. J Neurosurg 127:819–828. https://doi.org/10.3171/2016.9.JNS16431
Kreienbring K, Franz A, Richter R et al (2016) Predictive and prognostic value of sPRR in patients with primary epithelial ovarian cancer. Anal Cell Pathol 2016:6845213. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/6845213
Larrinaga G, Calvete-Candenas J, Solano-Iturri JD et al (2021) (Pro)renin receptor is a novel independent prognostic marker in invasive urothelial carcinoma of the bladder. Cancers (basel) 13:1–12. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13225642
Li XF, Ahmed A (1997) Compartmentalization and cyclic variation of immunoreactivity of renin and angiotensin converting enzyme in human endometrium throughout the menstrual cycle. Hum Reprod 12:2804–2809. https://doi.org/10.1093/humrep/12.12.2804
Li SY, Song Z, Yan YP et al (2020) Aldosterone from endometrial glands is benefit for human decidualization. Cell Death Dis 11:679. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-020-02844-9
Li S, Xu HX, Wu CT et al (2019) Angiogenesis in pancreatic cancer: current research status and clinical implications. Angiogenesis 22:15–36. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-018-9645-2
Lin PP (2020) Aneuploid circulating tumor-derived endothelial cell (CTEC): a novel versatile player in tumor neovascularization and cancer metastasis. Cells 9:1539. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9061539
Lonati C, Morganti A (2015) Are the antagonists of the renin-angiotensin system also anticancer agents? High Blood Press Cardiovasc Prev 22:99–102. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40292-014-0059-y
Lumbers ER, Wang Y, Delforce SJ et al (2015) Decidualisation of human endometrial stromal cells is associated with increased expression and secretion of prorenin. Reprod Biol Endocrinol 13:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12958-015-0127-8
Marquardt D, Center MS (1991) Involvement of vacuolar H(+)-adenosine triphosphatase activity in multidrug resistance in HL60 cells. JNCI J Natl Cancer Inst 83:1098–1102. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/83.15.1098
Martin JH, Mohammed R, Delforce SJ et al (2022) Role of the prorenin receptor in endometrial cancer cell growth. Oncotarget 13:587–599. https://doi.org/10.18632/ONCOTARGET.28224
Martinez-Zaguilan R, Lynch RM, Martinez GM, Gillies RJ (1993) Vacuolar-type H(+)-ATPases are functionally expressed in plasma membranes of human tumor cells. Am J Physiol Physiol 265:C1015–C1029. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpcell.1993.265.4.C1015
Miricescu D, Totan A, Stanescu-Spinu II et al (2020) PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in breast cancer: from molecular landscape to clinical aspects. Int J Mol Sci 22:173. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22010173
Mohammad AH, Assadian S, Couture F et al (2019) V-ATPase-associated prorenin receptor is upregulated in prostate cancer after PTEN loss. Oncotarget 10:4923–4936. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.27075
Mohammad AH, Kim SH, Bertos N et al (2020) Elevated V-ATPase activity following PTEN loss is required for enhanced oncogenic signaling in breast cancer. Mol Cancer Res 18:1477–1490. https://doi.org/10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-20-0088
Morimoto S, Morishima N, Watanabe D et al (2021) Immunohistochemistry for (Pro)renin receptor in humans. Int J Endocrinol 2021:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/8828610
Muller DN, Klanke B, Feldt S et al (2008) (Pro)renin receptor peptide inhibitor “handle-region” peptide does not affect hypertensive nephrosclerosis in Goldblatt rats. Hypertension 51:676–681. https://doi.org/10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.107.101493
Munro MJ, Wickremesekera AC, Davis PF et al (2017) Renin-angiotensin system and cancer: a review. Integr Cancer Sci Ther 4:1–6
Murakami T, Shibuya I, Ise T et al (2001) Elevated expression of vacuolar proton pump genes and cellular PH in cisplatin resistance. Int J Cancer 93:869–874. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.1418
Nguyen G (2011) Renin, (pro)renin and receptor: an update. Clin Sci 120:169–178. https://doi.org/10.1042/CS20100432
Nguyen G, Delarue F, Burcklé C et al (2002) Pivotal role of the renin/prorenin receptor in angiotensin II production and cellular responses to renin. J Clin Invest 109:1417–1427. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI14276
