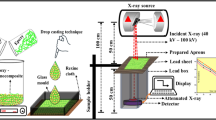
Abstract
PbO (lead oxide) particles with different sizes were incorporated into polystyrene (PS) with various weight fractions (0, 10, 15, 25, 35%). These novel PS/PbO nano-composites were produced by roll mill mixing and compressing molding techniques and then investigated for radiation attenuation of X-rays (N-series/ISO 4037) typically used in radiology. Properties of the PbO particles were studied by X-ray diffraction (XRD). Filler dispersion and elemental composition of the prepared nano-composites were characterized using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS), revealing better filler distribution and fewer agglomerations with smaller PbO particle size. Linear and mass attenuation coefficients (μ and μm), total molecular and atomic cross-sections (σmol and σatm), as well as effective atomic number and electron density (Zeff and Neff), were calculated for the energy range N40 to N200. The influence of PbO weight percentage on the enhancement of the shielding parameters of the nano-composites was expected; however, the effect of PbO particle size was surprising. Linear and mass attenuation coefficients for PS/PbO composites increased gradually with increasing PbO concentrations, and composites with a small size of nanoparticles showed best performance. In addition, increasing PbO concentration raised the effective atomic number Zeff of the composite. Hence, the electron density Neff increased, which provided a higher total interaction cross-section of X-rays with the composites. Maximum radiation shielding was observed for PS/PbO(B). It is concluded that this material might be used in developping low-cost and lightweight X-ray shielding to be used in radiology.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The Authors confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article. Raw data are available from the corresponding authors upon request.
References
Akimov DV, Andrienko OS, Egorov NB, Herin II, Usov VFZ (2012) Synthesis and properties of lead nanoparticles. Russ Chem Bull 61:225–229. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11172-012-0032-7
Al- Buriahi MS, Olarinoye IO, Mutuwong C, Alzahrani JS, Elsaeedy HI, Alomairy S, Tonguc BT (2021) Effects of reducing PbO content on the elastic and radiation attenuation properties of germanate glasses: a new non-toxic candidate for shielding applications. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 32:15080–15094. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-06060-9
Aldhuhaibat MJR, Amana MS, Jubier NJ, Salim AA (2021) Improved gamma radiation shielding traits of epoxy composites: evaluation of mass attenuation coefficient, effective atomic and electron number. Radiat Phys Chem 179:109183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radphyschem.2020.109183
Alotaibi BM, Sayyed MI, Kumar A, Alotiby M, Sharma A, Al-Yousef HA, Alsaif NAM, Al-Hadeethi Y (2021) Optical and gamma-ray shielding effectiveness of a newly fabricated P2O5–CaO–Na2O–K2O–PbO glass system. Prog Nucl Energy 138:103798. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnucene.2021.103798
Alsayed Z, Badawi MS, Awad R, El-khatib AM, Thabet AA (2020) Investigation of ɤ-ray attenuation coefficients, effective atomic number and electron density for ZnO/HDPE composite. Phys Scr 95:085301. https://doi.org/10.1088/1402-4896/ab9a6e
Ankerhold U (2019) Catalogue of X-ray spectra and their characteristic data: ISO and DIN radiation qualities, therapy and diagnostic radiation qualities, unfiltered X-ray spectra. PTB-Ber-34 3269094 Bytes. https://doi.org/10.7795/11020190315B
Aycik GA, Belgin EE (2018) Effect of polymer matrix type on electromagnetic radiation shielding performances of PbO reinforced / polyethylene, isophytalic polyester and bisphenol A vinylester based composites. Int J Chem Chem Eng Syst 3:1–4
Azman NZN, Siddiqui SA, Hart R, Low IM (2013) Microstructural design of lead oxide–epoxy composites for radiation shielding purposes. J Appl Polym Sci 128:3213–3219. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.38515
