Abstract
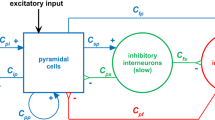
The phenomenon in which the response of a neuronal network to a weak signal is significantly enhanced in moderate noise is known as stochastic resonance (SR). Most of the previous studies on the transmission of signals by networks have been based on static synaptic connections, whereas dynamic synaptic connections modified by spike-time-dependent plasticity (STDP) are the basis of learning and memory in the nervous system. In this paper, we explore the phenomenon of SR in a neuronal network consisting of different ratios of excitatory vertebral neurons and inhibitory interneurons. The equivalent circuit method was employed to assess the average energy efficiency of the network. The differences in signal response before and after the introduction of STDP were compared for purely excitatory, purely inhibitory and excitatory-inhibitory networks, respectively. It was found that excitatory STDP promotes the network's response to weak signals, while inhibitory STDP has the opposite effect. The introduction of the inhibitory STDP makes the inhibitory network insensitive to the modulation of the coupling strength and increases its robustness. Furthermore, in the excitatory-inhibitory network, we found that STDP had little effect on the overall signalling of the network, and that the network's response to weak signals was more stable. Our findings contribute to the understanding of the importance of excitatory-inhibitory balance in ensuring accurate transmission and processing of information and provide new insights into the role of STDP in neuronal information processing.















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
No data were used in the studies described in this article.
References
Neiman, A., Silchenko, A., Anishchenko, V., Schimansky-Geier, L.: Stochastic resonance: noise-enhanced phase coherence. Phys. Rev. E 58, 7118 (1998)
Collins, J.J., Imhoff, T.T., Grigg, P.: Noise-enhanced information transmission in rat SA1 cutaneous mechanoreceptors via aperiodic stochastic resonance. J. Neurophysiol. 76, 642–645 (1996)
Wang, G.W., Wu, Y., Xiao, F.L., Ye, Z.Q., Jia, Y.: Non-Gaussian noise and autapse-induced inverse stochastic resonance in bistable Izhikevich neural system under electromagnetic induction. Physica A 598 (2022).
Gang, H., Ditzinger, T., Ning, C.-Z., Haken, H.: Stochastic resonance without external periodic force. Phys. Rev. Lett. 71, 807 (1993)
Liu, C., Yu, D., Li, T., Wang, X., Xie, Y., Jia, Y.: Effects of neuronal morphology and time delay on inverse stochastic resonance in two-compartment neuron model. Phys. Lett. A 493, 129268 (2024)
Li, T.Y., Yu, D., Wu, Y., Ding, Q.M., Jia, Y.: Stochastic resonance in the small-world networks with higher order neural motifs interactions. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjs/s11734-024-01139-w
Wiesenfeld, K., Moss, F.: Stochastic resonance and the benefits of noise: from ice ages to crayfish and SQUIDs. Nature 373, 33–36 (1995)
Xiao, F., Fu, Z., Jia, Y., Yang, L.: Resonance effects in neuronal-astrocyte model with ion channel blockage. Chaos Solit. Fract. 166, 112969 (2023)
Yu, D., Wang, G., Li, T., Ding, Q., Jia, Y.: Filtering properties of Hodgkin-Huxley neuron on different time-scale signals. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 117, 106894 (2023)
Benzi, R., Parisi, G., Sutera, A., Vulpiani, A.: Stochastic resonance in climatic change. Tellus 34, 10–16 (1982)
Liang, X., Dhamala, M., Zhao, L., Liu, Z.: Phase-disorder-induced double resonance of neuronal activity. Phys. Rev. E 82, 010902 (2010)
Destexhe, A., Contreras, D.: Neuronal computations with stochastic network states. Science 1979(314), 85–90 (2006)
Gluckman, B.J., Netoff, T.I., Neel, E.J., Ditto, W.L., Spano, M.L., Schiff, S.J.: Stochastic resonance in a neuronal network from mammalian brain. Phys. Rev. Lett. 77, 4098 (1996)
Hansel, D., Sompolinsky, H.: Synchronization and computation in a chaotic neural network. Phys. Rev. Lett. 68, 718 (1992)
Sussillo, D., Abbott, L.F.: Generating coherent patterns of activity from chaotic neural networks. Neuron 63, 544–557 (2009)
Baysal, V., Yılmaz, E.: Chaotic signal induced delay decay in Hodgkin-Huxley Neuron. Appl. Math. Comput. 411, 126540 (2021)
Yu, D., Zhou, X., Wang, G., Ding, Q., Li, T., Jia, Y.: Effects of chaotic activity and time delay on signal transmission in FitzHugh-Nagumo neuronal system. Cogn. Neurodyn. 16, 887–897 (2022)
