Abstract
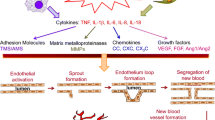
The paradigm of a therapy aimed at inhibiting the formation of blood vessels, which would consequentially deprive cells and tissues of oxygen and nutrients, was born from the concept pioneered by the late Judah Folkman that blood vessel formation is central to the progression and maintenance of diseases which involve cellular metabolism and tissue expansion, and cancer in particular. The prototype targeted angiogenesis inhibitor anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) antibody bevacizumab was approved in 2004 for colorectal cancer, and has since been approved for other cancers. Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic inflammatory disease, during which inflamed tissue invades and destroys cartilage and bone. The tissue expansion, invasion, expression of cytokines and growth factors and areas of hypoxia which are a feature of RA have resulted in the hypothesis that angiogenesis inhibition may also be beneficial in RA, drawing on the success of bevacizumab. This review focuses on our current understanding of the importance of angiogenesis in RA, and on the lessons which may be learnt from the clinical experiences of angiogenesis blockade, particularly in colorectal cancer.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Senger DR, Galli SJ, Dvorak AM, Perruzzi CA, Harvey VS, Dvorak HF (1983) Tumor cells secrete a vascular permeability factor that promotes accumulation of ascites fluid. Science 219:983–985
Senger DR, Perruzzi CA, Feder J, Dvorak HF (1986) A highly conserved vascular permeability factor secreted by a variety of human and rodent tumor cell lines. Cancer Res 46:5629–5632
Barrett EM, Scott DG, Wiles NJ, Symmons DP (2000) The impact of rheumatoid arthritis on employment status in the early years of disease: a UK community-based study. Rheumatology (Oxford) 39:1403–1409
Sokka T, Kautiainen H, Pincus T, Verstappen SM, Aggarwal A, Alten R, Andersone D, Badsha H, Baecklund E, Belmonte M, Craig-Muller J, da Mota LM, Dimic A, Fathi NA, Ferraccioli G, Fukuda W, Geher P, Gogus F, Hajjaj-Hassouni N, Hamoud H, Haugeberg G, Henrohn D, Horslev-Petersen K, Ionescu R, Karateew D, Kuuse R, Laurindo IM, Lazovskis J, Luukkainen R, Mofti A, Murphy E, Nakajima A, Oyoo O, Pandya SC, Pohl C, Predeteanu D, Rexhepi M, Rexhepi S, Sharma B, Shono E, Sibilia J, Sierakowski S, Skopouli FN, Stropuviene S, Toloza S, Valter I, Woolf A, Yamanaka H (2010) Work disability remains a major problem in rheumatoid arthritis in the 2000s: data from 32 countries in the QUEST-RA Study. Arthritis Res Ther 12:R42
Szekanecz Z, Gaspar L, Koch AE (2005) Angiogenesis in rheumatoid arthritis. Front Biosci 10:1739–1753
Szekanecz Z, Koch AE (2008) Targeting Angiogenesis in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Curr Rheumatol Rev 4:298–303
Szekanecz Z, Szegedi G, Koch AE (1998) Angiogenesis in rheumatoid arthritis: pathogenic and clinical significance. J Investig Med 46:27–41
Paleolog EM (2009) The vasculature in rheumatoid arthritis: cause or consequence? Int J Exp Pathol 90:249–261
Brown RA, Weiss JB, Tomlinson IW, Phillips P, Kumar S (1980) Angiogenic factor from synovial fluid resembling that from tumours. Lancet 1:682–685
Semble EL, Turner RA, McCrickard EL (1985) Rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis synovial fluid effects on primary human endothelial cell cultures. J Rheumatol 12:237–241
Kumar P, Erroi A, Sattar A, Kumar S (1985) Weibel-Palade bodies as a marker for neovascularization induced by tumor and rheumatoid angiogenesis factors. Cancer Res 45:4339–4348
Fearon U, Griosios K, Fraser A, Reece R, Emery P, Jones PF, Veale DJ (2003) Angiopoietins, growth factors, and vascular morphology in early arthritis. J Rheumatol 30:260–268
Ceponis A, Konttinen YT, Imai S, Tamulaitiene M, Li TF, Xu JW, Hietanen J, Santavirta S, Fassbender HG (1998) Synovial lining, endothelial and inflammatory mononuclear cell proliferation in synovial membranes in psoriatic and reactive arthritis: a comparative quantitative morphometric study. Br J Rheumatol 37:170–178
Walsh DA, Wade M, Mapp PI, Blake DR (1998) Focally regulated endothelial proliferation and cell death in human synovium. Am J Pathol 152:691–702
Izquierdo E, Canete JD, Celis R, Santiago B, Usategui A, Sanmarti R, Del Rey MJ, Pablos JL (2009) Immature blood vessels in rheumatoid synovium are selectively depleted in response to anti-TNF therapy. PLoS One 4:e8131
