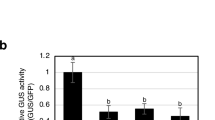
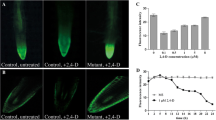
Abstract
The plant-tumorigenic 6b (AK-6b) gene of Agrobacterium tumefaciens strain AKE10 induces morphological alterations to tobacco plants, Nicotiana tabacum. To investigate the molecular mechanisms underlying these processes, we generated transgenic tobacco harboring the AK-6b gene under the control of a dexamethazone-inducible promoter. Upon induction, transgenic tobacco seedlings exhibited distinct classes of aberrant morphologies, most notably adventitious outgrowths and stunted epicotyls. Histological analysis revealed massive proliferation and altered venation in the newly established outgrowths. Prominent vascular development suggested that auxin metabolism or signaling had been altered. Indeed, basipetal auxin transport in the hypocotyls of the transgenic seedlings was reduced by 50–80%, whereas intracellular auxin contents were only slightly reduced. Analysis of cell extracts by HPLC revealed a large accumulation of phenolic compounds, including the flavonoid kaempferol-3-rutinoside, in transgenic plants compared with wild-type seedlings. As some naturally occurring flavonoids have been shown to affect auxin transport, we suggest that the AK-6b gene expression impairs auxin transport via modulation of phenylpropanoid metabolism, and ultimately results in the observed morphological alterations.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CaPu:
-
Caffeoylputrescine
- CGA:
-
Chlorogenic acid
- C4H:
-
Cinnamate 4-hydroxylase
- Dex:
-
Dexamethazone
- HFCA:
-
9-hydroxyfluorene-9-caboxylic acid
- hpt:
-
Hygromycin phosphotransferase
- NPA:
-
N-1-naphthylphthalamic acid
- Kp:
-
Kaempferol
- K-3-R:
-
Kaempferol-3-rutinoside
- PAL:
-
Phenylalanine ammonia-lyase
- SCT:
-
Scopoletin
References
Akiyoshi DE, Klee H, Amasino RM, Nester EW, Gordon MP (1984) T-DNA of Agrobacterium tumefaciens encodes an enzyme of cytokinin biosynthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81:5994–5998
Aloni R, Pradel KS, Ullrich CI (1995) The three-dimensional structure of vascular tissues in Agrobacterium tumefaciens-induced crown galls and in the host stems of Ricinus communis L. Planta 196:597–605
Aoyama T, Chua N-H (1997) A glucocorticoid-mediated transcriptional induction system in transgenic plants. Plant J 11:605–612
Avsian-Kretchmer O, Cheng J-C, Chen L, Moctezuma E, Sung ZR (2002) Indole acetic acid distribution coincides with vascular differentiation pattern during Arabidopsis leaf ontogeny. Plant Physiol 130:199–209
Brown DE, Rashotte AM, Murphy AS, Normanly J, Tague BW, Peer WA, Taiz L, Muday GK (2001) Flavonoids act as negative regulators of auxin transport in vivo in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 126:524–535
Carland FM, McHale NA (1996) LOP1: a gene involved in auxin transport and vascular pattering in Arabidopsis. Development 122:1811–1819
Chilton M-D, Drummond MH, Merlo DJ, Sciaky D, Montoya AL, Gordon MP, Nester EW (1977) Stable incorporation of plasmid DNA into higher plant cells: the molecular basis of crown gall tumorigenesis. Cell 11: 263–271
Fritig B, Hirth L, Ourisson G, (1970) Biosynthesis of the coumarins: scopoletin formation in tobacco tissue cultures. Phytochemistry 9: 1963–1975
Gális I, Šimek P, Macas, J, Zahradnčèková H, Vlasák J, Wabiko H, Van Dongen W, Van Onckelen HA, Ondøej M (1999) The Agrobacterium tumefaciens C58-6b gene confers resistance to N6(-benzyladenine without modifying cytokinin metabolism in tobacco seedlings. Planta 209:453–461
Gális I, Šimek P, Van Onckelen HA, Kakiuchi Y, Wabiko H (2002) Resistance of transgenic tobacco seedlings expressing the Agrobacterium tumefaciens C58-6b gene, to growth-inhibitory levels of cytokinin is associated with elevated IAA levels and activation of phenylpropanoid metabolism. Plant Cell Physiol 43: 939–950