Badawi MS, Gouda MM, Nafee SS, El-khatib AM, El-Mallah EA (2012) New algorithm for studying the effect of self attenuation factor on the efficiency of γ-rays detectors. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res Sect Accel Spectrometers Detect Assoc Equip 696:164–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nima.2012.08.089
Bagheri R, Adeli R (2020) Gamma-ray shielding properties of phosphate glasses containing Bi2O3, PbO, and BaO in different rates. Radiat Phys Chem 174:108918. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radphyschem.2020.108918
Bappah AU, Haryna A (2015) Fractionation of Pb in soil of abandoned Pb mine by SEM-EDX and XRD. J Appl Sci Environ Manag 19:403–409. https://doi.org/10.4314/jasem.v19i3.9
Baykal DŞ, Tekin H, Mutlu RBÇ (2021) An investigation on radiation shielding properties of borosilicate glass systems. Int J Comput Exp Sci Eng 7:99–108. https://doi.org/10.22399/ijcesen.960151
Botelho MZ, Künzel R, Okuno E, Levenhagen RS, Basegio T, Bergmann CP (2011) X-ray transmission through nanostructured and microstructured CuO materials. Appl Radiat Isot 69:527–530. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apradiso.2010.11.002
Chantler CT, Olsen K, Dragoset RA, Chang J, Kishore AR, Kotochigova SA, Zucker DS (2009) X-ray form factor, attenuation, and scattering tables. In: NIST. https://www.nist.gov/pml/x-ray-form-factor-attenuation-and-scattering-tables. Accessed 21 Jun 2022
Cherkashina NI, Pavlenko VI, Noskov AV, Samoilova ES (2020) Using multilayer polymer PI/Pb composites for protection against X-ray bremsstrahlung in outer space. Acta Astronaut 170:499–508. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actaastro.2020.02.022
Cinan ZM, Baskan T, Erol B, Mutlu S, Misirlioglu Y, Yilmaz SS, Yilmaz AH (2021a) Gamma irradiation, thermal conductivity, and phase change tests of the cement-hyperbranched poly amino-ester-block-poly cabrolactone-polyurathane plaster-lead oxide and arsenic oxide composite for development of radiation shielding material. Int J Energy Res 45:20729–20762. https://doi.org/10.1002/er.7136
Cinan ZM, Erol B, Baskan T, Mutlu S, Yilmaz SS, Yilmaz AH (2021b) Gamma irradiation and the radiation shielding characteristics: for the lead oxide doped the crosslinked polystyrene-b-polyethyleneglycol block copolymers and the polystyrene-b-polyethyleneglycol-boron nitride nanocomposites. Polymers 13:3246. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13193246
Cinan ZM, Erol B, Baskan T, Mutlu S, Ortac B, Yilmaz SS, Yilmaz AH (2022) Radiation shielding tests of crosslinked polystyrene-b-polyethyleneglycol block copolymers blended with nanostructured selenium dioxide and boron nitride particles. Nanomaterials 12:297. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12030297
Echevarria-Bonet C, Rojas DP, Espeso JI, Fernandez JR, Rodriguez MF, Barquin LF, Fernandez LR, Gorria P, Blanco JA, Fdez-Gubieda ML (2015) Magnetic phase diagram of super antiferromagnetic TbCu2 nanoparticles. J Phys Condens Matter 27:496002. https://doi.org/10.1088/0953-8984/27/49/496002
El-khatib AM, Thabet AA, Elzaher MA, Badawi MS, Salem BA (2014) Study on the effect of the self-attenuation coefficient on γ-ray detector efficiency calculated at low and high energy regions. Nucl Eng Technol 46:217–224. https://doi.org/10.5516/NET.04.2013.077
El-Khatib AM, Abbas MI, Elzaher MA, Badawi MS, Alabsy MT, Alharshan GA, Aloraini DA (2019) Gamma attenuation coefficients of nano cadmium oxide/high density polyethylene composites. Sci Rep 9:16012. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-52220-7
El-Khatib AM, Shalaby TI, Antar A, Elsafi M (2022) Improving gamma ray shielding behaviors of polypropylene using PbO nanoparticles: an experimental study. Materials 15:3908. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15113908
Elsafi M, Dib MF, Mustafa HE, Sayyed MI, Khandaker MU, Alsubaie A, Almalki ASA, Abbas MI, El-khatib AM (2021) Enhancement of ceramics based red-clay by bulk and nano metal oxides for photon shielding features. Materials 14:7878. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14247878
Gerward L, Guilbert N, Bjørn Jensen K, Levring H (2001) X-ray absorption in matter reengineering XCOM. Radiat Phys Chem 60:23–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0969-806X(00)00324-8