Baysal, V., Erkan, E., Yilmaz, E.: Impacts of autapse on chaotic resonance in single neurons and small-world neuronal networks. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A 379, 20200237 (2021)
Wang, H., Chen, Y.: Response of autaptic Hodgkin-Huxley neuron with noise to subthreshold sinusoidal signals. Physica A 462, 321–329 (2016)
Yilmaz, E., Uzuntarla, M., Ozer, M., Perc, M.: Stochastic resonance in hybrid scale-free neuronal networks. Physica A 392, 5735–5741 (2013)
Yu, D., Wang, G., Ding, Q., Li, T., Jia, Y.: Effects of bounded noise and time delay on signal transmission in excitable neural networks. Chaos Solit. Fract. 157, 111929 (2022)
Kawaguchi, M., Mino, H., Durand, D.M.: Stochastic resonance can enhance information transmission in neural networks. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 58, 1950–1958 (2011)
Perc, M.: Stochastic resonance on weakly paced scale-free networks. Phys. Rev. E 78, 036105 (2008)
Perc, M.: Stochastic resonance on excitable small-world networks via a pacemaker. Phys. Rev. E 76, 066203 (2007)
Yu, H., Li, K., Guo, X., Wang, J., Deng, B., Liu, C.: Firing rate oscillation and stochastic resonance in cortical networks with electrical–chemical synapses and time delay. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 28, 5–13 (2018)
Debanne, D., Inglebert, Y.: Spike timing-dependent plasticity and memory. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 80, 102707 (2023)
Gerstner, W., Kempter, R., Van Hemmen, J.L., Wagner, H.: A neuronal learning rule for sub-millisecond temporal coding. Nature 383, 76–78 (1996)
Markram, H., Lübke, J., Frotscher, M., Sakmann, B.: Regulation of synaptic efficacy by coincidence of postsynaptic APs and EPSPs. Science 1979(275), 213–215 (1997)
Bi, G., Poo, M.: Synaptic modifications in cultured hippocampal neurons: dependence on spike timing, synaptic strength, and postsynaptic cell type. J. Neurosci. 18, 10464–10472 (1998)
Hu, X., Wu, Y., Ding, Q., Xie, Y., Ye, Z., Jia, Y.: Synchronization of scale-free neuronal network with small-world property induced by spike-timing-dependent plasticity under time delay. Physica D 460, 134091 (2024)
Tzounopoulos, T., Rubio, M.E., Keen, J.E., Trussell, L.O.: Coactivation of pre-and postsynaptic signaling mechanisms determines cell-specific spike-timing-dependent plasticity. Neuron 54, 291–301 (2007)
Feldman, D.E., Brecht, M.: Map plasticity in somatosensory cortex. Science 310, 810–815 (2005)
Li, T., Wu, Y., Yang, L., Zhan, X., Jia, Y.: Spike-timing-dependent plasticity enhances chaotic resonance in small-world network. Physica A 606, 128069 (2022)
Lobov, S.A., Zhuravlev, M.O., Makarov, V.A., Kazantsev, V.B.: Noise enhanced signaling in STDP driven spiking-neuron network. Math. Model. Nat. Phenom. 12, 109–124 (2017)
Li, X., Zhang, J., Small, M.: Self-organization of a neural network with heterogeneous neurons enhances coherence and stochastic resonance. Chaos 19, (2009)
Xie, H.J., Gong, Y.B., Wang, B.Y.: Spike-timing-dependent plasticity optimized coherence resonance and synchronization transitions by autaptic delay in adaptive scale-free neuronal networks. Chaos Solit. Fract. 108, 1–7 (2018)
Li, X., Small, M.: Neuronal avalanches of a self-organized neural network with active-neuron-dominant structure. Chaos 22, (2012)
Madadi Asl, M., Valizadeh, A., Tass, P.A.: Dendritic and axonal propagation delays determine emergent structures of neuronal networks with plastic synapses. Sci. Rep. 7, 39682 (2017)
Madadi Asl, M., Valizadeh, A., Tass, P.A.: Decoupling of interacting neuronal populations by time-shifted stimulation through spike-timing-dependent plasticity. PLoS Comput. Biol. 19, e1010853 (2023)
D’amour, J.A., Froemke, R.C.: Inhibitory and excitatory spike-timing-dependent plasticity in the auditory cortex. Neuron 86, 514–528 (2015)
Di Lorenzo, F., Ponzo, V., Motta, C., Bonnì, S., Picazio, S., Caltagirone, C., Bozzali, M., Martorana, A., Koch, G.: Impaired spike timing dependent cortico-cortical plasticity in Alzheimer’s disease patients. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 66, 983–991 (2018)
Attwell, D., Laughlin, S.B.: An energy budget for signaling in the grey matter of the brain. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 21, 1133–1145 (2001)
Siekevitz, P.: Producing neuronal energy. Science 306, 410–411 (2004)
Magistretti, P.J.: Low-cost travel in neurons. Science 325, 1349–1351 (2009)
Xu, L., Qi, G., Ma, J.: Modeling of memristor-based Hindmarsh-Rose neuron and its dynamical analyses using energy method. Appl. Math. Model. 101, 503–516 (2022)