Larche MJ, Seymour M, Lim A, Eckersley RJ, Petavy F, Chiesa F, Rioja I, Lukey PT, Binks M, McClinton C, Dolan K, Taylor PC (2010) Quantitative power doppler ultrasonography is a sensitive measure of metacarpophalangeal joint synovial vascularity in rheumatoid arthritis and declines significantly following a 2-week course of oral low-dose corticosteroids. J Rheumatol 37:2493–2501
Taylor PC, Steuer A, Gruber J, Cosgrove DO, Blomley MJ, Marsters PA, Wagner CL, McClinton C, Maini RN (2004) Comparison of ultrasonographic assessment of synovitis and joint vascularity with radiographic evaluation in a randomized, placebo-controlled study of infliximab therapy in early rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 50:1107–1116
Ferrara N, Gerber HP, LeCouter J (2003) The biology of VEGF and its receptors. Nat Med 9:669–676
Ferrara N (2004) Vascular endothelial growth factor: basic science and clinical progress. Endocr Rev 25:581–611
Ho QT, Kuo CJ (2007) Vascular endothelial growth factor: biology and therapeutic applications. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 39:1349–1357
Ferrara N (2009) VEGF-A: a critical regulator of blood vessel growth. Eur Cytokine Netw 20:158–163
Koch AE, Harlow LA, Haines GK, Amento EP, Unemori EN, Wong WL, Pope RM, Ferrara N (1994) Vascular endothelial growth factor. A cytokine modulating endothelial function in rheumatoid arthritis. J Immunol 152:4149–4156
Fava RA, Olsen NJ, Spencer-Green G, Yeo KT, Yeo TK, Berse B, Jackman RW, Senger DR, Dvorak HF, Brown LF (1994) Vascular permeability factor/endothelial growth factor (VPF/VEGF): accumulation and expression in human synovial fluids and rheumatoid synovial tissue. J Exp Med 180:341–346
Kikuchi K, Kubo M, Kadono T, Yazawa N, Ihn H, Tamaki K (1998) Serum concentrations of vascular endothelial growth factor in collagen diseases. Br J Dermatol 139:1049–1051
Paleolog EM, Young S, Stark AC, McCloskey RV, Feldmann M, Maini RN (1998) Modulation of angiogenic vascular endothelial growth factor by tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin-1 in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 41:1258–1265
Ikeda M, Hosoda Y, Hirose S, Okada Y, Ikeda E (2000) Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor isoforms and their receptors Flt-1, KDR, and neuropilin-1 in synovial tissues of rheumatoid arthritis. J Pathol 191:426–433
Brouwer E, Gouw AS, Posthumus MD, van Leeuwen MA, Boerboom AL, Bijzet J, Bos R, Limburg PC, Kallenberg CG, Westra J (2009) Hypoxia inducible factor-1-alpha (HIF-1alpha) is related to both angiogenesis and inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 27:945–951
Lee SS, Joo YS, Kim WU, Min DJ, Min JK, Park SH, Cho CS, Kim HY (2001) Vascular endothelial growth factor levels in the serum and synovial fluid of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 19:321–324
Giatromanolaki A, Sivridis E, Athanassou N, Zois E, Thorpe PE, Brekken RA, Gatter KC, Harris AL, Koukourakis IM, Koukourakis MI (2001) The angiogenic pathway “vascular endothelial growth factor/flk-1(KDR)-receptor” in rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. J Pathol 194:101–108
Pufe T, Petersen W, Tillmann B, Mentlein R (2001) Splice variants VEGF121 and VEGF165 of the angiogenic peptide vascular endothelial cell growth factor are expressed in the synovial tissue of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 28:1482–1485
Sone H, Sakauchi M, Takahashi A, Suzuki H, Inoue N, Iida K, Shimano H, Toyoshima H, Kawakami Y, Okuda Y, Matsuo K, Yamada N (2001) Elevated levels of vascular endothelial growth factor in the sera of patients with rheumatoid arthritis correlation with disease activity. Life Sci 69:1861–1869
Kuryliszyn-Moskal A, Klimiuk PA, Sierakowski S, Ciolkiewicz M (2006) A study on vascular endothelial growth factor and endothelin-1 in patients with extra-articular involvement of rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Rheumatol 25:314–319
Kurosaka D, Hirai K, Nishioka M, Miyamoto Y, Yoshida K, Noda K, Ukichi T, Yanagimachi M, Furuya K, Takahashi E, Kingetsu I, Fukuda K, Yamada A (2010) Clinical significance of serum levels of vascular endothelial growth factor, angiopoietin-1, and angiopoietin-2 in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 37:1121–1128
