Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of the study is to identify potential key genes and pathways, using bioinformatics, underlying the potentially common molecular mechanisms between endometriosis (EMS) and ovarian cancer (OC).
Methods
Two datasets were collected from the Gene Expression Omnibus database, and the limma package identified common differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in the EMS and OC groups compared to controls. Gene Ontology, Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes, gene interaction network, and module analyses identified the enriched pathways associated with DEGs. A protein–protein interaction (PPI) network was then constructed, and the CytoHubba plugin of Cytoscape was used to calculate the degree of connectivity for proteins in the PPI network.
Results
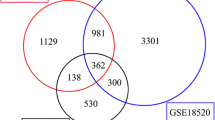
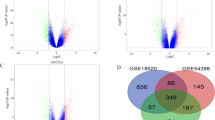
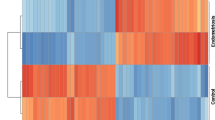
A total of 571 overlapping DEGs were identified between EMS and OC (vs. controls). Enriched DEGs were associated with 36 gene ontology terms and 7 Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathways, which were mainly associated with deactivation of the p53 signaling pathway. The Kaplan–Meier plotter platform confirmed the expression of the identified hub genes, and survival analysis suggested that CCNB1, CCNB2, BUB1B, CCNA2, KIF2C, and TOP2A are associated with decreased survival and disease-free survival rates of OC.
Conclusion
The key pathways identified herein elucidate the possible mechanism by which EMS evolves into OC; further, the identified hub genes may serve as potential biomarkers to predict OC occurrence and prognosis.










Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the current study are available in the [GEO] repository, through the following urls: (1) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSE7305; (2) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSE14407.
Code availability
The code used in this study is available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Reid BM, Permuth JB, Sellers TA (2017) Epidemiology of ovarian cancer: a review. Cancer Biol Med 14:9–32. https://doi.org/10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2016.0084
Králíčková M, Vetvicka V (2014) Endometriosis and ovarian cancer. World J Clin Oncol 5:800–805. https://doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v5.i5.800
Audebert A, Petousis S, Margioula-Siarkou C, Ravanos K, Prapas N, Prapas Y (2018) Anatomic distribution of endometriosis: a reappraisal based on series of 1101 patients. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 230:36–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejogrb.2018.09.001
Hunn J, Rodriguez GC (2012) Ovarian cancer: etiology, risk factors, and epidemiology. Clin Obstet Gynecol 55:3–23. https://doi.org/10.1097/grf.0b013e31824b4611
Dzatic-Smiljkovic O, Vasiljevic M, Djukic M, Vugdelic R, Vugdelic J (2011) Frequency of ovarian endometriosis in epithelial ovarian cancer patients. Clin Exp Obstet Gynecol 38:394–398
Wang C, Liang Z, Liu X, Zhang Q, Li S (2016) The association between endometriosis, tubal ligation, hysterectomy and epithelial ovarian cancer: meta-analyses. Int J Environ Res Public Health 13:1138. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph13111138
Brilhante AV, Augusto KL, Portela MC, Sucupira LC, Oliveira LA, Pouchaim AJ, Nόbrega LRM, de Magalhães TF, Sobreira LRP (2017) Endometriosis and ovarian cancer: an integrative review (endometriosis and ovarian cancer). Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 18:11–16. https://doi.org/10.22034/APJCP.2017.18.1.11
Ruderman R, Pavone ME (2017) Ovarian cancer in endometriosis: an update on the clinical and molecular aspects. Minerva Ginecol 69:286–294. https://doi.org/10.23736/S0026-4784.17.04042-4
