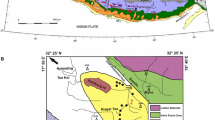
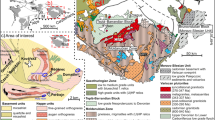
Abstract
Caledonian eclogite-facies metamorphism partially reworking Grenvillian granulite-facies anorthosite allows us to study the processes of garnet reequilibration at high pressure and to reconstruct the evolution of the unit near metamorphic peak conditions. Our results indicate that eclogite-facies metamorphism happened in two successive phases: first, inherited granulitic garnet was fractured and reequilibrated from their boundaries (crystal or fracture rims); then eclogite-facies minerals were crystallised in the fractures as overgrowths on inherited garnets. The reequilibration of inherited garnets is achieved through Fe2+Mg−1 exchange, whereas eclogite-facies garnets crystallised during the subsequent phase are notably richer in Ca than un- and re-equilibrated granulitic garnet. Pseudosection construction shows that this lack in Ca reequilibration cannot be related to variations in thermodynamic conditions (a H2O, reacting system composition) between the two phases. From the compilation of the available data, the reequilibration of granulitic garnet seems to be controlled by the inefficient intra- and inter-granular transport properties of Ca compared to Fe2+ and Mg. While these kinetic factors confine garnet reequilibration to Fe2+Mg−1 exchange, the extent of reequilibration along this exchange vector is controlled by partitioning with adjacent omphacite. On the contrary to the diffusional reequilibration of granulitic garnet that lasted for several My according to our modelling of the diffusional relaxation, the strong compositional gradients between eclogite-facies and reequilibrated garnets, which are almost unaffected by diffusional reequilibration, provide evidence that rapid exhumation followed the crystallisation of eclogite-facies minerals. We propose that the movement reversal itself, from burial to exhumation, and associated deformation and fluid flow, triggered this crystallisation event. The resulting evolution near metamorphic peak conditions is therefore strongly asymmetrical: on the one hand, the prograde diffusional relaxation profiles indicate slow movement during the last stages of burial, whereas the unaffected retrograde overgrowth indicates fast exhumation rates.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ai Y (1994) A revision of the garnet-clinopyroxene Fe2+-Mg exchange geothermometer. Contrib Mineral Petrol 115:467–473
Austrheim H (1987) Eclogitization of lower crustal granulites by fluid migration through shear zones. Earth Planet Sci Lett 81:221–232
Austrheim H (1990) The granulite-eclogite facies transition: A comparison of experimental work and a natural occurrence in the Bergen Arcs, western Norway. Lithos 25:163–169
Austrheim H (1998) Influence of fluid and deformation on metamorphism of the deep crust and consequences for the geodynamics of collision zones. In: Hacker BR, Liou JG (eds) When continents collide: geodynamics and geochemistry of ultrahigh-pressure rocks. Kluwer, The Netherlands, pp 297–323
Austrheim H, Griffin WL (1985) Shear deformation and eclogite formation within granulite-facies anorthosites of the Bergen Arcs, Western Norway. Chem Geol 50:267–281
Austrheim H, Mørk MBE (1988) The lower continental crust of the Caledonian mountain chain: evidence from former deep crustal sections in western Norway. Norges Geologiske Undersøkelse, Special publication 3:102–113