Ohba K, Endo M, Sato S et al (2020) (Pro)renin receptor/ATP6AP2 is required for autophagy and regulates proliferation in lung adenocarcinoma cells. Genes Cells 25:782–795. https://doi.org/10.1111/gtc.12812
Ohba K, Suzuki T, Nishiyama H et al (2014) Expression of (pro)renin receptor in breast cancers and its effect on cancercell proliferation. Biomed Res 35:117–126. https://doi.org/10.2220/biomedres.35.117
Ohgaki H, Kleihues P (2009) Genetic alterations and signaling pathways in the evolution of gliomas. Cancer Sci 100:2235–2241. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1349-7006.2009.01308.x
Pashirzad M, Khorasanian R, Fard MM et al (2021) The therapeutic potential of MAPK/ERK inhibitors in the treatment of colorectal cancer. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 21:932–943. https://doi.org/10.2174/1568009621666211103113339
Peach MJ (1977) Renin-angiotensin system: biochemistry and mechanisms of action. Physiol Rev 57:313–370. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.1977.57.2.313
Peng H, Li W, Seth DM et al (2013) (Pro)renin receptor mediates both angiotensin II-dependent and -independent oxidative stress in neuronal cells. PLoS ONE 8:e58339. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0058339
Perini MV, Dmello RS, Nero TL, Chand AL (2020) Evaluating the benefits of renin-angiotensin system inhibitors as cancer treatments. Pharmacol Ther 211:107527. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2020.107527
Pringle KG, Tadros MA, Callister RJ, Lumbers ER (2011) The expression and localization of the human placental prorenin/renin-angiotensin system throughout pregnancy: roles in trophoblast invasion and angiogenesis? Placenta 32:956–962. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.placenta.2011.09.020
Qin M, Xu C, Yu J (2021) The soluble (pro)renin receptor in health and diseases: foe or friend? J Pharmacol Exp Ther 378:251–261. https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.121.000576
Rahman A, Matsuyama M, Ebihara A et al (2020) Antiproliferative effects of monoclonal antibodies against (pro)renin receptor in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Mol Cancer Ther 19:1844–1855. https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-19-0228
Recarti C, Seccia TM, Caroccia B et al (2015) Expression and functional role of the prorenin receptor in the human adrenocortical zona glomerulosa and in primary aldosteronism. J Hypertens 33:1014–1022. https://doi.org/10.1097/HJH.0000000000000504
Sennoune SR, Bakunts K, Martínez GM et al (2004) Vacuolar H+-ATPase in human breast cancer cells with distinct metastatic potential: distribution and functional activity. Am J Physiol Physiol 286:C1443–C1452. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpcell.00407.2003
Shibayama Y, Fujimori T, Nguyen G et al (2015) (Pro)renin receptor is crucial for Wnt/β-catenin-dependent genesis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Sci Rep 5:15–19. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep08854
Siljee S, Milne B, Brasch HD et al (2021) Expression of components of the renin-angiotensin system by cancer stem cells in renal clear cell carcinoma. Biomolecules 11:1–14. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11040537
Soerjomataram I, Bray F (2021) Planning for tomorrow: global cancer incidence and the role of prevention 2020–2070. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 18:663–672. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41571-021-00514-z
Solano-Iturri JD, Echevarría E, Unda M et al (2021) Clinical implications of (Pro)renin receptor (prr) expression in renal tumours. Diagnostics. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11020272
Sun-Wada G-H, Wada Y (2015) Role of vacuolar-type proton ATPase in signal transduction. Biochim Biophys Acta 1847:1166–1172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbabio.2015.06.010
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL et al (2021) Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 71:209–249. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21660
Tamada S, Mitsui T, Ohira A et al (2019) Relationship between intracellular signaling of the (pro)renin receptor and the pathogenesis of preeclampsia. Acta Med Okayama 73:433–440
Thairu N, Kiriakidis S, Dawson P, Paleolog E (2011) Angiogenesis as a therapeutic target in arthritis in 2011: learning the lessons of the colorectal cancer experience. Angiogenesis 14:223–234. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-011-9208-2
