Abstract
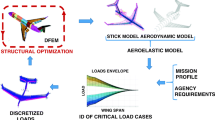
Projecting reduced-weight components with increased performance is a continuous engineering challenge, especially in the aircraft industry, where fuel consumption, emissions, and performance are highly dependent on structure weight. Nowadays, topology optimization is a growing computational technique capable of calculating optimal material configurations within a design domain and boundary conditions. Although the Finite Element Method (FEM) is the most disseminated discretization technique in engineering, meshless methods emerged as efficient alternatives to mesh-based methods. In meshless methods, the problem domain is discretized by an unstructured nodal distribution with no predetermined connectivity. Additionally, accurate and smooth stress fields can be obtained as a result of the elaborate shape functions and deep nodal connectivity allowed by meshless techniques. Despite, meshless methods application to topology optimization is still limited. In this work, an improved evolutionary topology optimization algorithm is combined with the Radial Point Interpolation Method (RPIM), a meshless technique. First, the proposed method was validated by solving two benchmark topology optimization problems, for which the developed algorithm efficiently achieved the optimal material configuration. Then, the capability of the topology optimization algorithm is demonstrated by extending the methodology to practical aircraft applications.















Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material (data transparency)
Not applicable.
Code availability (software application or custom code)
Not applicable.
References
Michell AGM (1904) LVIII. The limits of economy of material in frame-structures. Dublin Philos Mag J Sci 8(47):589–597. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786440409463229 (London, Edinburgh)
Rozvany GIN (1972) Grillages of maximum strength and maximum stiffness. Int J Mech Sci 14(10):651–666. https://doi.org/10.1016/0020-7403(72)90023-9
Rozvany GIN (1977) Optimum choice of determinate trusses under multiple loads. J Struct Div 103(12):2432–2433
Bendsøe MP, Kikuchi N (1988) Generating optimal topologies in structural design using a homogenization method. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 71(2):197–224. https://doi.org/10.1016/0045-7825(88)90086-2
Bendsøe MP (1989) Optimal shape design as a material distribution problem. Struct Optim 1(4):193–202. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01650949
Zhou M, Rozvany GIN (1991) The COC algorithm, Part II: topological, geometrical and generalized shape optimization. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 89(1–3):309–336. https://doi.org/10.1016/0045-7825(91)90046-9
Rozvany GIN, Zhou M, Birker T (1992) Generalized shape optimization without homogenization. Struct Optim 4(3–4):250–252. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf01742754
Xie YM, Steven GP (1993) A simple evolutionary procedure for structural optimization. Compurers Struct 49(5):885–896
Querin OM, Steven GP, Xie YM (1998) Evolutionary structural optimisation (ESO) using a bidirectional algorithm. Eng Comput 15(8):1031–1048. https://doi.org/10.1108/02644409810244129
Yang XY, Xie YM, Steven GP, Querin OM (1999) Bi-directional evolutionary method for stiffness optimisation. AIAA J 37(11):1488–1493. https://doi.org/10.2514/3.14346
Querin OM, Steven GP, Xie YM (2000) Evolutionary structural optimisation using an additive algorithm. Finite Elem Anal Des 34(3–4):291–308. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-874X(99)00044-X
Querin OM, Young V, Steven GP, Xie YM (2000) Computational efficiency and validation of bi-directional evolutionary structural optimization. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 189(2):559–573. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0045-7825(99)00309-6
Burger M, Hackl B, Ring W (2004) Incorporating topological derivatives into level set methods. J Comput Phys 194(1):344–362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcp.2003.09.033
Sokolowski J, Zochowski A (1999) On the topological derivative in shape optimization. SIAM J Control Optim 37(4):1251–1272. https://doi.org/10.1137/S0363012997323230
Eschenauer HA, Kobelev VV, Schumacher A (1994) Bubble method for topology and shape optimization of structures. Struct Optim 8(1):42–51. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01742933
Jia H, Beom HG, Wang Y, Lin S, Liu B (2011) Evolutionary level set method for structural topology optimization. Comput Struct 89(5–6):445–454. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruc.2010.11.003