Ghaseminejad M, Gholamzadeh L, Ostovari F (2021) Investigation of x-ray attenuation property of modification PbO with graphene in epoxy polymer. Mater Res Express 8:035008. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/abecea
Gusev AI, Kurlov AS (2008) Production of nanocrystalline powders by high-energy ball milling: model and experiment. Nanotechnology 19:265302. https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/19/26/265302
Hashemi SA, Mousavi SM, Faghihi R, Arjmand M, Sina S, Amani AM (2018) Lead oxide-decorated graphene oxide/epoxy composite towards X-Ray radiation shielding. Radiat Phys Chem 146:77–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radphyschem.2018.01.008
Hassan HE, Badran HM, Aydarous A, Sharshar T (2015) Studying the effect of nano lead compounds additives on the concrete shielding properties for γ-rays. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res Sect B Beam Interact Mater at 360:81–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nimb.2015.07.126
Herrati A, Arib M, Sidahmed T, Khalal-Kouache K (2017) Establishment of ISO 4037–1 X-ray narrow-spectrum series at SSDL of algiers. Radiat Prot Dosimetry 174:35–52. https://doi.org/10.1093/rpd/ncw093
Hussein AM, Dannoun EMA, Aziz SB, Brza MA, Abdulwahid RT, Hussen SA, Rostam S, Mustafa DMT, Muhammad DS (2020) Steps toward the band gap identification in polystyrene based solid polymer nanocomposites integrated with tin titanate nanoparticles. Polymers 12:2320. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12102320
Issa SAM (2016) Effective atomic number and mass attenuation coefficient of PbO–BaO–B2O3 glass system. Radiat Phys Chem 120:33–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radphyschem.2015.11.025
Jefremovas EM, Alonso J, Rodríguez MF, Fernandez JR, Espeso JI, Rojas DP, Garcia-Prieto A, Fernandez-Gubieda ML, Barquin LF (2020) Investigating the size and microstrain influence in the magnetic order/disorder state of GdCu2 nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 10:1117. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10061117
Kavun Y (2021) Comparison of the effective atomic numbers of some contrast agents compounds used in medical imaging. Erzincan Univ J Sci Technol 14:1055–1065. https://doi.org/10.18185/erzifbed.912373
Kavun Y, Boztosun İ, Ðapo H, Maras I, Segebade C (2018) Determination of the Sr/Ca ratio of tooth samples by photoactivation analysis in Southern Turkey. Radiochim Acta 106:759–768. https://doi.org/10.1515/ract-2017-2918
Kavun Y, Eskalen H, Kerli S, Kavgaci M (2021) Fabrication and characterization of GdxFe2O3(100–x) /PVA (x=0, 5, 10, 20) composite films for radiation shielding. Appl Radiat Isot 177:109918. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apradiso.2021.109918
Kavun Y, Kerli S, Eskalen H, Kavgacı M (2022) Characterization and nuclear shielding performance of Sm doped In2O3 thin films. Radiat Phys Chem 194:110014. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radphyschem.2022.110014
Khalil AT, Ovais M, Ullah I, Muhammad A, Jan SA, Shinwari ZK, Maaza M (2020) Bioinspired synthesis of pure massicot phase lead oxide nanoparticles and assessment of their biocompatibility, cytotoxicity and in-vitro biological properties. Arab J Chem 13:916–931. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2017.08.009
Kim S-C (2021) Analysis of shielding performance of radiation-shielding materials according to particle size and clustering effects. Appl Sci 11:4010. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11094010
Körpinar B, Canbaz B, Çam F, Akat H (2021) Gamma radiation shielding and thermal properties of the polystyrene/tungsten (VI) oxide composites. Erzincan Univ J Sci Technol 14:395–407. https://doi.org/10.18185/erzifbed.875739
Kozlovskiy A, Zdorovets MV, Kadyrzhanov KK (2021) Study of physical, optical properties and gamma radiation shielding efficiency of 0.5Bi2O3-(0.5–x)WO3-xPbO glasses. Opt Mater 114:111005. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2021.111005
Künzel R, Okuno E (2012) Effects of the particle sizes and concentrations on the X-ray absorption by CuO compounds. Appl Radiat Isot Data Instrum Methods Use Agric Ind Med 70:781–784. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apradiso.2011.12.040