Ballara SC, Taylor PC, Reusch P, Marmé D, Feldmann M, Maini RN, Paleolog EM (2001) Raised serum vascular endothelial growth factor levels are associated with destructive change in inflammatory arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 44:2055–2064
Kurosaka D, Hirai K, Nishioka M, Miyamoto Y, Yoshida K, Takahashi E, Ukichi T, Noda K, Yanagimachi M, Furuya K, Fukuda K, Yamada A (2009) Correlation between synovial blood flow signals and serum vascular endothelial growth factor levels in patients with refractory rheumatoid arthritis. Mod Rheumatol 19:187–191
Williams RO, Paleolog E, Feldmann M (2007) Cytokine inhibitors in rheumatoid arthritis and other autoimmune diseases. Curr Opin Pharmacol 7:412–417
Lu J, Kasama T, Kobayashi K, Yoda Y, Shiozawa F, Hanyuda M, Negishi M, Ide H, Adachi M (2000) Vascular endothelial growth factor expression and regulation of murine collagen-induced arthritis. J Immunol 164:5922–5927
Thornton S, Sowders D, Aronow B, Witte DP, Brunner HI, Giannini EH, Hirsch R (2002) DNA microarray analysis reveals novel gene expression profiles in collagen-induced arthritis. Clin Immunol 105:155–168
Hermann LM, Pinkerton M, Jennings K, Yang L, Grom A, Sowders D, Kersten S, Witte DP, Hirsch R, Thornton S (2005) Angiopoietin-like-4 is a potential angiogenic mediator in arthritis. Clin Immunol 115:93–101
de Bandt M, Grossin M, Weber AJ, Chopin M, Elbim C, Pla M, Gougerot-Pocidalo MA, Gaudry M (2000) Suppression of arthritis and protection from bone destruction by treatment with TNP-470/AGM-1470 in a transgenic mouse model of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 43:2056–2063
Arsenault AL, Lhotak S, Hunter WL, Banquerigo ML, Brahn E (1998) Taxol involution of collagen-induced arthritis: ultrastructural correlation with the inhibition of synovitis and neovascularization. Clin Immunol Immunopathol 86:280–289
Peacock DJ, Banquerigo ML, Brahn E (1992) Angiogenesis inhibition suppresses collagen arthritis. J Exp Med 175:1135–1138
Peacock DJ, Banquerigo ML, Brahn E (1995) A novel angiogenesis inhibitor suppresses rat adjuvant arthritis. Cell Immunol 160:178–184
Bainbridge J, Madden L, Essex D, Binks M, Malhotra R, Paleolog EM (2007) Methionine aminopeptidase-2 blockade reduces chronic collagen-induced arthritis: potential role for angiogenesis inhibition. Arthritis Res Ther 9:R127
Brahn E, Banquerigo ML, Lee JK, Park EJ, Fogler WE, Plum SM (2008) An angiogenesis inhibitor, 2-methoxyestradiol, involutes rat collagen-induced arthritis and suppresses gene expression of synovial vascular endothelial growth factor and basic fibroblast growth factor. J Rheumatol 35:2119–2128
Sone H, Kawakami Y, Sakauchi M, Nakamura Y, Takahashi A, Shimano H, Okuda Y, Segawa T, Suzuki H, Yamada N (2001) Neutralization of vascular endothelial growth factor prevents collagen-induced arthritis and ameliorates established disease in mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 281:562–568
Miotla J, Maciewicz R, Kendrew J, Feldmann M, Paleolog E (2000) Treatment with soluble VEGF receptor reduces disease severity in murine collagen-induced arthritis. Lab Invest 80:1195–1205
Afuwape AO, Feldmann M, Paleolog EM (2003) Adenoviral delivery of soluble VEGF receptor 1 (sFlt-1) abrogates disease activity in murine collagen-induced arthritis. Gene Ther 10:1950–1960
de Bandt M, Ben Mahdi MH, Ollivier V, Grossin M, Dupuis M, Gaudry M, Bohlen P, Lipson KE, Rice A, Wu Y, Gougerot-Pocidalo MA, Pasquier C (2003) Blockade of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor I (VEGF-RI), but not VEGF-RII, suppresses joint destruction in the K/BxN model of rheumatoid arthritis. J Immunol 171:4853–4859
Luttun A, Tjwa M, Moons L, Wu Y, Angelillo-Scherrer A, Liao F, Nagy JA, Hooper A, Priller J, De Klerck B, Compernolle V, Daci E, Bohlen P, Dewerchin M, Herbert JM, Fava R, Matthys P, Carmeliet G, Collen D, Dvorak HF, Hicklin DJ, Carmeliet P (2002) Revascularization of ischemic tissues by PlGF treatment, and inhibition of tumor angiogenesis, arthritis and atherosclerosis by anti-Flt1. Nat Med 8:831–840
Folkman J (1971) Tumor angiogenesis: therapeutic implications. N Engl J Med 285:1182–1186
Kabbinavar F, Hurwitz HI, Fehrenbacher L, Meropol NJ, Novotny WF, Lieberman G, Griffing S, Bergsland E (2003) Phase II, randomized trial comparing bevacizumab plus fluorouracil (FU)/leucovorin (LV) with FU/LV alone in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 21:60–65
