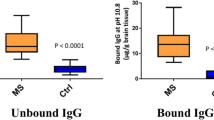
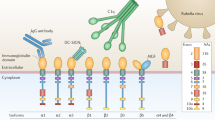
Abstract
Multiple sclerosis (MS) and neuromyelitis optica (NMO) are the most prevalent neuroinflammatory diseases of the central nervous system (CNS). The immunological cascade of these disorders is complex, and the exact spatial and temporal role of different immune cells is not fully understood. Although MS has been considered for many years to be primarily T cell driven, it is well established that B cells and the humoral immune response play an important role in its pathogenesis. This has long been evident from laboratory findings that include the presence of oligoclonal bands in the CSF. In NMO, the importance of the humoral immune system appears even more obvious as evidenced by pathogenic antibodies against aquaporin 4 (AQP4). Besides their capacity to mature into antibody-producing plasma cells, B cells are potent antigen-presenting cells to T lymphocytes and they can provide soluble factors for cell activation and differentiation to other immune-competent cells. In MS and NMO, there are substantial data from clinical trials that B cell depletion with CD20-directed agents is effective and relatively safe. Plasma cells, which produce antibodies against molecular targets expressed by the host, but which also provide humoral immune responses against pathogens, are not targeted by anti-CD20 therapies. Therefore, the depletion of CD19-expressing cells would offer potential advantages with regard to efficacy, but potentially higher risks with regard to infectious complications. This review will outline the rationale for CD19 as a molecular target in CNS autoimmunity. The current stage of drug development is illustrated. Potential safety concerns will be discussed.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asavapanumas N, Ratelade J, Papadopoulos MC, Bennett JL, Levin MH, Verkman AS (2014) Experimental mouse model of optic neuritis with inflammatory demyelination produced by passive transfer of neuromyelitis optica-immunoglobulin G. J Neuroinflamm 11:16. doi:10.1186/1742-2094-11-16
Ascherio A, Munger KL (2010) 99th Dahlem conference on infection, inflammation and chronic inflammatory disorders: Epstein-Barr virus and multiple sclerosis: epidemiological evidence. Clin Exp Immunol 160(1):120–124. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2249.2010.04121.x
Bennett JL, Lam C, Kalluri SR, Saikali P, Bautista K, Dupree C, Glogowska M, Case D, Antel JP, Owens GP, Gilden D, Nessler S, Stadelmann C, Hemmer B (2009) Intrathecal pathogenic anti-aquaporin-4 antibodies in early neuromyelitis optica. Ann Neurol 66(5):617–629. doi:10.1002/ana.21802
Blair PA, Norena LY, Flores-Borja F, Rawlings DJ, Isenberg DA, Ehrenstein MR, Mauri C (2010) CD19(+)CD24(hi)CD38(hi) B cells exhibit regulatory capacity in healthy individuals but are functionally impaired in systemic Lupus Erythematosus patients. Immunity 32(1):129–140. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2009.11.009
Bradbury LE, Kansas GS, Levy S, Evans RL, Tedder TF (1992) The CD19/CD21 signal transducing complex of human B lymphocytes includes the target of antiproliferative antibody-1 and Leu-13 molecules. J Immunol 149(9):2841–2850
Bradl M, Misu T, Takahashi T, Watanabe M, Mader S, Reindl M, Adzemovic M, Bauer J, Berger T, Fujihara K, Itoyama Y, Lassmann H (2009) Neuromyelitis optica: pathogenicity of patient immunoglobulin in vivo. Ann Neurol 66(5):630–643. doi:10.1002/ana.21837
