Abstract
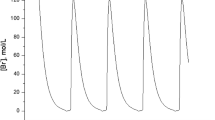
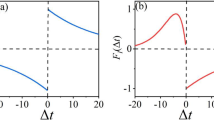
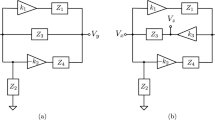
The problem of phase regulation for a population of oscillating systems is considered. The proposed control strategy is based on a phase response curve (PRC) model of an oscillator (the first-order reduced model obtained for linearized system and inputs with infinitesimal amplitude). It is proven that the control provides phase resetting for the original nonlinear system. Next, the problem of phase resetting for a network of oscillators is considered when applying a common control input. Performance of the obtained solutions is demonstrated via computer simulation for three different models of circadian/neural oscillators.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andronov AA, Vitt AA, Khaikin AE (1987) Theory of oscillators. Dover, reprint
Antle MC, Foley NC, Foley DK, Silver R (2007) Gates and oscillators II: zeitgebers and the network model of the brain clock. J Biol Rhythms 22:14–25
Astashev V, Babitsky V, Kolovsky M (2001) Dynamics and control of machines. Springer, New York
Bagheri N, Stelling J, Doyle FJ (2007) Circadian phase entrainment via nonlinear model predictive control. Int J Robust Nonlinear Control 17:1555–1571
Bagheri N, Stelling J, Doyle FJ (2008) Circadian phase resetting via single and multiple control targets. Comp Biol 7(4):1–10
Belykh VN, Osipov GV, Kucklander N, Blasius B, Kurths J (2005) Automatic control of phase synchronization in coupled complex oscillators. Phys D 200:81–104
Blekhman II (1971) Synchronization in science and technology. Moscow: Nauka (in Russian) [English translation: 1988, Synchronization in science and technology. New York: ASME Press]
Canavier CC, Achuthan S (2010) Pulse coupled oscillators and the phase resetting curve. Math Biosci 226(2):77–96
Cheal AJ, Delean S, Sweatman H, Thompson AA (2007) Spatial synchrony in coral reef fish populations and the influence of climate. Ecology 88(1):158–69
Danzl P, Moehlis J (2008) Spike timing control of oscillatory neuron models using impulsive and quasi-impulsive charge-balanced inputs. In: Proceedings 29th American control conference (ACC2008), Seattle, USA, pp 171–176
Datta AK, Stephens JA (1990) Synchronization of motor unit activity during voluntary contraction in man. J Physiol (Lond) 422:397–419
Efimov DV, Fradkov AL (2009) Oscillatority of nonlinear systems with static feedback. SIAM J Optim Control 48(2):618–640
Efimov D (2011) Phase resetting control based on direct phase response curve. J Math Biol 63(5):855–879
Efimov D, Sacre P, Sepulchre R (2009) Controlling the phase of an oscillator: a phase response curve approach. In: Proceedings IEEE CDC 2009, pp 7692–7697
Fradkov AL, Pogromsky AY (1998) Introduction to control of oscillations and chaos. World Scientific, Singapore
Forger DB, Paydarfar D (2004) Starting, stopping, and resetting biological oscillators: in search for optimum perturbations. J Theor Biol 230:521–532
Glass L, Nagai Y, Hall K, Talajic M, Nattel S (2002) Predicting the entrainment of reentrant cardiac waves using phase resetting curves. Phys Rev E 65:65–74
Govaerts W, Sautois B (2006) Computation of the phase response curve: a direct numerical approach. Neural Comput 18:817–847
Guckenheimer J, Holmes P (1990) Nonlinear oscillations, dynamical systems and bifurcations of vector fields. Springer, Berlin
Guevara MR, Glass L (1982) Phase locking, period doubling bifurcations and chaos in a mathematical model of a periodically driven oscillator: a theory for the entrainment of biological oscillators and the generation of cardiac dysrhythmias. J Math Biol 14:1–23
Guevara MR, Glass L, Shrier A (1981) Phase locking, period-doubling bifurcations, and irregular dynamics in periodically stimulated cardiac cells. Science 214:1350–1353
Hansel D, Mato G, Meunier C (1995) Synchrony in excitatory neural networks. Neural Comput 7:307–337
Izhikevich EM (2007) Dynamical systems in neuroscience: the geometry of excitability and bursting. The MIT press, Cambridge
Kawato M, Suzuki R (1978) Biological oscillators can be stopped—topological study of a phase response curve. Biol Cybern 30(4):241–248
Koenig WD, Knops JM (2013) Large-scale spatial synchrony and cross-synchrony in acorn production by two California oaks. Ecology 94(1):83–93