Hurwitz H, Fehrenbacher L, Novotny W, Cartwright T, Hainsworth J, Heim W, Berlin J, Baron A, Griffing S, Holmgren E, Ferrara N, Fyfe G, Rogers B, Ross R, Kabbinavar F (2004) Bevacizumab plus irinotecan, fluorouracil, and leucovorin for metastatic colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med 350:2335–2342
Giantonio BJ, Catalano PJ, Meropol NJ, O’Dwyer PJ, Mitchell EP, Alberts SR, Schwartz MA, Benson AB (2007) Bevacizumab in Combination With Oxaliplatin, Fluorouracil, and Leucovorin (FOLFOX4) for Previously Treated Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: Results From the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Study E3200. J Clin Oncol 25:1539–1544
Kabbinavar FF, Schulz J, McCleod M, Patel T, Hamm JT, Hecht JR, Mass R, Perrou B, Nelson B, Novotny WF (2005) Addition of bevacizumab to bolus fluorouracil and leucovorin in first-line metastatic colorectal cancer: results of a randomized phase II trial. J Clin Oncol Official J Am Soc Clin Oncol 23:3697–3705
Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, Hilgard P, Gane E, Blanc J-F, de Oliveira AC, Santoro A, Raoul J-L, Forner A, Schwartz M, Porta C, Zeuzem S, Bolondi L, Greten TF, Galle PR, Seitz J-F, Borbath I, Häussinger D, Giannaris T, Shan M, Moscovici M, Voliotis D, Bruix J (2008) Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med 359:378–390
Miller KD, Chap LI, Holmes FA, Cobleigh MA, Marcom PK, Fehrenbacher L, Dickler M, Overmoyer BA, Reimann JD, Sing AP, Langmuir V, Rugo HS (2005) Randomized phase III trial of capecitabine compared with bevacizumab plus capecitabine in patients with previously treated metastatic breast cancer. J Clin Oncol Official J Am Soc Clin Oncol 23:792–799
Sandler A, Gray R, Perry MC, Brahmer J, Schiller JH, Dowlati A, Lilenbaum R, Johnson DH (2006) Paclitaxel-carboplatin alone or with bevacizumab for non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 355:2542–2550
Escudier B, Eisen T, Stadler WM, Szczylik C, Oudard S, Siebels M, Negrier S, Chevreau C, Solska E, Desai AA, Rolland F, Demkow T, Hutson TE, Gore M, Freeman S, Schwartz B, Shan M, Simantov R, Bukowski RM (2007) Sorafenib in advanced clear-cell renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med 356:125–134
Chen HX, Cleck JN (2009) Adverse effects of anticancer agents that target the VEGF pathway. Nature Rev Clin Oncol 6:465–477
Wu S, Kim C, Baer L, Zhu X (2010) Bevacizumab increases risk for severe proteinuria in cancer patients. J Am Soc Nephrol 21:1381–1389
George BA, Zhou XJ, Toto R (2007) Nephrotic syndrome after bevacizumab: case report and literature review. Am J Kidney Dis 49:e23–e29
Scappaticci FA, Skillings JR, Holden SN, Gerber H-P, Miller K, Kabbinavar F, Bergsland E, Ngai J, Holmgren E, Wang J, Hurwitz H (2007) Arterial thromboembolic events in patients with metastatic carcinoma treated with chemotherapy and bevacizumab. J Natl Cancer Inst 99:1232–1239
Schutz FA, Je Y, Azzi GR, Nguyen PL, Choueiri TK (2010) Bevacizumab increases the risk of arterial ischemia: a large study in cancer patients with a focus on different subgroup outcomes. Ann Oncol. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdq587
Nalluri SR, Chu D, Keresztes R, Zhu X, Wu S (2008) Risk of venous thromboembolism with the angiogenesis inhibitor bevacizumab in cancer patients. J Am Med Assoc 300:2277–2285
Hapani S, Chu D, Wu S (2009) Risk of gastrointestinal perforation in patients with cancer treated with bevacizumab: a meta-analysis. Lancet Oncol 10:559–568
Hochster HS, Hart LL, Ramanathan RK, Childs BH, Hainsworth JD, Cohn AL, Wong L, Fehrenbacher L, Abubakr Y, Saif MW, Schwartzberg L, Hedrick E (2008) Safety and efficacy of oxaliplatin and fluoropyrimidine regimens with or without bevacizumab as first-line treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer: results of the TREE study. J Clin Oncol Official J Am Soc Clin Oncol 26:3523–3529
Allegra CJ, Yothers G, O’Connell MJ, Sharif S, Colangelo LH, Lopa SH, Petrelli NJ, Goldberg RM, Atkins JN, Seay TE, Fehrenbacher L, O’Reilly S, Chu L, Azar CA, Wolmark N (2009) Initial safety report of NSABP C-08: a randomized phase III study of modified FOLFOX6 with or without bevacizumab for the adjuvant treatment of patients with Stage II or III colon cancer. J Clin Oncol 27:3385–3390
August DA, Serrano D, Poplin E (2008) “Spontaneous”, delayed colon and rectal anastomotic complications associated with bevacizumab therapy. J Surg Oncol 97:180–185