Cambridge G, Leandro MJ, Edwards JC, Ehrenstein MR, Salden M, Bodman-Smith M, Webster AD (2003) Serologic changes following B lymphocyte depletion therapy for rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 48(8):2146–2154. doi:10.1002/art.11181
Carter L, Knappertz V, Wang Y, Groves C, Ward E, Gallagher S, Yusuf I, Karnell J, Ettinger R, Rajan B, Herbst R (2012) MEDI-551, a novel antibody that depletes CD19 + B cells: rationale for clinical development in multiple sclerosis. ECTRIMS, Lyon
Cepok S, Rosche B, Grummel V, Vogel F, Zhou D, Sayn J, Sommer N, Hartung HP, Hemmer B (2005) Short-lived plasma blasts are the main B cell effector subset during the course of multiple sclerosis. Brain 128(Pt 7):1667–1676. doi:10.1093/brain/awh486
Cheson BD, Pfistner B, Juweid ME, Gascoyne RD, Specht L, Horning SJ, Coiffier B, Fisher RI, Hagenbeek A, Zucca E, Rosen ST, Stroobants S, Lister TA, Hoppe RT, Dreyling M, Tobinai K, Vose JM, Connors JM, Federico M, Diehl V, International Harmonization Project on L (2007) Revised response criteria for malignant lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 25(5):579–586. doi:10.1200/JCO.2006.09.2403
Chihara N, Aranami T, Sato W, Miyazaki Y, Miyake S, Okamoto T, Ogawa M, Toda T, Yamamura T (2011) Interleukin 6 signaling promotes anti-aquaporin 4 autoantibody production from plasmablasts in neuromyelitis optica. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108(9):3701–3706. doi:10.1073/pnas.1017385108
Choe J, Choi YS (1998) IL-10 interrupts memory B cell expansion in the germinal center by inducing differentiation into plasma cells. Eur J Immunol 28(2):508–515. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1521-4141(199802)28:02508::AID-IMMU5083.0.CO;2-I
Connolly DL, Shanahan CM, Weissberg PL (1998) The aquaporins. A family of water channel proteins. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 30(2):169–172
Cooper LJ, Al-Kadhimi Z, DiGiusto D, Kalos M, Colcher D, Raubitschek A, Forman SJ, Jensen MC (2004) Development and application of CD19-specific T cells for adoptive immunotherapy of B cell malignancies. Blood Cells Mol Dis 33(1):83–89. doi:10.1016/j.bcmd.2004.03.003
Cree BA, Goodin DS, Hauser SL (2002) Neuromyelitis optica. Semin Neurol 22(2):105–122. doi:10.1055/s-2002-36534
Cree BA, Lamb S, Morgan K, Chen A, Waubant E, Genain C (2005) An open label study of the effects of rituximab in neuromyelitis optica. Neurology 64(7):1270–1272. doi:10.1212/01.WNL.0000159399.81861.D5
Cross AH, Klein RS, Piccio L (2012) Rituximab combination therapy in relapsing multiple sclerosis. Ther Adv Neurol Disord 5(6):311–319. doi:10.1177/1756285612461165
Durie BG, Harousseau JL, Miguel JS, Blade J, Barlogie B, Anderson K, Gertz M, Dimopoulos M, Westin J, Sonneveld P, Ludwig H, Gahrton G, Beksac M, Crowley J, Belch A, Boccadaro M, Cavo M, Turesson I, Joshua D, Vesole D, Kyle R, Tricot G, Attal M, Merlini G, Powles R, Richardson P, Shimizu K, Tosi P, Morgan G, Rajkumar SV, International Myeloma Working G (2006) International uniform response criteria for multiple myeloma. Leukemia 20(9):1467–1473. doi:10.1038/sj.leu.2404284
Engel P, Zhou LJ, Ord DC, Sato S, Koller B, Tedder TF (1995) Abnormal B lymphocyte development, activation, and differentiation in mice that lack or overexpress the CD19 signal transduction molecule. Immunity 3(1):39–50
Fagraeus A (1948) The plasma cellular reaction and its relation to the formation of antibodies in vitro. J Immunol 58(1):1–13