Kovaleva AS (2004) Frequency and phase control of the resonance oscillations of a non-linear system under conditions of uncertainty. J Appl Math Mech 68:699–706
Kuramoto Y (1984) Chemical oscillations, waves and turbulence. Springer, Berlin
Kurths J (Ed.) (2000) A special issue on phase synchronization in chaotic systems. Int J Bifur Chaos 11
Leloup JC, Goldbeter A (1998) A model for circadian rhythms in Drosophila incorporating the formation of a complex between the PER and TIM proteins. J Biol Rhythms 13:70–87
Leloup JC, Goldbeter A (1999) Chaos and birhythmicity in a model for circadian oscillations of the PER and TIM proteins in Drosophila. J Theor Biol 198(3):445–459
Leloup J-C, Gonze D, Goldbeter A (1999) Limit cycle models for circadian rhythms based on transcriptional regulation in Drosophila and Neurospora. J Biol Rhythms 14:433–448
Li J-S, Dasanayake I, Ruths J (2013) Control and synchronization of neuron ensembles. IEEE Trans Autom Control 58(8):1919– 1930
Lin Y, Sontag ED, Wang Y (1996) A smooth converse Lyapunov theorem for robust stability. SIAM J Control Optim 34:124–160
Moran PAP (1953) The statistical analysis of the Canadian lynx cycle. II. Synchronization and meteorology. Aust J Zool 1:291–298
Mosekilde E, Maistrenko Yu, Postnov D (2002) Chaotic synchronization. Applications to living systems. World Scientific, Singapore
Nakao H, Arai K, Nagai K, Tsubo Y, Kuramoto Y (2005) Synchrony of limit-cycle oscillators induced by random external impulses. Phys Rev E 72(2):026220
Ogata K (2006) Discrete time control systems, 2nd edn. Paperback, New York
Pampus M, Winkel W (2007) The extended Moran effect and large-scale synchronous fluctuations in the size of great tit and blue tit populations. J Anim Ecol 76:315–325
Pikovsky A, Rosenblum M, Kurths J (2001) Synchronization. A universal concept in nonlinear sciences. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Rand DA, Shulgin BV, Salazar D, Millar AJ (2004) Design principles underlying circadian clocks. J R Soc Interface 1:119–130
Rosenstock TS, Hastings A, Koenig WD, Lyles DJ, Brown PH (2011) Testing Moran’s theorem in an agroecosystem. Oikos 120:1434–1440
Roy R, Thornburg KS (1994) Experimental synchronization of chaotic lasers. Phys Rev Lett 72(13):2009–2012
Schmied A, Ivarsson C, Fetz EE (1993) Short-term synchronization of motor units in human extensor digitorum communis muscle: relation to contractile properties and voluntary control. Exp Brain Res 97:159–172
Smeal RM, Ermentrout GB, White JA (2010) Phase-response curves and synchronized neural networks. Phil Trans R Soc B 365:2407–2422
Sparrow C (1982) The Lorenz equations: bifurcations, chaos and strange attractors. Springer, Berlin
Tass PA (1999) Phase resetting in medicine and biology. Stochastic modeling and data analysis. Springer, Berlin
Tass PA (2002) Desynchronization of brain rhythms with soft phase-resetting techniques. Biol Cybern 87(2):102–115
Taylor SR, Gunawan R, Petzold LR, Doyle FJ (2008) Sensitivity measures for oscillating systems: application to mammalian circadian gene network. IEEE Trans Autom Control 53(12):177–188
Thommen Q (2010) Pfeuty B. PLoS Comput Biol 6(11):e1000990
Tran D, Nadau A, Durrieu G, Ciret P, Parisot JC, Massabuau JC (2011) Field chronobiology in a molluscan bivalve: how the moon and sun cycles interact to drive oyster activity rhythms. Chronobiol Int 28:307–317
Wang Y, Núñez F, Doyle FJ III (2013) Increasing sync rate of pulse-coupled oscillators via phase response function design: theory and application to wireless networks. IEEE Trans Control Syst Technol 21(4):1455–1462
Winfree AT (1980) The geometry of biological time. Springer, Berlin
Yakubovich VA, Starzhinskii VM (1975) Linear differential equations with periodic coefficients. Wiley, New York
Zhao G (2010) Phase organization of circadian oscillators in extended gate and oscillator models. J Theor Biol 264(2):367–376
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was partially supported by the Government of Russian Federation (Grant 074-U01) and the Ministry of Education and Science of Russian Federation (Project 14.Z50.31.0031).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Efimov, D. Phase resetting for a network of oscillators via phase response curve approach. Biol Cybern 109, 95–108 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00422-014-0629-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00422-014-0629-z