Austrheim H, Erambert M, Engvik AK (1997) Processing of crust in the root of the Caledonian continental collision zone: the role of eclogitization. Tectonophysics 273:129–153
Barrer RM, Bartholomew RF, Rees LVC (1963) Ion exchange in porous crystals. Part II. The relationship between self and exchange-diffusion coefficients. J Phys Chem Solids 24:309–317
Bejina F, Jaoul O, Liebermann (2003) Diffusion in minerals at high pressure: a review. Phys Earth Planet Int 139:3–20
Berman RG, Aranovich L, Pattison DR (1995) Reassessment of the garnet-clinopyroxene Fe-Mg exchange thermometer: II. Thermodynamic analysis. Contrib Mineral Petrol 119:30–42
Bingen B, Davis WJ, Austrheim H (2001) Zircon U-Pb geochronology in the Bergen arc eclogites and their Proterozoic protoliths, and implications for the pre-Scandian evolution of the Caledonides in western Norway. Geol Soc Am Bull 113(5):640–649
Bingen B, Austrheim H, Whitehouse MJ, Davis WJ (2004) Trace element signature and U-Pb geochronology of eclogite-facies zircon, Bergen Arcs, Caledonides of W Norway. Contrib Mineral Petrol 147:671–683
Boundy TM, Fountain DM, Austrheim H (1992) Structural development and petrofabrics of eclogite facies shear zones, Bergen Arcs, Western Norway: implications for deep crustal deformational processes. J Metamorph Geol 10:127–146
Boundy TM, Essene EJ, Hall CM, Austrheim H, Halliday AN (1996) Rapid exhumation of lower crust during continent-continent collision and late extension: Evidence from 40Ar/39Ar incremental heating of hornblendes and muscovites, Caledonian orogen, western Norway. Geol Soc Am Bull 108(9):1425–1437
Boundy TM, Hall CM, Li G, Essene EJ, Halliday AN (1997a) Fine-scale isotopic heterogeneities and fluids in the deep crust; a 40Ar/39Ar laser ablation and TEM study of muscovites from a granulite-eclogite transition zone. Earth Planet Sci Lett 148:223–242
Boundy TM, Mezger K, Essene EJ (1997b) Temporal and tectonic evolution of the granulite-eclogite association of the Bergen Arcs, western Norway. Lithos 39:159–178
Burton KW, O’Nions RK (1991) High-resolution garnet chronometry and the rates of metamorphic processes. Earth Planet Sci Lett 107:649–671
Carlson WD (1989) The significance of intergranular diffusion to the mechanisms and kinetics of porphyroblast crystallization. Contrib Mineral Petrol 103:1–24
Carlson WD (2002) Scales of disequilibrium and rates of equilibration during metamorphism. Am Mineral 87:185–204
Carlson WD (2006) Rates of Fe, Mg, Mn, and Ca diffusion in garnet. Am Mineral 91:1–11
Chakraborty S, Ganguly J (1990) Compositional zoning and cation diffusion in aluminosilicate garnets. In: Ganguly J (ed)) Diffusion, atomic ordering and mass transfer, vol 8. Advances in physical geochemistry. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 120–175
Chakraborty S, Ganguly J (1992) Cation diffusion in aluminosilicate garnets: experimental determination in spessartine-almandine diffusion couples, evaluation of effective binary diffusion coefficients, and applications. Contrib Mineral Petrol 111:74–86
Chakraborty S, Rubie DC (1996) Mg tracer diffusion in aluminosilicate garnets at 750–850°C, 1 atm. and 1300°C, 8.5 GPa. Contrib Mineral Petrol 122:406–414
Chernoff CB, Carlson WD (1997) Disequilibrium for Ca during growth of pelitic garnet. J Metamorph Geol 15:421–438
Chernoff CB, Carlson WD (1999) Trace element zoning as a record of chemical disequilibrium during garnet growth. Geology 27(6):555–558
Cohen AS, O’Nions RK, Siegenthaler R, Griffin WL (1988) Chronology of the pressure–temperature history recorded by a granulite terrain. Contrib Mineral Petrol 99:303–311