Bège T, Lelong B, Viret F, Turrini O, Guiramand J, Topart D, Moureau-Zabotto L, Giovannini M, Gonçalves A, Delpero JR (2009) Bevacizumab-related surgical site complication despite primary tumor resection in colorectal cancer patients. Ann Surg Oncol 16:856–860
FDA (2010) FDA begins process to remove breast cancer indication from Avastin label. United States Food and Drug Administration; [updated 2010; cited 2010 16th December]. Available from http://www.fda.gov/NewsEvents/Newsroom/PressAnnouncements/ucm237172.htm
NICE (2010) Colorectal cancer (metastatic)—bevacizumab. National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence; [updated 2010; cited]. Available from http://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/index.jsp?action=byID&o=13291
Sano H, Forough R, Maier JA, Case JP, Jackson A, Engleka K, Maciag T, Wilder RL (1990) Detection of high levels of heparin binding growth factor-1 (acidic fibroblast growth factor) in inflammatory arthritic joints. J Cell Biol 110:1417–1426
Sano H, Engleka K, Mathern P, Hla T, Crofford LJ, Remmers EF, Jelsema CL, Goldmuntz E, Maciag T, Wilder RL (1993) Coexpression of phosphotyrosine-containing proteins, platelet-derived growth factor-B, and fibroblast growth factor-1 in situ in synovial tissues of patients with rheumatoid arthritis and Lewis rats with adjuvant or streptococcal cell wall arthritis. J Clin Invest 91:553–565
Remmers EF, Sano H, Lafyatis R, Case JP, Kumkumian GK, Hla T, Maciag T, Wilder RL (1991) Production of platelet derived growth factor B chain (PDGF-B/c-sis) mRNA and immunoreactive PDGF B-like polypeptide by rheumatoid synovium: coexpression with heparin binding acidic fibroblast growth factor-1. J Rheumatol 18:7–13
Koch AE, Halloran MM, Hosaka S, Shah MR, Haskell CJ, Baker SK, Panos RJ, Haines GK, Bennett GL, Pope RM, Ferrara N (1996) Hepatocyte growth factor. A cytokine mediating endothelial migration in inflammatory arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 39:1566–1575
Scott BB, Zaratin PF, Colombo A, Hansbury MJ, Winkler JD, Jackson JR (2002) Constitutive expression of angiopoietin-1 and -2 and modulation of their expression by inflammatory cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts. J Rheumatol 29:230–239
Gravallese EM, Pettit AR, Lee R, Madore R, Manning C, Tsay A, Gaspar J, Goldring MB, Goldring SR, Oettgen P (2003) Angiopoietin-1 is expressed in the synovium of patients with rheumatoid arthritis and is induced by tumour necrosis factor alpha. Ann Rheum Dis 62:100–107
DeBusk LM, Chen Y, Nishishita T, Chen J, Thomas JW, Lin PC (2003) Tie2 receptor tyrosine kinase, a major mediator of tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced angiogenesis in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 48:2461–2471
Shahrara S, Volin MV, Connors MA, Haines GK, Koch AE (2002) Differential expression of the angiogenic Tie receptor family in arthritic and normal synovial tissue. Arthritis Res 4:201–208
Uchida T, Nakashima M, Hirota Y, Miyazaki Y, Tsukazaki T, Shindo H (2000) Immunohistochemical localisation of protein tyrosine kinase receptors Tie-1 and Tie-2 in synovial tissue of rheumatoid arthritis: correlation with angiogenesis and synovial proliferation. Ann Rheum Dis 59:607–614
Chen Y, Donnelly E, Kobayashi H, Debusk LM, Lin PC (2005) Gene therapy targeting the Tie2 function ameliorates collagen-induced arthritis and protects against bone destruction. Arthritis Rheum 52:1585–1594
Jin P, Zhang J, Sumariwalla PF, Ni I, Jorgensen B, Crawford D, Phillips S, Feldmann M, Shepard HM, Paleolog EM (2008) Novel splice variants derived from the receptor tyrosine kinase superfamily are potential therapeutics for rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther 10:R73
Malik NM, Jin P, Raatz Y, Sumariwalla PF, Kiriakidis S, Shepard M, Feldmann M, Paleolog EM (2010) Regulation of the Angiopoietin-Tie ligand-receptor system with a novel splice variant of Tie1 reduces the severity of murine arthritis. Rheumatology 49:1828–1839
Yarden Y (2001) The EGFR family and its ligands in human cancer. Signalling mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities. Eur J Cancer 37(Suppl 4):S3–S8
Yarden Y, Sliwkowski MX (2001) Untangling the ErbB signalling network. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2:127–137
Huang Z, Brdlik C, Jin P, Shepard HM (2009) A pan-HER approach for cancer therapy: background, current status and future development. Expert Opin Biol Ther 9:97–110