Madbouly AM, Atta ER (2016) Comparative study between lead oxide and lead nitrate polymer as gamma-radiation shielding materials. J Environ Prot 7:268–276. https://doi.org/10.4236/jep.2016.72023
Mahmoud ME, El-Khatib AM, Badawi MS, Rashad AR, El-Sharkawy RM, Thabet AA (2018) Fabrication, characterization and gamma rays shielding properties of nano and micro lead oxide-dispersed-high density polyethylene composites. Radiat Phys Chem 145:160–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radphyschem.2017.10.017
Manjunatha H (2016) Mass attenuation coefficient and its photon interaction derivables of some skeletal muscle relaxants. J Radiat Cancer Res 7:18–26
Mathew BB (2018) Evaluation of lead oxide nanoparticles synthesized by chemical and biological methods. J Nanomedicine Res. https://doi.org/10.15406/jnmr.2018.07.00187
Mirzaei M, Zarrebini M, Shirani A, Shanbeh M, Borhani S (2019) X-ray shielding by a novel garment woven with melt-spun monofilament weft yarn containing lead and Tin particles. Text Res J 89:63–75. https://doi.org/10.1177/0040517517736475
Mokhtari K, Kheradmand Saadi M, Ahmadpanahi H, Jahanfarnia Gh (2021) Fabrication, characterization, simulation and experimental studies of the ordinary concrete reinforced with micro and nano lead oxide particles against gamma radiation. Nucl Eng Technol 53:3051–3057. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.net.2021.04.001
More CV, Alsayed Z, Badawi MS, Thabet AA, Pawar PP (2021) Polymeric composite materials for radiation shielding: a review. Environ Chem Lett 19:2057–2090. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-021-01189-9
Neves JS, de Souza Jr FG, Suarez PAZ, Umpierre AP, Machado F (2011) In situ production of polystyrene magnetic nanocomposites through a batch suspension polymerization Process. Macromol Mater Eng 296:1107–1118. https://doi.org/10.1002/mame.201100050
Newbury DE, Ritchie NWM (2015) Performing elemental microanalysis with high accuracy and high precision by scanning electron microscopy/silicon drift detector energy-dispersive X-ray spectrometry (SEM/SDD-EDS). J Mater Sci 50:493–518. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-014-8685-2
Ng SH, Wang J, Konstantinov K, Wexler D, Chen J, Liu HK (2006) Spray Pyrolyzed PbO-carbon nanocomposites as anode for lithium-ion batteries. J Electrochem Soc 153:A787. https://doi.org/10.1149/1.2172570
Noor Azman NZ, Siddiqui SA, Low IM (2013) Synthesis and characterization of epoxy composites filled with Pb, Bi or W compound for shielding of diagnostic x-rays. Appl Phys A 110:137–144. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-012-7464-7
Noukelag SK, Mohamed HEA, Razanamahandry LC, Ntwampe SKO, Arendse CJ (2021) Bio-inspired synthesis of PbO nanoparticles (NPs) via an aqueous extract of Rosmarinus officinalis (rosemary) leaves. Mater Today Proc 36:421–426. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.04.852
Obaid SS, Sayyed MI, Gaikwad DK, Pawar PP (2018) Attenuation coefficients and exposure buildup factor of some rocks for gamma ray shielding applications. Radiat Phys Chem 148:86–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radphyschem.2018.02.026
Pavlenko VI, Epifanovskii IS, Yastrebinskii RN, Kuprieva OV (2011) Thermoplastic constructional composite material for radiation protection. Inorg Mater Appl Res 2:136–141. https://doi.org/10.1134/S207511331102016X
Prabhu S, Bubbly SG, Gudennavar SB (2022) X-ray and γ-ray shielding efficiency of polymer composites: choice of fillers, effect of loading and filler size, photon energy and multifunctionality. Polym Rev. https://doi.org/10.1080/15583724.2022.2067867
Priamo F, Bell D, Sangheli A (2023) Linear attenuation coefficient radiology reference article. Radiopaedia.org.radiopaedia. https://doi.org/10.53347/rID-31918
Saboor A, Khalid SM, Jan R, Khan AN, Zia T, Farooq MU, Afridi S, Sadiq M, Arif M (2019) PS/PANI/MoS2 hybrid polymer composites with high dielectric behavior and electrical conductivity for emi shielding effectiveness. Materials 12:2690. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12172690