Crank J (1975) The mathematics of diffusion. Oxford University Press, Oxford, 414 pp
Cristensen JN, Rosenfeld J, DePaolo kDJ (1989) Rates of tectonometamorphic processes from rubidium and strontium isotopes in garnet. Science 244:1465–1469
Cygan RT, Lasaga AC (1985) Self-diffusion of magnesium in garnet at 750° to 950°C. Am J Sci 285:328–350
Dachs E, Proyer A (2002) Constraints on the duration of high-pressure metamorphism in the Tauern Window from diffusion modelling of discontinuous growth zones in eclogite garnet. J Metamorph Geol 20:769–780
Dale J, Holland TJB, Powell R (2000) Hornblende-garnet-plagioclase thermobarometry: a natural assemblage calibration of the thermodynamics of hornblende. Contrib Mineral Petrol 140:353–362
Dipple GM, Ferry JM (1992) Metasomatism and fluid flow in ductile fault zones. Contrib Mineral Petrol 112:149–164
Dodson M (1973) Closure temperature in cooling geochronological and petrological systems. Contrib Mineral Petrol 40:259–274
Dohmen R, Chakraborty S (2003) Mechanism and kinetics of element and isotopic exchange mediated by a fluid phase. Am Mineral 88:1251–1270
Droop GTR (1987) A general equation for estimating Fe3+ concentrations in ferromagnesian silicates and oxydes from microprobe analysis using stoechiometric criteria. Mineral Mag 51:431–435
Ellis DJ, Green DH (1979) An experimental study of the effect of Ca upon garnet-clinopyroxene Fe–Mg exchange equilibria. Contrib Mineral Petrol 71:13–22
Elphick SC, Ganguly J, Loomis TP (1985) Experimental determination of cation diffusivities in aluminosilicate garnets. Contrib Mineral Petrol 90:36–44
Elvevold S, Gilotti JA (2000) Pressure–temperature evolution of retrogressed kyanite eclogites, Weinschenk Island, North-East Greenland Caledonides. Lithos 53:127–147
Erambert M, Austrheim H (1993) The effect of fluid and deformation on zoning and inclusion patterns in poly-metamorphic garnets. Contrib Mineral Petrol 115:204–214
Florence FP, Spear FS (1995) Intergranular diffusion kinetics of Fe and Mg during retrograde metamorphism of a pelitic gneiss from the Adirondack Mountains. Earth Planet Sci Lett 134(3–4):329–340
Freer R, Edwards A (1999) An experimental study of Ca-(Fe,Mg) interdiffusion in silicate garnets. Contrib Mineral Petrol 134:370–379
Ganguly J, Tirone M (1999) Diffusion closure temperature and age of a mineral with arbitrary extent of diffusion: theoretical formulation and applications. Earth Planet Sci Lett 170:131–140
Ganguly J, Chakraborty S, Sharp TG, Rumble III D (1996) Constraint on the time scale of biotite-grade metamorphism during Acadian orogeny from a natural garnet–garnet diffusion couple. Am Mineral 81:1208–1216
Ganguly J, Cheng W, Chakraborty S (1998) Cation diffusion in aluminosilicate garnets: experimental determination in pyrope–almandine diffusion couples. Contrib Mineral Petrol 131:171–180
Getty S, Selverstone J, Wernicke BP, Jacobsen SB, Aliberti E, Lux DR (1993) Sm-dating of multiple garnet growth events in an arc-continent collision zone, northwestern US Cordillera. Contrib Mineral Petrol 115:45–57
Glodny J, Kühn A, Austrheim H (2002) Rb/Sr record of fluid-rock interaction in eclogites, Bergen Arcs, Norway. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 66(15A):A280
Hacker BR, Andersen TB, Root DB, Mehl L, Mattinson JM, Wooden JL (2003) Exhumation of high-pressure rocks beneath the Solund Basin, Western Gneiss Region of Norway. J Metamorph Geol 21:613–629