Gális I, Kakiuchi Y, Šimek P, Wabiko H (2004) Agrobacterium tumefaciens AK-6b gene modulates phenolic compound metabolism in tobacco. Phytochemistry 65:169–179
Grémillon L, Helfer A, Clément B, Otten L (2004) New plant growth-modifying properties of the Agrobacterium T-6b oncogene revealed by the use of a dexamethasone-inducible promoter. Plant J 37:218–228
Harborne JB (1980) Plant phenolics. In: Bell EA, Charlwood BV (eds) Secondary plant products. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 329–402
Helfer A, Clément B, Michler P, Otten L (2003) The Agrobacterium oncogene AB-6b causes a graft-transmissible enation syndrome in tobacco. Plant Mol Biol 52:483–493
Hooykaas PJJ, den Dulk-Ras H, Schilperoort RA (1988) The Agrobacterium tumefaciens T-DNA gene 6b is an onc gene. Plant Mol Biol 11:791–794
Jacobs M, Rubery PH (1988) Naturally occurring auxin transport regulators. Science 241:346–349
Kitakura S, Fujita T, Ueno Y, Terakura S, Wabiko H, Machida Y (2002) The protein encoded by oncogene 6b from Agrobacterium tumefaciens interacts with a nuclear protein of tobacco. Plant Cell 14: 451–463
Koizumi K, Sugiyama M, Fukuda H (2000) A series of novel mutants of Arabidopsis thaliana that are defective in the formation of continuous vascular network: calling the auxin signal flow canalization hypothesis into question. Development 127:3197–3204
Kojima K (1999) Physiological studies on development in fruits and vegetables—Plant hormones in growth stage and softening mechanism in ripening stage [Japanese]. Chem Regul Plants 34:21–30
Mattsson J, Sung ZR, Berleth T (1999) Responses of plant vascular systems to auxin transport inhibition. Development 126:2979–2991
Murphy A, Peer WA, Taiz L (2000) Regulation of auxin transport by aminopeptidases and endogenous flavonoids. Planta 211:315–324
Okada K, Ueda J, Komaki MK, Bell CJ, Shimura Y (1991) Requirement of the auxin polar transport system in early stages of Arabidopsis floral bud formation. Plant Cell 3:677–684
Peer WA, Brown DE, Tague BW, Muday GK, Taiz L, Murphy AS (2001) Flavonoid accumulation patterns of transparent testa mutants of Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 126:536–548
Rakwal R, Tamogami S, Agrawal GK, Iwahashi H (2002) Octadecanoid signaling component "burst" in rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedling leaves upon wounding by cut and treatment with fungal elicitor chitosan. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 295:1041–1045
Reinhardt D, Mandel T, Kuhlemeier C (2000) Auxin regulates the initiation and radial position of plant lateral organs. Plant Cell 12: 507–518
Scanlon MJ (2003) The polar auxin transport inhibitor N-1-naphthylphthalamic acid disrupts leaf initiation, KNOX protein regulation, and formation of leaf margins in maize. Plant Physiol 133: 597–605
Schoch G, Goepfert S, Morant M, Hehn A, Meyer D, Ullmann P, Werck-Reichhart D (2001) CYP98A3 from Arabidopsis thaliana is a 3′-hydroxylase of phenolic esters, a missing link in the phenylpropanoid pathway. J Biol Chem 276:36566–36574
Schröder G Waffenschmidt S, Weiler EW, Schröder J (1984) The T-region of Ti plasmids codes for an enzyme synthesizing indole-3-acetic acid. Eur J Biochem 138:387–391
Schwalm K, Aloni R, Langhans M, Heller W, Stich S, Ullrich CI (2003) Flavonoid-related regulation of auxin accumulation in Agrobacterium tumefaciens-induced plant tumors. Planta 218:163–178
Sieburth LE (1999) Auxin is required for leaf vein pattern in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 121:1179–1190
Spanier K, Schell J, Schreier PH (1989) A functional analysis of T-DNA gene 6b: The fine tuning of cytokinin effects on shoot development. Mol Gen Genet 219:209–216
Steck W (1967) The biosynthetic pathway from caffeic acid to scopolin in tobacco leaves. Can J Biochem 45:1995–2003