Forero-Torres A, Hamadani M, Sonet A, Verhoef G, Fanale M, Bello C, Goswami T, Huang W, Yao Z, Ibrahim R, Herbst R, Cheson BD (2012) Phase 1/2 study of MEDI-551, a humanized monoclonal antibody targeting CD19, in subjects with relapsed or refractory advanced B-cell malignancies. In: ASCO annual meeting, Chicago
Furman CS, Gorelick-Feldman DA, Davidson KG, Yasumura T, Neely JD, Agre P, Rash JE (2003) Aquaporin-4 square array assembly: opposing actions of M1 and M23 isoforms. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100(23):13609–13614. doi:10.1073/pnas.2235843100
Greenberg BM, Graves D, Remington G, Hardeman P, Mann M, Karandikar N, Stuve O, Monson N, Frohman E (2012) Rituximab dosing and monitoring strategies in neuromyelitis optica patients: creating strategies for therapeutic success. Multiple Scler 18(7):1022–1026. doi:10.1177/1352458511432896
Haas KM, Tedder TF (2005) Role of the CD19 and CD21/35 receptor complex in innate immunity, host defense and autoimmunity. Adv Exp Med Biol 560:125–139. doi:10.1007/0-387-24180-9_16
Hallek M, Cheson BD, Catovsky D, Caligaris-Cappio F, Dighiero G, Dohner H, Hillmen P, Keating MJ, Montserrat E, Rai KR, Kipps TJ, International Workshop on Chronic Lymphocytic L (2008) Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia: a report from the international workshop on chronic lymphocytic leukemia updating the National Cancer Institute-Working Group 1996 guidelines. Blood 111(12):5446–5456. doi:10.1182/blood-2007-06-093906
Harris DP, Goodrich S, Gerth AJ, Peng SL, Lund FE (2005) Regulation of IFN-gamma production by B effector 1 cells: essential roles for T-bet and the IFN-gamma receptor. J Immunol 174(11):6781–6790
Harris DP, Gooelectrophoretic study of the protein components in cerebrospinal fluid and their drich S, Mohrs K, Mohrs M, Lund FE (2005) Cutting edge: the development of IL-4-producing B cells (B effector 2 cells) is controlled by IL-4, IL-4 receptor alpha, and Th2 cells. J Immunol 175(11):7103–7107
Hartung HP, Kieseier BC (2010) Atacicept: targeting B cells in multiple sclerosis. Ther Adv Neurol Disord 3(4):205–216. doi:10.1177/1756285610371146
Hauser SL, Waubant E, Arnold DL, Vollmer T, Antel J, Fox RJ, Bar-Or A, Panzara M, Sarkar N, Agarwal S, Langer-Gould A, Smith CH, Group HT (2008) B-cell depletion with rituximab in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. N Engl J Med 358(7):676–688. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa0706383
Herbst R, Wang Y, Gallagher S, Mittereder N, Kuta E, Damschroder M, Woods R, Rowe DC, Cheng L, Cook K, Evans K, Sims GP, Pfarr DS, Bowen MA, Dall’Acqua W, Shlomchik M, Tedder TF, Kiener P, Jallal B, Wu H, Coyle AJ (2010) B-cell depletion in vitro and in vivo with an afucosylated anti-CD19 antibody. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 335(1):213–222. doi:10.1124/jpet.110.168062
http://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT01585766N. Accessed 18 June 2014
http://www.fda.gov/Drugs/DrugSafety/PostmarketDrugSafetyInformationforPatientsandProviders/ucm126519.htm. Accessed 18 June 2014
http://www.fda.gov/Drugs/DrugSafety/ucm366406.htm. Accessed 18 June 2014
http://www.xencor.com/2010/12/xencor-and-morphosys-initiate-phase-1-study-of-anti-cd19-antibody-in-chronic-lymphocytic-leukemia/. Accessed 18 June 2014
Jacob A, Weinshenker BG, Violich I, McLinskey N, Krupp L, Fox RJ, Wingerchuk DM, Boggild M, Constantinescu CS, Miller A, De Angelis T, Matiello M, Cree BA (2008) Treatment of neuromyelitis optica with rituximab: retrospective analysis of 25 patients. Arch Neurol 65(11):1443–1448. doi:10.1001/archneur.65.11.noc80069