Hauzenberger CA (2005) Garnet zoning in high pressure granulite-facies metapelites, Mozambique belt, SE-Kenya: constraints on the cooling history. Eur J Mineral 17(1):43–55
Holland TJB, Powell R (1990) An enlarged and updated internal consistent dataset with incertainties and correlations: the system K2O − Na2O − CaO − MgO − MnO − FeO − Fe2O3 − Al2O3 − TiO2 − C − H2O − O2. J Metamorph Geol 8:89–124
Holland TJB, Powell R (1996a) Thermodynamics of order–disorder in minerals 1: symmetric formalism applied to minerals of fixed composition. Am Mineral 81:1413–1424
Holland TJB, Powell R (1996b) Thermodynamics of order–disorder in minerals 2: symmetric formalism applied to solid solutions. Am Mineral 81:1425–1437
Holland TJB, Powell R (1998) An internally-consistent thermodynamic data set for phases of petrological interest. J Metamorph Geol 16:309–343
Hollister LS (1966) Garnet zoning—an interpretation based on Rayleigh fractionation model. Science 154:1647–1651
Indares A (1995) Metamorphic interpretation of high pressure-temperature metapelites with preserved growth zoning in garnet, eastern Grenville Province, Canadian Shield. J Metamorph Geol 13:475–486
Jamieson RA, O’Beirne-Ryan AM (1991) Decompression-induced growth of albite porphyroblasts, Fleur de Lys Supergroup, western Newfoundland. J Metamorph Geol 9:433–439
Jamtveit B, Bucher-Nurminen K, Austrheim H (1990) Fluid controlled eclogitization of granulites in deep crustal shear zones, Bergen arcs, Western Norway. Contrib Mineral Petrol 104:184–193
Johnson JW, Oelkers EH, Helgeson HC (1992) SUPCRT92—a software package for calculating the standard molal thermodynamic properties of minerals, gases, aqueous species, and reactions from 1-bar to 5000-bar and 0°C to 1000°C. Comput Geosci 18(7):899–947
Kolderup CF, Kolderup NH (1940) Geology of the Bergen Arc System vol 20, vol 20. Bergens Museum Skrifter, 137 pp
Konrad-Schmolke M, Handy MR, Babist J, O’Brien PJ (2005) Thermodynamic modelling of diffusion-controlled granet growth. Contrib Mineral Petrol 149(2):181–195
Krogh Ravna EJ (2000a) Distribution of Fe2+ and Mg between coexisting garnet and hornblende in synthetic and natural systems: an empirical calibration of the garnet-hornblende Fe–Mg geothermometer. Lithos 53(3–4):265–277
Krogh Ravna EJ (2000b) The garnet-clinopyroxene Fe2+-Mg geothermometer: an updated calibration. J Metamorph Geol 18:211–219
Kühn A (2002) The influence of fluid on the granulite to eclogite and amphibolite facies transition: a study in the anorthositic rocks from the Lindås Nappe, Bergen Arcs, West Norway. Unpublished Ph.D. thesis, University of Oslo, 330 pp
Labrousse L, Jolivet L, Andersen TB, Agard P, Maluski H, Schärer U (2004) Pressure–temperature–time-deformation history of the exhumation of ultra-high-pressure rocks in the Western Gneiss Region, Norway. GSA Spec Pap 380:155–183
Lang HM, Gilotti JA (2001) Plagioclase replacement textures in partially eclogitised gabbros from the Sanddal mafic-ultramafic complex, Greenland Caledonides. J Metamorph Geol 19:497–517
Lasaga AC (1979) Multicomponent exchange and diffusion in silicates. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 43:455–469
Lasaga AC (1983) Geospeedometry: an extension of geothermometry. Kinetics and equilibrium in mineral reactions. Adv Phys Geochem 3:81–114
Loomis TP (1982) Numerical simulation of the disequilibrium growth of garnet in chlorite-bearing aluminous pelitic rocks. Can Mineral 20:411–423
Loomis TP, Ganguly J, Elphick SC (1985) Experimental determination of cation diffusivities in aluminosilicate garnets. Contrib Mineral Petrol 90:45–51
