Abstract
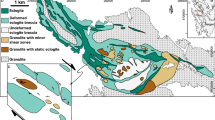
During the Caledonian orogeny large parts of the western margin of the Baltic shield were disrupted, sliced and stacked. Caledonian deformation resulted in a massif thickening of the continental crust. Mafic granulites and granulite facies meta-anorthosites build up a large portion of the Bergen Arcs terrane in southwestern Norway. The rocks represent typical Precambrian continental lower crust. These rocks experienced extensive eclogitization in response to stacking and crustal thickening during the Caledonian orogenic cycle. Eclogite formation resulted from shear deformation and associated infiltration of H2O-rich fluids (X H2O≥0.75). During an early stage, eclogite facies mineralogy formed in extension fractures (veins). The veins are probably related to hydraulic fracture systems which transported the inferred fluid phase. During the main stage, eclogitization occurred along shear zones ranging from centimeters to tens of meters in thickness. Eclogite forming reactions are shown to consume H2O, alkalies and to release SiO2. Much of the SiO2 released by the eclogitization process can be found in late quartz vein systems. The eclogitization took place at a temperature of about 700°C and a pressure between 18 and 21 kbar. Fluid infiltration was supported by a decrease in rock volume during reaction (ΔV solids<0). The negative volume change of reaction occurs despite that the process of eclogitization involves hydration reactions. The formation of eclogite from granulite produces approximately 15 KJ heat per 100 cm3 original granulite. Numerical modeling of the regional temperature effects associated with partial hydration of the lower crust suggests that these processes may not cause large perturbations on the geotherm. Both, transport of heat and matter by advection of the fluid phase is negligible on a regional scale.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahrens TJ, Schubert G (1975) Gabbro-eclogite reaction rate and its geophysical significance. Rev Geophys Space Phys 13:383–400
Austrheim H (1987) Eclogitization of lower crustal granulites by fluid migration through shear zones. Earth Planet Sci Lett 81:221–232
Austrheim H, Griffin WL (1985) Shear deformation and eclogite formation within granulite facies anorthosites of the Bergen Arcs, western Norway. Chem Geol 50:267–281
Austrheim H, Mørk MBE (1988) The lower continental crust of the Caledonian mountain chain: evidence from former deep crustal sections in western Norway. Norges Geol Unders Spec Publ 3:102–113
Berman RG (1988) Internally-consistent thermodynamic data for minerals in the system. Na2O−K2O−CaO−MgO−FeO−Fe2O3−Al2O3−SiO2−TiO2−H2O−CO2. J Petrol 29:445–522
Bickle MJ, McKenzie D (1987) The transport of heat and matter by fluids during metamorphism. Contrib Mineral Petrol 95:384–392
Brady JB (1988) The role of volatiles in the thermal history of metamorphic terranes. J Petrol 29:1187–1213
Carpenter MA (1980) Mechanisms of exsolution in sodic pyroxenes. Contrib Mineral Petrol 17:289–300
Cohen AS, O'Nions RL, Sigenthaler R, Griffin WL (1988) Chronology of the pressure-temperature history recorded by a granulite terrain. Contrib Mineral Petrol 98:303–311
Delany JM, Helgeson HC (1978) Calculation of the thermodynamic consequences of dehydration in subducting oceanic crust to 100 kb and >800°C. Am J Sci 278:638–686
Ellis DJ, Green DH (1979) An experimental study of effect of Ca upon garnet-clinopyroxene Fe−Mg exchange equilibria. Contrib Mineral Petrol 71:13–22
England PC, Thompson AB (1986) Some thermal and tectonic models for crustal melting in continental collision zones. In: Coward MP, Ries AC (eds) Collision tectonics. Geol Soc Spec Publ 19:83–94
Ferry JM (1983) Application of reaction progress variable in metamorphic petrology. J Petrol 24:343–376