Jarius S, Franciotta D, Bergamaschi R, Wright H, Littleton E, Palace J, Hohlfeld R, Vincent A (2007) NMO-IgG in the diagnosis of neuromyelitis optica. Neurology 68(13):1076–1077. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000256822.01222.bd
Jarius S, Paul F, Franciotta D, Ruprecht K, Ringelstein M, Bergamaschi R, Rommer P, Kleiter I, Stich O, Reuss R, Rauer S, Zettl UK, Wandinger KP, Melms A, Aktas O, Kristoferitsch W, Wildemann B (2011) Cerebrospinal fluid findings in aquaporin-4 antibody positive neuromyelitis optica: results from 211 lumbar punctures. J Neurol Sci 306(1–2):82–90. doi:10.1016/j.jns.2011.03.038
Jarius S, Ruprecht K, Wildemann B, Kuempfel T, Ringelstein M, Geis C, Kleiter I, Kleinschnitz C, Berthele A, Brettschneider J, Hellwig K, Hemmer B, Linker RA, Lauda F, Mayer CA, Tumani H, Melms A, Trebst C, Stangel M, Marziniak M, Hoffmann F, Schippling S, Faiss JH, Neuhaus O, Ettrich B, Zentner C, Guthke K, Hofstadt-van Oy U, Reuss R, Pellkofer H, Ziemann U, Kern P, Wandinger KP, Bergh FT, Boettcher T, Langel S, Liebetrau M, Rommer PS, Niehaus S, Munch C, Winkelmann A, Zettl UU, Metz I, Veauthier C, Sieb JP, Wilke C, Hartung HP, Aktas O, Paul F (2012) Contrasting disease patterns in seropositive and seronegative neuromyelitis optica: A multicentre study of 175 patients. J Neuroinflamm 9:14. doi:10.1186/1742-2094-9-14
Jiao Y, Fryer JP, Lennon VA, Jenkins SM, Quek AM, Smith CY, McKeon A, Costanzi C, Iorio R, Weinshenker BG, Wingerchuk DM, Shuster EA, Lucchinetti CF, Pittock SJ (2013) Updated estimate of AQP4-IgG serostatus and disability outcome in neuromyelitis optica. Neurology 81(14):1197–1204. doi:10.1212/WNL.0b013e3182a6cb5c
Kabat EA, Moore DH, Landow H (1942) An electrophoretic study of the protein components in cerebrospinal fluid and their relationship to the serum proteins. J Clin Investig 21(5):571–577. doi:10.1172/JCI101335
Kappos L, Hartung HP, Freedman, Boyko A, Radu EW, Mikol DD, Lamarine M, Hyvert Y, Freudensprung U, Plitz T, van Beek J, Group AS (2014) Atacicept in multiple sclerosis (ATAMS): a randomised, placebo-controlled, double-blind, phase 2 trial. Lancet Neurol 13(4):353–363. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(14)70028-6
Kappos L, Li D, Calabresi PA, O’Connor P, Bar-Or A, Barkhof F, Yin M, Leppert D, Glanzman R, Tinbergen J, Hauser SL (2011) Ocrelizumab in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis: a phase 2, randomised, placebo-controlled, multicentre trial. Lancet 378(9805):1779–1787. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(11)61649-8
Kausar F, Mustafa K, Sweis G, Sawaqed R, Alawneh K, Salloum R, Badaracco M, Niewold TB, Sweiss NJ (2009) Ocrelizumab: a step forward in the evolution of B-cell therapy. Exp Opin Biol Ther 9(7):889–895. doi:10.1517/14712590903018837
Kim S, Davis M, Sinn E, Patten P, Hood L (1981) Antibody diversity: somatic hypermutation of rearranged VH genes. Cell 27(3 Pt 2):573–581
Kim SH, Kim W, Li XF, Jung IJ, Kim HJ (2011) Repeated treatment with rituximab based on the assessment of peripheral circulating memory B cells in patients with relapsing neuromyelitis optica over 2 years. Arch Neurol 68(11):1412–1420. doi:10.1001/archneurol.2011.154
Kitley J, Waters P, Woodhall M, Leite MI, Murchison A, George J, Kuker W, Chandratre S, Vincent A, Palace J (2014) Neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders with aquaporin-4 and myelin-oligodendrocyte glycoprotein antibodies: a comparative study. JAMA Neurol 71(3):276–283. doi:10.1001/jamaneurol.2013.5857