Marmo BA, Clarke GL, Powell R (2002) Fractionation of bulk rock composition due to porphyroblast growth: effects on eclogite facies mineral equilibria, Pam Peninsula, New Caledonia. J Metamorph Geol 20:151–165
Mattey D, Jackson DH, Harris BW, Kelly S (1994) Isotopic constraints on fluid infiltration from an eclogite facies shear zone, Holsnøy, Norway. J Metamorph Geol 12:311–325
Mezger K, Hanson GN, Bohlen SR (1989) U–Pb systematics of garnet: dating the growth of garnet in the Late Archean Pikwitonei granulite domain at Cauchon and Natawahunan, Manitoba, Canada. Contrib Mineral Petrol 101:136–148
O’Brien PJ (1997) Garnet zoning and reaction textures in overprinted eclogites, Bohemian Massif, European Variscides: a record of their thermal history during exhumation. Lithos 41:119–133
O’Brien PJ (1999) Asymmetric profiles in garnet from HP-HT granulite and implications for volume and grain-boundary diffusion. Mineral Mag 63(2):227–238
O’Brien PJ, Vrana S (1995) Eclogites with a short-lived granulite facies overprint in the Moldanubian Zone, Czech Republic: petrology, geochemistry and diffusion modelling of garnet zoning. Geol Rundsch 84:473–488
Perchuk AL (2002) Eclogites of the Bergen Arcs complex, Norway: petrology and mineral chronometry. Petrologiya 10(2):115–137
Perchuk A, Philippot P, Erdmer P, Fialin M (1999) Rates of thermal equilibration at the onset of subduction deduced from diffusion modeling of eclogitic garnets, Yukon-Tanana terrane, Canada. Geology 27(6):531–534
Powell R (1985) Regression diagnostics and robust regression in geothermometer/geobarometer calibration: the garnet–clinopyroxene geothermometer revisited. J Metamorph Geol 3:327–342
Powell R, Holland TJB (1988) An internally consistent dataset with uncertainties and correlations: 3. Applications to geobarometry, worked examples and a computer program. J Metamorph Geol 6:173–204
Ragnhildsveit J, Helliksen D (1997) Geologisk kart over Norge, begrunnskart Bergen, 1:250000. In: Norges Geologiske Undersøkelse
Raimbourg H (2005) Mécanismes d’éclogitization et conséquences pour l’exhumation des roches métamorphiques de haute pression. Unpublished Ph.D. thesis, University Pierre et Marie Curie, 407 pp
Raimbourg H, Jolivet L, Labrousse L, Leroy YM, Avigad D (2005a) Kinematics of syneclogite deformation in the Bergen Arcs, Norway: implications for exhumation mechanisms. In: Gapais D, Brun JP, Cobbold PR (eds) Deformation Mechanisms, Rheology and Tectonics: from Minerals to the Lithosphere, vol 243. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, pp 175–192
Raimbourg H, Jolivet L, Leroy Y, Labrousse L (2005b) Consequences of progressive eclogitization on crustal exhumation, a mechanical study. Geophys J Int (in press)
Roberts D, Gee DG (1985) An introduction to the structure of the Scandinavian Caledonides. In: Gee DG, Sturt BA (eds) The Caledonide Orogen: Scandinavia and related areas, vol 1. Wiley, Chichester, pp 55–68
Schmid R, Altenberger U, Oberhansli R (1998) Polyphase tectonometamorphic evolution of the northwestern Lindås Nappe on Holsnøy, Bergen Arcs, Caledonides, S-W Norway. Zbl Geol Paläont Teil I 1–2:1–18
Schwandt CS, Cygan RT, Westrich HR (1995) Mg self-diffusion in pyrope garnet. Am Mineral 80:483–490
Schwandt CS, Cygan RT, Westrich HR (1996) Ca self-diffusion in grossular garnet. Am Mineral 81:448–451
Spear FS, Daniel CG (2001) Diffusion control of garnet growth, Harpswell Neck, Maine, USA. J Metamorph Geol 19:179–195