Stieger P, Reinhardt D, Kuhlemeier C (2002) The auxin influx carrier is essential for correct leaf positioning. Plant J 32:509–517
Takahashi Y, Nagata T (1992) parB: An auxin-regulated gene encoding glutathione S-transferase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:56–59
Takahashi Y, Sakai T, Ishida S, Nagata T (1995) Identification of auxin-responsive elements of parB and their expression in apices of shoot and root. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:6359–6363
Thomashow LS, Reeves S, Thomashow MF (1984) Crown gall oncogenesis: evidence that a T-DNA gene from the Agrobacterium Ti plasmid pTiA6 encodes an enzyme that catalyzes synthesis of indoleacetic acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81:5071–5075
Thomashow MF, Hugly S, Buchholz WG, Thomashow LS (1986) Molecular basis for the auxin-independent phenotype of crown gall tumor tissues. Science 231:616–618
Tinland B, Huss B, Paulus F, Bonnard, Otten L (1989) Agrobacterium tumefaciens 6b genes are strain-specific and affect the activity of auxin as well as cytokinin genes. Mol Gen Genet 219:217–224
Van Larebeke N, Engler G, Holsters M, Van Den Elsacker S, Zaenen I, Schilperoort RA, Schell J (1974) Large plasmid in Agrobacterium tumefaciens essential for crown gall-inducing ability. Nature 252: 169–170
Van Onckelen H, Prinsen E, Inzé D, Rüdelsheim P, Van Lijsebettens M, Follin A, Schell J, Van Montagu M, De Greef J (1986) Agrobacterium T-DNA gene 1 codes for tryptophan-2-monooxygenase activity in tobacco crown gall cells. FEBS Lett 198:357–360
Vereecke D, Messens E, Klarskov K, De Bruyn A, Van Montagu M, Goethals K (1997) Patterns of phenolic compounds in leafy galls of tobacco. Planta 201:342–348
Verhoeyen ME, Bovy A, Collins G, Muir S, Robinson S, de Vos CHR, Colliver S (2002) Increasing antioxidant levels in tomatoes through modification of the flavonoid biosynthetic pathway. J Exp Bot 53: 2099–2106
Veselov D, Langhans M, Hartung W, Aloni R, Feussner I, Götz C, Veselova S, Schlomski S, Dickler C, Bächmann K, Ullrich CI (2003) Development of Agrobacterium tumefaciens C58-induced plant tumors and impact on host shoots are controlled by a cascade of jasmonic acid, auxin, cytokinin, ethylene and abscisic acid. Planta 216:512–522
Wabiko H, Minemura M (1996) Exogenous phytohormone-independent growth and regeneration of tobacco plants transgenic for the 6b gene of Agrobacterium tumefaciens AKE10. Plant Physiol 112:939–951
Wächter R, Langhans M, Aloni R, Götz S, Weilmünster A, Koops A, Temguia L, Mistrik I, Pavlovkin J, Rascher U, Schwalm K, Koch KE, Ullrich CI (2003) Vascularization, high-volume solution flow, and localized roles for enzymes of sucrose metabolism during tumorigenesis by Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Plant Physiol 133:1024–1037
Wen-jun S, Forde BG (1989) Efficient transformation of Agrobacterium spp. by high voltage electroporation. Nucleic Acids Res 17:8385
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. N. Sakurai (Hiroshima University) for providing us with [13C]IAA and Dr. S. Youssefian (Akita Prefectural University) for critical reading of the manuscript. This work was supported by Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (13660055) from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports Science and Technology, Japan and by the Sasagawa Scientific Research Grant (No. 13–238) from the Japan Science Society.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kakiuchi, Y., Gàlis, I., Tamogami, S. et al. Reduction of polar auxin transport in tobacco by the tumorigenic Agrobacterium tumefaciens AK-6b gene. Planta 223, 237–247 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-005-0080-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-005-0080-4