van Schaijik B, Tan ST, Marsh RW, Itinteang T (2019) Expression of (pro)renin receptor and its effect on endothelial cell proliferation in infantile hemangioma. Pediatr Res 86:202–207. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41390-019-0430-8
Wang J, Nishiyama A, Matsuyama M et al (2020) The (pro)renin receptor: a novel biomarker and potential therapeutic target for various cancers. Cell Commun Signal 18:39. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12964-020-0531-3
Wang J, Shibayama Y, Zhang A et al (2019) (Pro)renin receptor promotes colorectal cancer through the Wnt/beta-catenin signalling pathway despite constitutive pathway component mutations. Br J Cancer 120:229–237. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41416-018-0350-0
Watanabe D, Morimoto S, Morishima N et al (2020) Adrenal (pro)renin receptor expression and serum soluble (pro)renin receptor concentration in primary aldosteronism. Int J Endocrinol 2020:9640103. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/9640103
Wegman-Ostrosky T, Soto-Reyes E, Vidal-Millán S, Sánchez-Corona J (2015) The renin-angiotensin system meets the hallmarks of cancer. J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst 16:227–233. https://doi.org/10.1177/1470320313496858
Xie Y, Peng Z, Shi M et al (2014) Metformin combined with p38 MAPK inhibitor improves cisplatin sensitivity in cisplatin-resistant ovarian cancer. Mol Med Rep 10:2346–2350. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2014.2490
Xu C, Liu C, Xiong J, Yu J (2022) Cardiovascular aspects of the (pro)renin receptor: function and significance. FASEB J 36:e22237. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.202101649RRR
Yamamoto H, Kaneko K, Ohba K et al (2013) Increased expression of (pro)renin receptor in aldosterone-producing adenomas. Peptides 49:68–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.peptides.2013.08.022
Yu F, Yu C, Li F et al (2021) Wnt/β-catenin signaling in cancers and targeted therapies. Signal Transduct Target Ther 6:307. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-021-00701-5
Zanconato F, Cordenonsi M, Piccolo S (2016) YAP/TAZ at the roots of cancer. Cancer Cell 29:783–803. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2016.05.005
Zanconato F, Cordenonsi M, Piccolo S (2019) YAP and TAZ: a signalling hub of the tumour microenvironment. Nat Rev Cancer 19:454–464. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41568-019-0168-y
Zhang J, Noble NA, Border WA et al (2008) Receptor-dependent prorenin activation and induction of PAI-1 expression in vascular smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol Metab 295:E810–E819. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.90264.2008
Zhang Y, Wang X (2020) Targeting the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in cancer. J Hematol Oncol 13:165. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-020-00990-3
Zhao K, Wang M, Wu A (2020) ATP6AP2 is overexpressed in breast cancer and promotes breast cancer progression. Cancer Manag Res 12:10449–10459. https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S270024
Ziaja M, Urbanek KA, Kowalska K, Piastowska-Ciesielska AW (2021) Angiotensin II and angiotensin receptors 1 and 2-multifunctional system in cells biology, what do we know? Cells 10:381. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10020381
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful for valuable comments and suggestions for improvements from editors and reviewers.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82160051 and 81660819), Jiangxi “Double thousand plan” (No. jxsq2020101074), Jiangxi Provincial Natural Science Foundation (No. 20212BAB216005), the PhD Start-up Research Fund in Jiangxi University of Chinese Medicine (No. 2020BSZR009), Jiangxi Key Laboratory grant in Science and Technology Department of Jiangxi Province (No. 20202BCD42014), and Key Program for Science and Technology Projects of Jiangxi Province of China (No. GJJ201208).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All the authors contributed to the current study. XOY wrote the manuscript; CMX supervised the project and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ouyang, X., Xu, C. Targeting the (pro)renin receptor in cancers: from signaling to pathophysiological effects. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 149, 2595–2605 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-022-04373-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-022-04373-8