Kleiter I, Hellwig K, Berthele A, Kumpfel T, Linker RA, Hartung HP, Paul F, Aktas O, Neuromyelitis Optica Study G (2012) Failure of natalizumab to prevent relapses in neuromyelitis optica. Arch Neurol 69(2):239–245. doi:10.1001/archneurol.2011.216
Kraus V, Srivastava R, Kalluri SR, Seidel U, Schuelke M, Schimmel M, Rostasy K, Leiz S, Hosie S, Grummel V, Hemmer B (2014) Potassium channel KIR4.1-specific antibodies in children with acquired demyelinating CNS disease. Neurology 82(6):470–473. doi:10.1212/WNL.0000000000000097
Lehmann-Horn K, Kronsbein HC, Weber MS (2013) Targeting B cells in the treatment of multiple sclerosis: recent advances and remaining challenges. Ther Adv Neurol Disord 6(3):161–173. doi:10.1177/1756285612474333
Lennon VA, Kryzer TJ, Pittock SJ, Verkman AS, Hinson SR (2005) IgG marker of optic-spinal multiple sclerosis binds to the aquaporin-4 water channel. J Exp Med 202(4):473–477. doi:10.1084/jem.20050304
Lennon VA, Wingerchuk DM, Kryzer TJ, Pittock SJ, Lucchinetti CF, Fujihara K, Nakashima I, Weinshenker BG (2004) A serum autoantibody marker of neuromyelitis optica: distinction from multiple sclerosis. Lancet 364(9451):2106–2112. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(04)17551-X
Li J, Barreda DR, Zhang YA, Boshra H, Gelman AE, Lapatra S, Tort L, Sunyer JO (2006) B lymphocytes from early vertebrates have potent phagocytic and microbicidal abilities. Nat Immunol 7(10):1116–1124. doi:10.1038/ni1389
Loken MR, Shah VO, Dattilio KL, Civin CI (1987) Flow cytometric analysis of human bone marrow. II. Normal B lymphocyte development. Blood 70(5):1316–1324
Lucchinetti C, Bruck W, Parisi J, Scheithauer B, Rodriguez M, Lassmann H (2000) Heterogeneity of multiple sclerosis lesions: implications for the pathogenesis of demyelination. Ann Neurol 47(6):707–717
Lucchinetti CF, Mandler RN, McGavern D, Bruck W, Gleich G, Ransohoff RM, Trebst C, Weinshenker B, Wingerchuk D, Parisi JE, Lassmann H (2002) A role for humoral mechanisms in the pathogenesis of Devic’s neuromyelitis optica. Brain 125(Pt 7):1450–1461
Madan R, Demircik F, Surianarayanan S, Allen JL, Divanovic S, Trompette A, Yogev N, Gu Y, Khodoun M, Hildeman D, Boespflug N, Fogolin MB, Grobe L, Greweling M, Finkelman FD, Cardin R, Mohrs M, Muller W, Waisman A, Roers A, Karp CL (2009) Nonredundant roles for B cell-derived IL-10 in immune counter-regulation. J Immunol 183(4):2312–2320. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.0900185
Magliozzi R, Howell O, Vora A, Serafini B, Nicholas R, Puopolo M, Reynolds R, Aloisi F (2007) Meningeal B-cell follicles in secondary progressive multiple sclerosis associate with early onset of disease and severe cortical pathology. Brain 130(Pt 4):1089–1104. doi:10.1093/brain/awm038
Mahevas M, Patin P, Huetz F, Descatoire M, Cagnard N, Bole-Feysot C, Le Gallou S, Khellaf M, Fain O, Boutboul D, Galicier L, Ebbo M, Lambotte O, Hamidou M, Bierling P, Godeau B, Michel M, Weill JC, Reynaud CA (2013) B cell depletion in immune thrombocytopenia reveals splenic long-lived plasma cells. J Clin Investig 123(1):432–442. doi:10.1172/JCI65689
Mei HE, Schmidt S, Dorner T (2012) Rationale of anti-CD19 immunotherapy: an option to target autoreactive plasma cells in autoimmunity. Arthritis Res Ther 14(Suppl 5):S1. doi:10.1186/ar3909
Misu T, Fujihara K, Kakita A, Konno H, Nakamura M, Watanabe S, Takahashi T, Nakashima I, Takahashi H, Itoyama Y (2007) Loss of aquaporin 4 in lesions of neuromyelitis optica: distinction from multiple sclerosis. Brain 130(Pt 5):1224–1234. doi:10.1093/brain/awm047