Stüwe K (1997) Effective bulk composition changes due to cooling: a model predicting complexities in retrograde reaction textures. Contrib Mineral Petrol 129:43–52
Svensen H, Jamtveit B, Yardley B, Engvik AK, Austrheim H, Broman C (1999) Lead and bromine enrichment in eclogite-facies fluids: extreme fractionation during lower-crustal hydration. Geology 27(5):467–470
Svensen H, Jamtveit B, Banks DA, Austrheim H (2001) Halogen contents of eclogite facies fluid inclusions and minerals: Caledonides, western Norway. J Metamorph Geol 19:165–178
Terry MP, Robinson P, Hamilton M, Jercinovic MJ (2000) Monazite geochronology of UHP and HP metamorphism, deformation, and exhumation, Nordøyane; Western Gneiss Region, Norway. Am Mineral 85:1651–1664
Tinkham DK, Zuluaga CA, Stowell HH (2001) Metapelite phase equilibria modeling in MnNCKFMASH: the effect of variable 2O3 and MgO/(MgO+FeO) on mineral stability. Geol Mater Res 3(1):1–42
Vance D, O’Nions RK (1990) Isotopic chronometry of zoned garnets: growth kinetics and metamorphic histories. Earth Planet Sci Lett 97:227–240
Vance D, Strachan RA, Jones KA (1998) Extensional versus compressional settings for metamorphism: garnet chronometry and pressure–temperature–time histories in the Moine Supergroup, northwest Scotland. Geology 26(10):927–930
Waters DJ, Martin HN (1993) Geobarometry in phengite-bearing eclogites. Terra Abstr 5:410–411
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by J. Hoefs.
Appendices
Appendix: activity models
The following activity models were used to build the pseudosections:
-
White micas: Endmembers muscovite–paragonite–celadonite–ferroceladonite, non-ideal mixing with symmetric formalism interaction energies (Holland and Powell 1998).
-
Paragonite: Endmembers paragonite–margarite, mixing in the A site, no mixing in the tetrahedral site (Tinkham et al. 2001), from Thermocalc v2.7.
-
Amphibole: Endmembers tremolite–tschermakite–pargasite–ferroactinolite–glaucophane, non-ideal mixing with symmetric formalism interaction energies (adapted from Dale et al. 2000).
-
Clinopyroxene: P2/n omphacite is assumed, endmembers jadeite–diopside–hedenbergite–acmite, ideal mixing (Holland and Powell 1998).
-
Garnet: Endmembers grossular–almandin–pyrope–andradite, non-ideal mixing with symmetric formalism interaction energies (Holland and Powell 1998).
-
Orthopyroxene: Endmembers enstatite–ferrosilite–MgTschermak pyroxene (+ fictious ordered Fe–Mg pyroxene), non-ideal mixing with symmetric formalism interaction energies (Holland and Powell 1996a, b, 1998).
-
Epidotes: Endmembers clinozoisite–ferroepidote–epidote, non-ideal mixing with symmetric formalism interaction energies (Holland and Powell 1996a, b, 1998).
Analytical conditions and apparatus
-
Electronic microprobe: Two Cameca electron microprobes (CAMEBAX and SX50) available at Camparis (University Pierre et Marie Curie) using the wavelength dispersive technique with ZAF corrections. Operating conditions 15 kV and 10 nA.
-
BSE imaging: Annular Centaurus detector attached to a SEM Hitachi 2500 with a super Fevex-Sigma EDS system and a Quest Imaging software, available at Laboratoire de Geologie de l’Ecole Normale Supérieure de Paris. Operating conditions 20 kV and 0.5–5 nA.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Raimbourg, H., Goffé, B. & Jolivet, L. Garnet reequilibration and growth in the eclogite facies and geodynamical evolution near peak metamorphic conditions. Contrib Mineral Petrol 153, 1–28 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00410-006-0130-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00410-006-0130-3