Sarshough S, Hadad K, Faghihi R (2018) Particle size and concentration effects on low energy X-ray attenuation in nanostructure and microstructure materials. Nucl Technol Radiat Prot 33:75–80
Shik NA, Gholamzadeh L (2018) X-ray shielding performance of the EPVC composites with micro- or nanoparticles of WO3, PbO or Bi2O3. Appl Radiat Isot 139:61–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apradiso.2018.03.025
Shojaei M, Shokuhfar A, Zolriasatein A (2021) Synthesis and characterization of CuAlS2 nanoparticles by mechanical milling. Mater Today Commun 27:102243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2021.102243
Torabi M (2011) Electrochemical evaluation of PbO nanoparticles as anode for lithium batteries. Int J Eng 24:351–356. https://doi.org/10.5829/idosi.ije.2011.24.04b.05
Tudose IV, Mouratis K, Ionescu ON, Romanitan C, Pachiu C, Popescu M, Khomenko V, Butenko O, Chernysh O, Kenanakis G, Barsukov VZ, Suchea MP, Koudoumas E (2022) Novel water-based paints for composite materials used in electromagnetic shielding applications. Nanomaterials 12:487. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12030487
Un A, Sahin Y (2011) Determination of mass attenuation coefficients, effective atomic and electron numbers, mean free paths and kermas for PbO, barite and some boron ores. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res Sect B Beam Interact Mater at 269:1506–1511. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nimb.2011.04.011
Verdipoor K, Alemi A, Mesbahi A (2018) Photon mass attenuation coefficients of a silicon resin loaded with WO3, PbO, and Bi2O3 Micro and Nano-particles for radiation shielding. Radiat Phys Chem 147:85–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radphyschem.2018.02.017
Viegas J, Silva LA, Batista AMS, Furtado CA, Nascimento JP, Faria LO (2017) Increased X-ray attenuation efficiency of graphene-based nanocomposite. Ind Eng Chem Res 56:11782–11790. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.7b02711
Wang Y, Zhong R, Li Q, Liao J, Liu N, Joshi NS, Shi B, Liao X, Guo J (2020) Lightweight and wearable X-ray shielding material with biological structure for low secondary radiation and metabolic saving performance. Adv Mater Technol 5:2000240. https://doi.org/10.1002/admt.202000240
Yalçın Z, İçelli O, Okutan M, Boncukçuoğlu R, Artun O, Orak S (2012) A different perspective to the effective atomic number (Zeff) for some boron compounds and trommel sieve waste (TSW) with a new computer program ZXCOM. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res Sect Accel Spectrometers Detect Assoc Equip 686:43–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nima.2012.05.041
Yaykaşlı H, Eskalen H, Kavun Y, Gögebakan M (2022) Microstructural, thermal, and radiation shielding properties of Al50B25Mg25 alloy prepared by mechanical alloying. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 33:2350–2359. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-07434-9
Zhang G, Gou B, Yang Y, Liu M, Li X, Xiao L, Hao G, Zhao F, Jiang W (2020) CuO/PbO nanocomposite: preparation and catalysis for ammonium perchlorate thermal decomposition. ACS Omega 5:32667–32676. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.0c05050
Acknowledgements
This work was done in the frame of a scientific collaboration between the Physics Department, Faculty of Science, Beirut Arab University (BAU), and the Lebanese Atomic Energy Commission (LAEC). This work was partially funded by a research grant (number: 12-05-18) from the Lebanese National Council for Scientific Research- (CNRSL), Beirut, Lebanon.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AFO performed the experimental part with the valuable supervision of MSB and HEB. MSB, RA, and OES carried out the theoretical analysis and numerical testing performance. MSB and AFO arranged all the figures. All authors reviewed and discussed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Osman, A.F., El Balaa, H., El Samad, O. et al. Assessment of X-ray shielding properties of polystyrene incorporated with different nano-sizes of PbO. Radiat Environ Biophys 62, 235–251 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00411-023-01017-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00411-023-01017-4