Barrett T, Wilhite SE, Ledoux P, Evangelista C, Kim IF, Tomashevsky M et al (2013) NCBI GEO: archive for functional genomics data sets—update. Nucleic Acids Res 41:D991–D995. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gks1193
Hever A, Roth RB, Hevezi P, Marin ME, Acosta JA, Acosta H et al (2007) Human endometriosis is associated with plasma cells and overexpression of B lymphocyte stimulator. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:12451–12456. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0703451104
Bowen NJ, Walker LD, Matyunina LV, Logani S, Totten KA, Benigno BB, McDonald JF (2009) Gene expression profiling supports the hypothesis that human ovarian surface epithelia are multipotent and capable of serving as ovarian cancer initiating cells. BMC Med Genomics 2:71. https://doi.org/10.1186/1755-8794-2-71
Robinson MD, McCarthy DJ, Smyth GK (2010) edgeR: a Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics 26:139–140. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btp616
Huang DW, Sherman BT, Tan Q, Kir J, Liu D, Bryant D et al (2007) DAVID Bioinformatics Resources: expanded annotation database and novel algorithms to better extract biology from large gene lists. Nucleic Acids Res 35:W169–W175. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkm415
Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein D, Butler H, Cherry JM et al (2000) Gene ontology: tool for the unification of biology. The Gene Ontology Consortium. Nat Genet 25:25–29. https://doi.org/10.1038/75556
Alonso-Calvo R, Maojo V, Billhardt H, Martin-Sanchez F, Garcia-Remesal M, Perez-Rey D (2007) An agent- and ontology-based system for integrating public gene, protein, and disease databases. J Biomed Inform 40:17–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbi.2006.02.014
Yao T (2002) Bioinformatics for the genomic sciences and towards systems biology. Japanese activities in the post-genome era. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 80:23–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0079-6107(02)00011-1
Luo W, Pant G, Bhavnasi YK, Blanchard SG Jr, Brouwer C (2017) Pathview Web: user friendly pathway visualization and data integration. Nucleic Acids Res 45:W501–W508. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkx372
Doncheva NT, Morris JH, Gorodkin J, Jensen LJ (2019) Cytoscape StringApp: network analysis and visualization of proteomics data. J Proteome Res 18:623–632. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jproteome.8b00702
Chin CH, Chen SH, Wu HH, Ho CW, Ko MT, Lin CY (2014) cytoHubba: identifying hub objects and sub-networks from complex interactome. BMC Syst Biol 8(Suppl 4):S11. https://doi.org/10.1186/1752-0509-8-s4-s11
Hess AS, Hess JR (2020) Kaplan-Meier survival curves. Transfusion 60:670–672. https://doi.org/10.1111/trf.15725
Lagana AS, Garzon S, Gotte M, Vigano P, Franchi M, Ghezzi F, Martin DC (2019) The pathogenesis of endometriosis: molecular and cell biology insights. Int J Mol Sci 20:5615. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20225615
Brilhante AV, Augusto KL, Portela MC, Sucupira LC, Oliveira LA, Pouchaim AJ, Nobrega LR, Magalhaes TF, Sobreira LR (2017) Endometriosis and ovarian cancer: an integrative review (Endometriosis and Ovarian Cancer). Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 18:11–16. https://doi.org/10.22034/apjcp.2017.18.1.11
Králíčková M, Laganà AS, Ghezzi F, Vetvicka V (2020) Endometriosis and risk of ovarian cancer: what do we know? Arch Gynecol Obstet 301:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00404-019-05358-8
Saavalainen L, Lassus H, But A, Tiitinen A, Harkki P, Gissler M, Pukkala E, Heikinheimo O (2018) Risk of gynecologic cancer according to the type of endometriosis. Obstet Gynecol 131:1095–1102. https://doi.org/10.1097/AOG.0000000000002624
Dochez V, Caillon H, Vaucel E, Dimet J, Winer N, Ducarme G (2019) Biomarkers and algorithms for diagnosis of ovarian cancer: CA125, HE4, RMI and ROMA, a review. J Ovarian Res 12:28. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13048-019-0503-7