Scaltriti M, Baselga J (2006) The epidermal growth factor receptor pathway: a model for targeted therapy. Clin Cancer Res Official J Am Assoc Cancer Res 12:5268–5272
Spano JP, Lagorce C, Atlan D, Milano G, Domont J, Benamouzig R, Attar A, Benichou J, Martin A, Morere JF, Raphael M, Penault-Llorca F, Breau JL, Fagard R, Khayat D, Wind P (2005) Impact of EGFR expression on colorectal cancer patient prognosis and survival. Ann Oncol 16:102–108
Zlobec I, Vuong T, Hayashi S, Haegert D, Tornillo L, Terracciano L, Lugli A, Jass J (2007) A simple and reproducible scoring system for EGFR in colorectal cancer: application to prognosis and prediction of response to preoperative brachytherapy. Br J Cancer 96:793–800
Shiozawa S, Shiozawa K, Tanaka Y, Morimoto I, Uchihashi M, Fujita T, Hirohata K, Hirata Y, Imura S (1989) Human epidermal growth factor for the stratification of synovial lining layer and neovascularisation in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 48:820–828
Di Cosimo S, Baselga J (2008) Targeted therapies in breast cancer: where are we now? Eur J Cancer 44:2781–2790
Johnston JB, Navaratnam S, Pitz MW, Maniate JM, Wiechec E, Baust H, Gingerich J, Skliris GP, Murphy LC, Los M (2006) Targeting the EGFR pathway for cancer therapy. Curr Med Chem 13:3483–3492
Hallbeck AL, Walz TM, Briheim K, Wasteson A (2005) TGF-alpha and ErbB2 production in synovial joint tissue: increased expression in arthritic joints. Scand J Rheumatol 34:204–211
Satoh K, Kikuchi S, Sekimata M, Kabuyama Y, Homma MK, Homma Y (2001) Involvement of ErbB-2 in rheumatoid synovial cell growth. Arthritis Rheum 44:260–265
Schreiber AB, Winkler ME, Derynck R (1986) Transforming growth factor-alpha: a more potent angiogenic mediator than epidermal growth factor. Science 232:1250–1253
Yamane S, Ishida S, Hanamoto Y, Kumagai K, Masuda R, Tanaka K, Shiobara N, Yamane N, Mori T, Juji T, Fukui N, Itoh T, Ochi T, Suzuki R (2008) Proinflammatory role of amphiregulin, an epidermal growth factor family member whose expression is augmented in rheumatoid arthritis patients. J Inflamm (Lond) 5:5
Sumariwalla PF, Jin P, Zhang J, Ni I, Crawford D, Shepard HM, Paleolog EM, Feldmann M (2008) Antagonism of the human epidermal growth factor receptor family controls disease severity in murine collagen-induced arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 58:3071–3080
Semenza GL (2009) Regulation of oxygen homeostasis by hypoxia-inducible factor 1. Physiology (Bethesda) 24:97–106
Wang GL, Jiang BH, Rue EA, Semenza GL (1995) Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 is a basic-helix-loop-helix-PAS heterodimer regulated by cellular O2 tension. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:5510–5514
Maxwell PH, Wiesener MS, Chang GW, Clifford SC, Vaux EC, Cockman ME, Wykoff CC, Pugh CW, Maher ER, Ratcliffe PJ (1999) The tumour suppressor protein VHL targets hypoxia-inducible factors for oxygen-dependent proteolysis. Nature 399:271–275
Sivakumar B, Akhavani MA, Winlove CP, Taylor PC, Paleolog EM, Kang N (2008) Synovial hypoxia as a cause of tendon rupture in rheumatoid arthritis. J Hand Surg [Am] 33:49–58
Lund-Olesen K (1970) Oxygen tension in synovial fluids. Arthritis Rheum 13:769–776
Treuhaft PS, McCarty D (1971) Synovial fluid pH, lactate, oxygen and carbon dioxide partial pressure in various joint diseases. Arthritis Rheum 14:475–484
Blake DR, Merry P, Unsworth J, Kidd BL, Outhwaite JM, Ballard R, Morris CJ, Gray L, Lunec J (1989) Hypoxic-reperfusion injury in the inflamed human joint. Lancet 1:289–293
Naughton D, Whelan M, Smith EC, Williams R, Blake DR, Grootveld M (1993) An investigation of the abnormal metabolic status of synovial fluid from patients with rheumatoid arthritis by high field proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. FEBS Lett 317:135–138
Lee YA, Kim JY, Hong SJ, Lee SH, Yoo MC, Kim KS, Yang HI (2007) Synovial proliferation differentially affects hypoxia in the joint cavities of rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis patients. Clin Rheumatol 26:2023–2029
Naughton DP (2003) Hypoxia-induced upregulation of the glycolytic enzyme glucose-6-phosphate isomerase perpetuates rheumatoid arthritis. Med Hypotheses 60:332–334
Hitchon CA, El-Gabalawy HS, Bezabeh T (2009) Characterization of synovial tissue from arthritis patients: a proton magnetic resonance spectroscopic investigation. Rheumatol Int 29:1205–1211