Ferry Jm (1986) A monitor of fluid-rock interaction during metamorphic and hydrothermal event. In: Walther JV, Wood BJ (eds) Fluid-rock interactions during metamorphism. Springer, New York Berlin Heidelberg, pp 60–88
Fyfe WS, Price NJ, Thompson AB (1978) Fluids in the Earth's crust. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 383
Griffin WL (1972) Formation of eclogites and the coronas in anorthosites, Bergen Arcs Norway. Geol Soc Am Mem 135:37–63
Helgeson HC (1968) Evaluation of irreversible reactions in geochemical processes involving minerals and aqueous solutions — I. Thermodynamic relations. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 32:853–877
Helgeson HC, Delany JM, Nesbitt HW, Bird BK (1978) Summary and critique of the thermodynamic properties of rock-forming minerals. Am J Sci 278A:1–229
Hill RET, Boettcher AL (1970) Water in the Earth's mantle: Melting curves of basalt-water and basalt-water-carbon dioxide. Science 167:980–982
Holland TJB (1979a) Experimental determination of the reaction paragonite=jadeite+kyanite+H2O, and internally consistent thermodynamic data for part of the system Na2O−Al2O3−SiO2−H2O, with applications to eclogites and blueschists. Contrib Mineral Petrol 68:293–301
Holland TJB (1979b) High water acitivites in the generation of high pressure kyanite eclogites of the Tauern Window, Austria. J Geol 87:1–28
Holland TJB (1980) The reaction albite=jadeite+quartz determined experimentally in the range 600–1200°C. Am Mineral 65:129–134
Holland TJB (1983) The experimental determination of activities in disordered and short-range ordered jadeitic pyroxenes. Contrib Mineral Petrol 82:214–220
Hollister LS, Crawford ML (1986) Melt-enhanced deformation: a major tectonic process. Geology 14:558–561
Huang W-L, Wyllie PJ (1986) Phase relationships of gabbro-tonalite-granite-water at 15 kbar with applications to differentation and anatexis. Am Mineral 71:301–316
Kerrick DM, Jacobs GK (1981) A modified Redlich-Kwong equation for H2O, CO2 and H2O−CO2 mixtures at elevated pressures and temperatures. Am J Sci 281:735–767
Kolderup CF (1903) Die Labradorfelsen des westlichen Norwegens, II. Die Labradorfelsen und die mit denselben verwandten Gesteine in dem Bergensgebiete. Bergen Mus Årbog 12:1–129
Koons PO, Rubie DC, Frueh-Green G (1987) The effects of disequilibrium and deformation on the mineralogical evolution of quartz-diorite during metamorphism in the eclogite facies. J Petrol 28:679–700
Kretz R (1983) Symbols for rock-forming minerals. Am Mineral 68:277–279
Meyer J (1983a) Mineralogie und Petrologie des Allalingabbros. Doctoral dissertation, University of Basel, pp 329
Meyer J (1983b) The development of the high-pressure metamorphism in the Allalin metagabbro (Switzerland). Terra Cognita 3:187 (abstr)
Perkins EH, Brown TH, Berman RG (1986) PT-system, TX-system, PX-system: three programs which calculate Pressure-Temperature-Composition phase diagrams. Comp Geosci 12:749–755
Rumble DIII, Ferry JM, Hoering TC, Boucot AJ (1982) Fluid flow during metamorphism at the Beaver Brook fossil locality, New Hampshire. Am J Sci 282:886–919
Walther JV, Orville PM (1982) Volatile production and transport in regional metamorphism. Contrib Mineral Petrol 79:252–257
Wayte GJ, Worden RH, Rubie DC, Droop GTR (1989) A TEM study of disequilibrium plagioclase breakdown at high pressure: the role of infiltrating fluid. Contrib Mineral Petrol 101:426–437
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jamtveit, B., Bucher-Nurminen, K. & Austrheim, H. Fluid controlled eclogitization of granulites in deep crustal shear zones, Bergen arcs, Western Norway. Contr. Mineral. and Petrol. 104, 184–193 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00306442
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00306442