Montalvao F, Garcia Z, Celli S, Breart B, Deguine J, Van Rooijen N, Bousso P (2013) The mechanism of anti-CD20-mediated B cell depletion revealed by intravital imaging. J Clin Investig 123(12):5098–5103. doi:10.1172/JCI70972
Nakashima I, Takahashi T, Cree BA, Kim HJ, Suzuki C, Genain CP, Vincent T, Fujihara K, Itoyama Y, Bar-Or A (2011) Transient increases in anti-aquaporin-4 antibody titers following rituximab treatment in neuromyelitis optica, in association with elevated serum BAFF levels. J Clin Neurosci 18(7):997–998. doi:10.1016/j.jocn.2010.12.011
Nerrant E, Salsac C, Charif M, Ayrignac X, Carra-Dalliere C, Castelnovo G, Goulabchand R, Tisseyre J, Raoul C, Eliaou JF, Labauge P, Vincent T (2014) Lack of confirmation of anti-inward rectifying potassium channel 4.1 antibodies as reliable markers of multiple sclerosis. Multiple Scler. doi:10.1177/1352458514531086
Otero DC, Anzelon AN, Rickert RC (2003) CD19 function in early and late B cell development: I. Maintenance of follicular and marginal zone B cells requires CD19-dependent survival signals. J Immunol 170(1):73–83
Parratt JD, Prineas JW (2010) Neuromyelitis optica: a demyelinating disease characterized by acute destruction and regeneration of perivascular astrocytes. Multiple Scler 16(10):1156–1172. doi:10.1177/1352458510382324
Pellkofer HL, Krumbholz M, Berthele A, Hemmer B, Gerdes LA, Havla J, Bittner R, Canis M, Meinl E, Hohlfeld R, Kuempfel T (2011) Long-term follow-up of patients with neuromyelitis optica after repeated therapy with rituximab. Neurology 76(15):1310–1315. doi:10.1212/WNL.0b013e3182152881
Pieper K, Grimbacher B, Eibel H (2013) B-cell biology and development. J Allergy Clin Immunol 131(4):959–971. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2013.01.046
Pistoia V (1997) Production of cytokines by human B cells in health and disease. Immunol Today 18(7):343–350
Pittock SJ, Weinshenker BG, Lucchinetti CF, Wingerchuk DM, Corboy JR, Lennon VA (2006) Neuromyelitis optica brain lesions localized at sites of high aquaporin 4 expression. Arch Neurol 63(7):964–968. doi:10.1001/archneur.63.7.964
Poe JC, Minard-Colin V, Kountikov EI, Haas KM, Tedder TF (2012) A c-Myc and surface CD19 signaling amplification loop promotes B cell lymphoma development and progression in mice. J Immunol 189(5):2318–2325. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1201000
Prineas JW, Wright RG (1978) Macrophages, lymphocytes, and plasma cells in the perivascular compartment in chronic multiple sclerosis. Lab Invest 38(4):409–421
Ratelade J, Asavapanumas N, Ritchie AM, Wemlinger S, Bennett JL, Verkman AS (2013) Involvement of antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity in inflammatory demyelination in a mouse model of neuromyelitis optica. Acta Neuropathol 126(5):699–709. doi:10.1007/s00401-013-1172-z
Roemer SF, Parisi JE, Lennon VA, Benarroch EE, Lassmann H, Bruck W, Mandler RN, Weinshenker BG, Pittock SJ, Wingerchuk DM, Lucchinetti CF (2007) Pattern-specific loss of aquaporin-4 immunoreactivity distinguishes neuromyelitis optica from multiple sclerosis. Brain 130(Pt 5):1194–1205. doi:10.1093/brain/awl371
Rommer PS, Dudesek A, Stuve O, Zettl UK (2014) Monoclonal antibodies in treatment of multiple sclerosis. Clin Exp Immunol 175(3):373–384. doi:10.1111/cei.12197
Saadoun S, Bridges LR, Verkman AS, Papadopoulos MC (2012) Paucity of natural killer and cytotoxic T cells in human neuromyelitis optica lesions. NeuroReport 23(18):1044–1047. doi:10.1097/WNR.0b013e32835ab480