Carter JH, Deddens JA, Mueller G, Lewis TG, Dooley MK, Robillard MC, Frydl M, Duvall L, Pemberton JO, Douglass LE (2018) Transcription factors WT1 and p53 combined: a prognostic biomarker in ovarian cancer. Br J Cancer 119:462–470. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41416-018-0191-x
Hodgson DR, Dougherty BA, Lai Z, Fielding A, Grinsted L, Spencer S et al (2018) Candidate biomarkers of PARP inhibitor sensitivity in ovarian cancer beyond the BRCA genes. Br J Cancer 119:1401–1409. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41416-018-0274-8
Kawashima N, Yoshida H, Miwa M, Fujiwara K (2019) MLH1 is a prognostic biomarker for serous ovarian cancer treated with platinum- and taxane-based chemotherapy. Anticancer Res 39:5505–5513. https://doi.org/10.21873/anticanres.13743
Greene AD, Lang SA, Kendziorski JA, Sroga-Rios JM, Herzog TJ, Burns KA (2016) Endometriosis: where are we and where are we going? Reproduction 152:R63–R78. https://doi.org/10.1530/REP-16-0052
Wenzel ES, Singh ATK (2018) Cell-cycle checkpoints and aneuploidy on the path to cancer. In Vivo 32:1–5. https://doi.org/10.21873/invivo.11197
Potapova TA, Zhu J, Li R (2013) Aneuploidy and chromosomal instability: a vicious cycle driving cellular evolution and cancer genome chaos. Cancer Metastasis Rev 32:377–389. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-013-9436-6
Lingle WL, Lukasiewicz K, Salisbury JL (2005) Deregulation of the centrosome cycle and the origin of chromosomal instability in cancer. Adv Exp Med Biol 570:393–421. https://doi.org/10.1007/1-4020-3764-3_14
Bennett DC, Cazet A, Charest J, Contessa JN (2018) MPDU1 regulates CEACAM1 and cell adhesion in vitro and in vivo. Glycoconj J 35:265–274. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10719-018-9819-6
Campos A, Salomon C, Bustos R, Diaz J, Martinez S, Silva V et al (2018) Caveolin-1-containing extracellular vesicles transport adhesion proteins and promote malignancy in breast cancer cell lines. Nanomedicine (Lond) 13:2597–2609. https://doi.org/10.2217/nnm-2018-0094
Galvagni F, Nardi F, Maida M, Bernardini G, Vannuccini S, Petraglia F, Santucci A, Orlandini M (2016) CD93 and dystroglycan cooperation in human endothelial cell adhesion and migration adhesion and migration. Oncotarget 7:10090–10103. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.7136
Daigo K, Takano A, Thang PM, Yoshitake Y, Shinohara M, Tohnai I, Murakami Y, Maegawa J, Daigo Y (2018) Characterization of KIF11 as a novel prognostic biomarker and therapeutic target for oral cancer. Int J Oncol 52:155–165. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2017.4181
Pérez-Fidalgo JA, Gambardella V, Pineda B, Burgues O, Piñero O, Cervantes A (2020) Aurora kinases in ovarian cancer. ESMO Open 5:e000718. https://doi.org/10.1136/esmoopen-2020-000718
Chang WH, Forde D, Lai AG (2019) Dual prognostic role of 2-oxoglutarate-dependent oxygenases in ten cancer types: implications for cell cycle regulation and cell adhesion maintenance. Cancer Commun (Lond) 39:23. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40880-019-0369-5
Capasso A, Pitts TM, Klauck PJ, Bagby SM, Westbrook L, Kaplan J et al (2018) Dual compartmental targeting of cell cycle and angiogenic kinases in colorectal cancer models. Anticancer Drugs 29:827–838. https://doi.org/10.1097/CAD.0000000000000673
Mladenov E, Magin S, Soni A, Iliakis G (2016) DNA double-strand-break repair in higher eukaryotes and its role in genomic instability and cancer: cell cycle and proliferation-dependent regulation. Semin Cancer Biol 37–38:51–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcancer.2016.03.003
Icard P, Fournel L, Wu Z, Alifano M, Lincet H (2019) Interconnection between metabolism and cell cycle in cancer. Trends Biochem Sci 44:490–501. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibs.2018.12.007