Biniecka M, Kennedy A, Fearon U, Ng CT, Veale DJ, O’Sullivan JN (2010) Oxidative damage in synovial tissue is associated with in vivo hypoxic status in the arthritic joint. Ann Rheum Dis 69:1172–1178
Ng CT, Biniecka M, Kennedy A, McCormick J, Fitzgerald O, Bresnihan B, Buggy D, Taylor CT, O’Sullivan J, Fearon U, Veale DJ (2010) Synovial tissue hypoxia and inflammation in vivo. Ann Rheum Dis 69:1389–1395
Richman AI, Su EY, Ho G Jr (1981) Reciprocal relationship of synovial fluid volume and oxygen tension. Arthritis Rheum 24:701–705
Hitchon C, Wong K, Ma G, Reed J, Lyttle D, El-Gabalawy H (2002) Hypoxia-induced production of stromal cell-derived factor 1 (CXCL12) and vascular endothelial growth factor by synovial fibroblasts. Arthritis Rheum 46:2587–2597
Hollander AP, Corke KP, Freemont AJ, Lewis CE (2001) Expression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha by macrophages in the rheumatoid synovium: implications for targeting of therapeutic genes to the inflamed joint. Arthritis Rheum 44:1540–1544
Giatromanolaki A, Sivridis E, Maltezos E, Athanassou N, Papazoglou D, Gatter KC, Harris AL, Koukourakis MI (2003) Upregulated hypoxia inducible factor-1alpha and -2alpha pathway in rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res Ther 5:R193–R201
Westra J, Molema G, Kallenberg CG (2010) Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 as regulator of angiogenesis in rheumatoid arthritis—therapeutic implications. Curr Med Chem 17:254–263
Peters CL, Morris CJ, Mapp PI, Blake DR, Lewis CE, Winrow VR (2004) The transcription factors hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha and Ets-1 colocalize in the hypoxic synovium of inflamed joints in adjuvant-induced arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 50:291–296
Kim HL, Cho YS, Choi H, Chun YS, Lee ZH, Park JW (2009) Hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha is deregulated by the serum of rats with adjuvant-induced arthritis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 378:123–128
Akhavani MA, Madden L, Buysschaert I, Sivakumar B, Kang N, Paleolog EM (2009) Hypoxia upregulates angiogenesis and synovial cell migration in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther 11:R64
Ahn JK, Koh EM, Cha HS, Lee YS, Kim J, Bae EK, Ahn KS (2008) Role of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha in hypoxia-induced expressions of IL-8, MMP-1 and MMP-3 in rheumatoid fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Rheumatology (Oxford) 47:834–839
Matsumoto K, Imagawa S, Obara N, Suzuki N, Takahashi S, Nagasawa T, Yamamoto M (2006) 2-Oxoglutarate downregulates expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and erythropoietin through decreasing hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha and inhibits angiogenesis. J Cell Physiol 209:333–340
Matsumoto K, Obara N, Ema M, Horie M, Naka A, Takahashi S, Imagawa S (2009) Antitumor effects of 2-oxoglutarate through inhibition of angiogenesis in a murine tumor model. Cancer Sci 100:1639–1647
Yeo EJ, Chun YS, Cho YS, Kim J, Lee JC, Kim MS, Park JW (2003) YC-1: a potential anticancer drug targeting hypoxia-inducible factor 1. J Natl Cancer Inst 95:516–525
Manabe H, Nasu Y, Komiyama T, Furumatsu T, Kitamura A, Miyazawa S, Ninomiya Y, Ozaki T, Asahara H, Nishida K (2008) Inhibition of histone deacetylase down-regulates the expression of hypoxia-induced vascular endothelial growth factor by rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts. Inflamm Res 57:4–10
Shankar J, Thippegowda PB, Kanum SA (2009) Inhibition of HIF-1alpha activity by BP-1 ameliorates adjuvant induced arthritis in rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 387:223–228
Paleolog EM, Miotla JM (1998) Angiogenesis in arthritis: role in disease pathogenesis and as a potential therapeutic target. Angiogenesis 2:295–307
Khong TL, Larsen H, Raatz Y, Paleolog E (2007) Angiogenesis as a therapeutic target in arthritis: learning the lessons of the colorectal cancer experience. Angiogenesis 10:243–258
Ferrara N, Carver-Moore K, Chen H, Dowd M, Lu L, O’Shea KS, Powell-Braxton L, Hillan KJ, Moore MW (1996) Heterozygous embryonic lethality induced by targeted inactivation of the VEGF gene. Nature 380:439–442
Gonzalez-Gay MA, Gonzalez-Juanatey C, Martin J (2005) Rheumatoid arthritis: a disease associated with accelerated atherogenesis. Semin Arthritis Rheum 35:8–17