Saito E, Fujimoto M, Hasegawa M, Komura K, Hamaguchi Y, Kaburagi Y, Nagaoka T, Takehara K, Tedder TF, Sato S (2002) CD19-dependent B lymphocyte signaling thresholds influence skin fibrosis and autoimmunity in the tight-skin mouse. J Clin Investig 109(11):1453–1462. doi:10.1172/JCI15078
Sato DK, Callegaro D, Lana-Peixoto MA, Waters PJ, de Haidar Jorge FM, Takahashi T, Nakashima I, Apostolos-Pereira SL, Talim N, Simm RF, Lino AM, Misu T, Leite MI, Aoki M, Fujihara K (2014) Distinction between MOG antibody-positive and AQP4 antibody-positive NMO spectrum disorders. Neurology 82(6):474–481. doi:10.1212/WNL.0000000000000101
Schirmer L, Srivastava R, Kalluri SR, Bottinger S, Herwerth M, Carassiti D, Srivastava B, Gempt J, Schlegel J, Kuhlmann T, Korn T, Reynolds R, Hemmer B (2014) Differential loss of KIR4.1 immunoreactivity in multiple sclerosis lesions. Ann Neurol. doi:10.1002/ana.24168
Serafini B, Rosicarelli B, Franciotta D, Magliozzi R, Reynolds R, Cinque P, Andreoni L, Trivedi P, Salvetti M, Faggioni A, Aloisi F (2007) Dysregulated Epstein-Barr virus infection in the multiple sclerosis brain. J Exp Med 204(12):2899–2912. doi:10.1084/jem.20071030
Serafini B, Rosicarelli B, Magliozzi R, Stigliano E, Aloisi F (2004) Detection of ectopic B-cell follicles with germinal centers in the meninges of patients with secondary progressive multiple sclerosis. Brain Pathol 14(2):164–174
Shen P, Roch T, Lampropoulou V, O’Connor RA, Stervbo U, Hilgenberg E, Ries S, Dang VD, Jaimes Y, Daridon C, Li R, Jouneau L, Boudinot P, Wilantri S, Sakwa I, Miyazaki Y, Leech MD, McPherson RC, Wirtz S, Neurath M, Hoehlig K, Meinl E, Grutzkau A, Grun JR, Horn K, Kuhl AA, Dorner T, Bar-Or A, Kaufmann SH, Anderton SM, Fillatreau S (2014) IL-35-producing B cells are critical regulators of immunity during autoimmune and infectious diseases. Nature 507(7492):366–370. doi:10.1038/nature12979
Shimizu J, Hatanaka Y, Hasegawa M, Iwata A, Sugimoto I, Date H, Goto J, Shimizu T, Takatsu M, Sakurai Y, Nakase H, Uesaka Y, Hashida H, Hashimoto K, Komiya T, Tsuji S (2010) IFNbeta-1b may severely exacerbate Japanese optic-spinal MS in neuromyelitis optica spectrum. Neurology 75(16):1423–1427. doi:10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181f8832e
Simpson JA (1960) Myasthenia gravis: a new hypothesis. Scott Med J 5:419–436
Sinclair C, Kirk J, Herron B, Fitzgerald U, McQuaid S (2007) Absence of aquaporin-4 expression in lesions of neuromyelitis optica but increased expression in multiple sclerosis lesions and normal-appearing white matter. Acta Neuropathol 113(2):187–194. doi:10.1007/s00401-006-0169-2
Sorensen PS, Lisby S, Grove R, Derosier F, Shackelford S, Havrdova E, Drulovic J, Filippi M (2014) Safety and efficacy of ofatumumab in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis: a phase 2 study. Neurology 82(7):573–581. doi:10.1212/WNL.0000000000000125
Srivastava R, Aslam M, Kalluri SR, Schirmer L, Buck D, Tackenberg B, Rothhammer V, Chan A, Gold R, Berthele A, Bennett JL, Korn T, Hemmer B (2012) Potassium channel KIR4.1 as an immune target in multiple sclerosis. N Engl J Med 367(2):115–123. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1110740
Stashenko P, Nadler LM, Hardy R, Schlossman SF (1980) Characterization of a human B lymphocyte-specific antigen. J Immunol 125(4):1678–1685
Stashenko P, Nadler LM, Hardy R, Schlossman SF (1981) Expression of cell surface markers after human B lymphocyte activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 78(6):3848–3852