Grunewald T, Ledermann JA (2017) Targeted therapies for ovarian cancer. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol 41:139–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpobgyn.2016.12.001
Stadler M, Scherzer M, Walter S, Holzner S, Pudelko K, Riedl A et al (2018) Exclusion from spheroid formation identifies loss of essential cell-cell adhesion molecules in colon cancer cells. Sci Rep 8:1151. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-19384-0
Labernadie A, Kato T, Brugues A, Serra-Picamal X, Derzsi S, Arwert E et al (2017) A mechanically active heterotypic E-cadherin/N-cadherin adhesion enables fibroblasts to drive cancer cell invasion. Nat Cell Biol 19:224–237. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb3478
Harjunpaa H, llort Asens Guenther Fagerholm MCSC (2019) Cell adhesion molecules and their roles and regulation in the immune and tumor microenvironment. Front Immunol 10:1078. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.01078
Guo S (2020) Cancer-associated mutations in endometriosis: shedding light on the pathogenesis and pathophysiology. Hum Reprod Update 26:423–449. https://doi.org/10.1093/humupd/dmz047
Macedo GS, Vieira IA, Vianna FSL, Alemar B, Giacomazzi J, Brandalize APC et al (2018) p53 signaling pathway polymorphisms, cancer risk and tumor phenotype in TP53 R337H mutation carriers. Fam Cancer 17:269–274. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10689-017-0028-4
Liu Y, Li L, Liu Y, Geng P, Li G, Yang Y, Song H (2018) RECK inhibits cervical cancer cell migration and invasion by promoting p53 signaling pathway. J Cell Biochem 119:3058–3066. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.26441
Duffy MJ, Synnott NC, Crown J (2018) Mutant p53 in breast cancer: potential as a therapeutic target and biomarker. Breast Cancer Res Treat 170:213–219. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-018-4753-7
Yan C, Yuan J, Xu J, Zhang G, Li X, Zhang B, Hu T, Huang X, Mao Y, Song G (2019) Ubiquitin-specific peptidase 39 regulates the process of proliferation and migration of human ovarian cancer via p53/p21 pathway and EMT. Med Oncol 36:95. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-019-1308-7
Zheng MJ, Li X, Hu YX, Dong H, Gou R, Nie X, Liu Q, Ying-Ying H, Liu J-J, Lin B (2019) Identification of molecular marker associated with ovarian cancer prognosis using bioinformatics analysis and experiments. J Cell Physiol 234:11023–11036. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.27926
Tocci P, Cianfrocca R, Di Castro V, Rosano L, Sacconi A, Donzelli S et al (2019) β-arrestin1/YAP/mutant p53 complexes orchestrate the endothelin A receptor signaling in high-grade serous ovarian cancer. Nat Commun 10:3196. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-11045-8
Zhang YB, Jiang Y, Wang J, Ma J, Han S (2019) Evaluation of core serous epithelial ovarian cancer genes as potential prognostic markers and indicators of the underlying molecular mechanisms using an integrated bioinformatics analysis. Oncol Lett 18:5508–5522. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2019.10884
Lee J, Minasian L, Kohn EC (2019) New strategies in ovarian cancer treatment 125(Suppl 24):4623–4629. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.32544
Feng H, Gu ZY, Li Q, Liu QH, Yang XY, Zhang JJ (2019) Identification of significant genes with poor prognosis in ovarian cancer via bioinformatical analysis. J Ovarian Res 12:35. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13048-019-0508-2
Legal T, Hayward D, Gluszek-Kustusz A, Blackburn EA, Spanos C, Rappsilber J, Gruneberg U, Welburn JPI (2020) The C-terminal helix of BubR1 is essential for CENP-E-dependent chromosome alignment. J Cell Sci 133:jcs246025. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.246025