Sun, J., Li, C., Wang, Z., Wang, Y.: Dynamic analysis of HR-FN-HR neural network coupled by locally active hyperbolic memristors and encryption application based on Knuth-Durstenfeld algorithm. Appl. Math. Model. 121, 463–483 (2023)
Xie, Y., Ye, Z.Q., Li, X.N., Wang, X.Q., Jia, Y.: A novel memristive neuron model and its energy characteristics. Cogn. Neurodyn. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11571-024-10065-5
Wang, Y., Wang, R., Xu, X.: Neural energy supply-consumption properties based on Hodgkin-Huxley model. Neural. Plast. 2017, (2017)
Wang, Y., Xu, X., Wang, R.: The place cell activity is information-efficient constrained by energy. Neural Netw. 116, 110–118 (2019)
Wang, Y., Xu, X., Zhu, Y., Wang, R.: Neural energy mechanism and neurodynamics of memory transformation. Nonlinear Dyn. 97, 697–714 (2019)
Moujahid, A., d’Anjou, A., Torrealdea, F.J., Torrealdea, F.: Energy and information in Hodgkin-Huxley neurons. Phys. Rev. E 83, 031912 (2011)
Yu, L., Yu, Y.: Energy-efficient neural information processing in individual neurons and neuronal networks. J. Neurosci. Res. 95, 2253–2266 (2017)
Liu, Y., Yue, Y., Yu, Y., Liu, L., Yu, L.: Effects of channel blocking on information transmission and energy efficiency in squid giant axons. J. Comput. Neurosci. 44, 219–231 (2018)
Yu, D., Yang, L., Zhan, X., Fu, Z., Jia, Y.: Logical stochastic resonance and energy consumption in stochastic Hodgkin-Huxley neuron system. Nonlinear Dyn. 111, 6757–6772 (2023)
Yu, D., Zhan, X., Yang, L., Jia, Y.: Theoretical description of logical stochastic resonance and its enhancement: Fast Fourier transform filtering method. Phys. Rev. E 108, 014205 (2023)
Wang, S., Wang, W., Liu, F.: Propagation of firing rate in a feed-forward neuronal network. Phys. Rev. Lett. 96, 018103 (2006)
Fox, R.F.: Stochastic versions of the Hodgkin-Huxley equations. Biophys. J. 72, 2068–2074 (1997)
Watts, D.J., Strogatz, S.H.: Collective dynamics of ‘small-world’networks. Nature 393, 440–442 (1998)
Meinecke, D.L., Peters, A.: GABA immunoreactive neurons in rat visual cortex. J. Comp. Neurol. 261, 388–404 (1987)
Wang, Y., Shi, X., Si, B., Cheng, B., Chen, J.: Synchronization and oscillation behaviors of excitatory and inhibitory populations with spike-timing-dependent plasticity. Cogn. Neurodyn. 17, 715–727 (2023)
Yu, H., Guo, X., Wang, J., Liu, C., Deng, B., Wei, X.: Adaptive stochastic resonance in self-organized small-world neuronal networks with time delay. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 29, 346–358 (2015)
Lobov, S., Simonov, A., Kastalskiy, I., Kazantsev, V.: Network response synchronization enhanced by synaptic plasticity. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 225, 29–39 (2016)
Ding, Q., Jia, Y.: Effects of temperature and ion channel blocks on propagation of action potential in myelinated axons. Chaos 31, (2021)
Lv, M., Wang, C., Ren, G., Ma, J., Song, X.: Model of electrical activity in a neuron under magnetic flow effect. Nonlinear Dyn. 85, 1479–1490 (2016)
Wang, X., Yu, D., Li, T., Jia, Y.: Logistic stochastic resonance in the Hodgkin-Huxley neuronal system under electromagnetic induction. Physica A 630, 129247 (2023)
Yu, D., Wu, Y., Yang, L., Zhao, Y., Jia, Y.: Effect of topology on delay-induced multiple resonances in locally driven systems. Physica A 609, 128330 (2023)
Udhayakumar, K., Shanmugasundaram, S., Kashkynbayev, A., Janani, K., Rakkiyappan, R.: Saturated and asymmetric saturated impulsive control synchronization of coupled delayed inertial neural networks with time-varying delays. Appl. Math. Model. 113, 528–544 (2023)
Yang, F., Ma, J.: A controllable photosensitive neuron model and its application. Opt. Laser Technol. 163, 109335 (2023)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China under No. 12175080, also financially supported by self-determined research funds of CCNU from the colleges’ basic research and operation of MOE under No. CCNU22JC009.
Funding
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XW, DY and TL contributed to conceptualization, software, writing-original draft preparation; XL, WH and XZ contributed to methodology and visualization; and YJ supervised the study. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Yu, D., Li, T. et al. Effects of spike-time-dependent plasticity on stochastic resonance in excitatory-inhibitory neuronal networks. Nonlinear Dyn (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-024-09682-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-024-09682-w