Kaplan MJ (2006) Cardiovascular disease in rheumatoid arthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol 18:289–297
Van Doornum S, Brand C, King B, Sundararajan V (2006) Increased case fatality rates following a first acute cardiovascular event in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 54:2061–2068
Sihvonen S, Korpela M, Laippala P, Mustonen J, Pasternack A (2004) Death rates and causes of death in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a population-based study. Scand J Rheumatol 33:221–227
Nadareishvili Z, Michaud K, Hallenbeck JM, Wolfe F (2008) Cardiovascular, rheumatologic, and pharmacologic predictors of stroke in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a nested, case-control study. Arthritis Rheum 59:1090–1096
Solomon DH, Karlson EW, Rimm EB, Cannuscio CC, Mandl LA, Manson JE, Stampfer MJ, Curhan GC (2003) Cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in women diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis. Circulation 107:1303–1307
Kremers HM, Crowson CS, Therneau TM, Roger VL, Gabriel SE (2008) High ten-year risk of cardiovascular disease in newly diagnosed rheumatoid arthritis patients: a population-based cohort study. Arthritis Rheum 58:2268–2274
Solomon DH, Goodson NJ, Katz JN, Weinblatt ME, Avorn J, Setoguchi S, Canning C, Schneeweiss S (2006) Patterns of cardiovascular risk in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 65:1608–1612
Soltesz P, Der H, Kerekes G, Szodoray P, Szucs G, Danko K, Shoenfeld Y, Szegedi G, Szekanecz Z (2009) A comparative study of arterial stiffness, flow-mediated vasodilation of the brachial artery, and the thickness of the carotid artery intima-media in patients with systemic autoimmune diseases. Clin Rheumatol 28:655–662
Warnecke C, Weidemann A, Volke M, Schietke R, Wu X, Knaup KX, Hackenbeck T, Bernhardt W, Willam C, Eckardt KU, Wiesener MS (2008) The specific contribution of hypoxia-inducible factor-2alpha to hypoxic gene expression in vitro is limited and modulated by cell type-specific and exogenous factors. Exp Cell Res 314:2016–2027
Carroll VA, Ashcroft M (2006) Role of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1alpha versus HIF-2alpha in the regulation of HIF target genes in response to hypoxia, insulin-like growth factor-I, or loss of von Hippel-Lindau function: implications for targeting the HIF pathway. Cancer Res 66:6264–6270
Sowter HM, Raval RR, Moore JW, Ratcliffe PJ, Harris AL (2003) Predominant role of hypoxia-inducible transcription factor (Hif)-1alpha versus Hif-2alpha in regulation of the transcriptional response to hypoxia. Cancer Res 63:6130–6134
Raval RR, Lau KW, Tran MG, Sowter HM, Mandriota SJ, Li JL, Pugh CW, Maxwell PH, Harris AL, Ratcliffe PJ (2005) Contrasting properties of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1) and HIF-2 in von Hippel-Lindau-associated renal cell carcinoma. Mol Cell Biol 25:5675–5686
Bongartz T, Sutton AJ, Sweeting MJ, Buchan I, Matteson EL, Montori V (2006) Anti-TNF antibody therapy in rheumatoid arthritis and the risk of serious infections and malignancies: systematic review and meta-analysis of rare harmful effects in randomized controlled trials. JAMA 295:2275–2285
Bongartz T, Warren FC, Mines D, Matteson EL, Abrams KR, Sutton AJ (2009) Etanercept therapy in rheumatoid arthritis and the risk of malignancies: a systematic review and individual patient data meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Ann Rheum Dis 68:1177–1183
Furst DE (2008) The risk of infections with biologic therapies for rheumatoid arthritis. Semin Arthritis Rheum 39:327–346
Tubach F, Salmon D, Ravaud P, Allanore Y, Goupille P, Breban M, Pallot-Prades B, Pouplin S, Sacchi A, Chichemanian RM, Bretagne S, Emilie D, Lemann M, Lorthololary O, Mariette X (2009) Risk of tuberculosis is higher with anti-tumor necrosis factor monoclonal antibody therapy than with soluble tumor necrosis factor receptor therapy: the three-year prospective french research axed on tolerance of biotherapies registry. Arthritis Rheum 60:1884–1894
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thairu, N., Kiriakidis, S., Dawson, P. et al. Angiogenesis as a therapeutic target in arthritis in 2011: learning the lessons of the colorectal cancer experience. Angiogenesis 14, 223–234 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-011-9208-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-011-9208-2