Stohl W, Gomez-Reino J, Olech E, Dudler J, Fleischmann RM, Zerbini CA, Ashrafzadeh A, Grzeschik S, Bieraugel R, Green J, Francom S, Dummer W (2012) Safety and efficacy of ocrelizumab in combination with methotrexate in MTX-naive subjects with rheumatoid arthritis: the phase III FILM trial. Ann Rheum Dis 71(8):1289–1296. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2011-200706
Stuve O, Cepok S, Elias B, Saleh A, Hartung HP, Hemmer B, Kieseier BC (2005) Clinical stabilization and effective B-lymphocyte depletion in the cerebrospinal fluid and peripheral blood of a patient with fulminant relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. Arch Neurol 62(10):1620–1623. doi:10.1001/archneur.62.10.1620
Tedder TF (2009) CD19: a promising B cell target for rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol 5(10):572–577. doi:10.1038/nrrheum.2009.184
Uchida J, Lee Y, Hasegawa M, Liang Y, Bradney A, Oliver JA, Bowen K, Steeber DA, Haas KM, Poe JC, Tedder TF (2004) Mouse CD20 expression and function. Int Immunol 16(1):119–129
Uzawa A, Mori M, Arai K, Sato Y, Hayakawa S, Masuda S, Taniguchi J, Kuwabara S (2010) Cytokine and chemokine profiles in neuromyelitis optica: significance of interleukin-6. Multiple Scler 16(12):1443–1452. doi:10.1177/1352458510379247
Vallerskog T, Gunnarsson I, Widhe M, Risselada A, Klareskog L, van Vollenhoven R, Malmstrom V, Trollmo C (2007) Treatment with rituximab affects both the cellular and the humoral arm of the immune system in patients with SLE. Clin Immunol 122(1):62–74. doi:10.1016/j.clim.2006.08.016
van Zelm MC, Reisli I, van der Burg M, Castano D, van Noesel CJ, van Tol MJ, Woellner C, Grimbacher B, Patino PJ, van Dongen JJ, Franco JL (2006) An antibody-deficiency syndrome due to mutations in the CD19 gene. N Engl J Med 354(18):1901–1912. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa051568
Willis SN, Stadelmann C, Rodig SJ, Caron T, Gattenloehner S, Mallozzi SS, Roughan JE, Almendinger SE, Blewett MM, Bruck W, Hafler DA, O’Connor KC (2009) Epstein-Barr virus infection is not a characteristic feature of multiple sclerosis brain. Brain 132(Pt 12):3318–3328. doi:10.1093/brain/awp200
Wingerchuk DM, Lennon VA, Pittock SJ, Lucchinetti CF, Weinshenker BG (2006) Revised diagnostic criteria for neuromyelitis optica. Neurology 66(10):1485–1489. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000216139.44259.74
Wingerchuk DM, Pittock SJ, Lucchinetti CF, Lennon VA, Weinshenker BG (2007) A secondary progressive clinical course is uncommon in neuromyelitis optica. Neurology 68(8):603–605. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000254502.87233.9a
Yazawa N, Hamaguchi Y, Poe JC, Tedder TF (2005) Immunotherapy using unconjugated CD19 monoclonal antibodies in animal models for B lymphocyte malignancies and autoimmune disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102(42):15178–15183. doi:10.1073/pnas.0505539102
Zhang B (2009) Ofatumumab. mAbs 1(4):326–331
Zhou LJ, Smith HM, Waldschmidt TJ, Schwarting R, Daley J, Tedder TF (1994) Tissue-specific expression of the human CD19 gene in transgenic mice inhibits antigen-independent B-lymphocyte development. Mol Cell Biol 14(6):3884–3894
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stüve, O., Warnke, C., Deason, K. et al. CD19 as a molecular target in CNS autoimmunity. Acta Neuropathol 128, 177–190 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-014-1313-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-014-1313-z