Simmons AJ, Park R, Sterling NA, Jang MH, van Deursen JMA, Yen TJ, Cho SH, Kim S (2019) Nearly complete deletion of BubR1 causes microcephaly through shortened mitosis and massive cell death. Hum Mol Genet 28:1822–1836. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddz022
Zhang L, Sun L, Zhang B, Chen L (2019) Identification of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) relevant to prognosis of ovarian cancer by use of integrated bioinformatics analysis and validation by immunohistochemistry assay. Med Sci Monit 25:9902–9912. https://doi.org/10.12659/msm.921661
Sun Q, Zhao H, Zhang C, Hu T, Wu J, Lin X, Luo D, Wang C, Meng L, Xi L, Li K, Hu J, Ma D, Zhu T (2017) Gene co-expression network reveals shared modules predictive of stage and grade in serous ovarian cancers. Oncotarget 8:42983–42996. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.17785
Yang D, He Y, Wu B, Deng Y, Wang N, Li M, Liu Y (2020) Integrated bioinformatics analysis for the screening of hub genes and therapeutic drugs in ovarian cancer. J Ovarian Res 13:10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13048-020-0613-2
Zhao Y, Pi J, Liu L, Yan W, Ma S, Hong L (2021) Identification of the hub genes associated with the prognosis of ovarian cancer patients via integrated bioinformatics analysis and experimental validation. Cancer Manag Res 13:707–721. https://doi.org/10.2147/cmar.s282529
Lee D, Hokinson D, Park S, Elvira R, Kusuma F, Lee JM, Yun M, Lee SG, Han J (2019) ER stress induces cell cycle arrest at the G2/M phase through eIF2alpha phosphorylation and GADD45alpha. Int J Mol Sci 20:6309. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20246309
Batool A, Liu H, Liu Y, Chen S (2020) CD83, a novel MAPK signaling pathway interactor, determines ovarian cancer cell fate. Cancers (Basel) 128:2269. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12082269
Wang L, Chen T, Li X, Yan W, Lou Y, Liu Z, Chen H, Cui Z (2019) USP39 promotes ovarian cancer malignant phenotypes and carboplatin chemoresistance. Int J Oncol 55:277–288. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2019.4818
Yu C, Chen F, Jiang J, Zhang H, Zhou M (2019) Screening key genes and signaling pathways in colorectal cancer by integrated bioinformatics analysis. Mol Med Rep 20:1259–1269. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2019.10336
Deng JL, Xu YH, Wang G (2019) Identification of potential crucial genes and key pathways in breast cancer using bioinformatic analysis. Front Genet 10:695. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2019.00695
Wu X, Peng L, Zhang Y, Chen S, Lei Q, Li G, Zhang C (2019) Identification of key genes and pathways in cervical cancer by bioinformatics analysis. Int J Med Sci 16:800–812. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijms.34172
You F, Gao C (2019) Topoisomerase inhibitors and targeted delivery in cancer therapy. Curr Top Med Chem 19:713–729. https://doi.org/10.2174/1568026619666190401112948
Gao Y, Zhao H, Ren M, Chen Q, Li J, Li Z, Yin C, Yue W (2020) TOP2A promotes tumorigenesis of high-grade serous ovarian cancer by regulating the TGF-β/Smad pathway. J Cancer 11:4181–4192. https://doi.org/10.7150/jca.42736
Ghisoni E, Maggiorotto F, Borella F et al (2019) TOP2A as marker of response to pegylated lyposomal doxorubicin (PLD) in epithelial ovarian cancers. J Ovarian Res 12:17. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13048-019-0492-6
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LN: project development, data collection, data analysis, manuscript writing, writing—original draft preparation, and writing—review and editing. CC, YC and JY: manuscript editing, formal analysis, and investigation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ni, L., Chen, Y., Yang, J. et al. Bioinformatic analysis of key pathways and genes shared between endometriosis and ovarian cancer. Arch Gynecol Obstet 305, 1329–1342 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00404-021-06285-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00404-021-06285-3