Wang MY, Chen S, Wang X, Mei Y (2005) Design of multimaterial compliant mechanisms using level-set methods. J Mech Des Trans ASME 127(5):941–956. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.1909206
Allaire G, Jouve F, Toader AM (2004) Structural optimization using sensitivity analysis and a level-set method. J Comput Phys 194(1):363–393. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcp.2003.09.032
Sethian JA, Wiegmann A (2000) Structural boundary design via level set and immersed interface methods. J Comput Phys 163(2):489–528. https://doi.org/10.1006/jcph.2000.6581
Allaire G, Jouve F, Toader AM (2002) A level-set method for shape optimization. Comptes Rendus Math 334:1125–1130. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1631-073X(02)02412-3
Wallin M, Ristinmaa M (2014) Boundary effects in a phase-field approach to topology optimization. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 278:145–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cma.2014.05.012
Bourdin B, Chambolle A (2003) Design-dependent loads in topology optimization. ESAIM Control Optim Calc Var 9:19–48. https://doi.org/10.1051/cocv:2002070
Wang SY, Tai K (2005) Structural topology design optimization using Genetic Algorithms with a bit-array representation. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 194(36–38):3749–3770. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cma.2004.09.003
Liu X, Yi WJ, Li QS, Shen P-S (2008) Genetic evolutionary structural optimization. J Constr Steel Res 64:305–311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcsr.2007.08.002
Daxini SD, Prajapati JM (2019) Numerical shape optimization based on meshless method and stochastic optimization technique. Eng Comput. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-019-00714-3
Daxini SD, Prajapati JM (2019) Structural shape optimization with meshless method and swarm-intelligence based optimization. Int J Mech Mater Des. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10999-019-09451-3
Liu GR, Gu YT (2005) An introduction to meshfree methods and their programming. Springer, Netherlands
Belinha J (2014) Meshless methods in biomechanics—bone tissue remodelling analysis, 1st edn. Springer, Cham
Gingold RA, Monaghan JJ (1977) Smoothed particle hydrodynamics: theory and application to non-spherical stars. Mon Not R Astron Soc 181:375–389
Libersky LD, Petschek AG (1991) Smooth particle hydrodynamics with strength of materials. Lect Notes Phys 395:248–257
Nayroles B, Touzot G, Villon P (1992) Generalizing the finite element method: diffuse approximation and diffuse elements. Comput Mech 10(5):307–318. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00364252
Belytschko T, Lu YY, Gu L (1994) Element-free Galerkin methods. Int J Numer Methods Eng 37(2):229–256. https://doi.org/10.1002/nme.1620370205
Wing Kam L, Jun S, Yi Fei Z (1995) Reproducing kernel particle methods. Int J Numer Methods Fluids 20(8–9):1081–1106
Atluri SN, Zhu T (1998) A new Meshless Local Petrov-Galerkin (MLPG) approach in computational mechanics. Comput Mech 22(2):117–127. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004660050346
De S, Bathe KJ (2000) The method of finite spheres. Comput Mech 25(4):329–345. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004660050481
Braun J, Sambridge M (1995) A numerical method for solving partial differential equations on highly irregular evolving grids. Nature 376:655–660. https://doi.org/10.1038/376655a0
Sukumar N, Moran B, Belytschko T (1998) The natural element method in solid mechanics. Int J Numer Methods Eng 43:839–887. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-0207(19981115)43:5%3c839::AID-NME423%3e3.0.CO;2-R
Wang JG, Liu GR (2002) A point interpolation meshless method based on radial basis functions. Int J Numer Methods Eng 54(11):1623–1648. https://doi.org/10.1002/nme.489
Liu GR, Gu YT (2001) A point interpolation method for two-dimensional solids. Int J Numer Methods Eng 50(4):937–951. https://doi.org/10.1002/1097-0207(20010210)50:4%3c937::AID-NME62%3e3.0.CO;2-X
Dinis LMJS, Natal Jorge RM, Belinha J (2007) Analysis of 3D solids using the natural neighbour radial point interpolation method. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 196:2009–2028. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cma.2006.11.002
Belinha J, Dinis LMJS, Jorge RMN (2012) The natural radial element method. Int J Numer Methods Eng. https://doi.org/10.1002/nme
Belinha J, Dinis LMJS, Jorge RMN (2013) Composite laminated plate analysis using the natural radial element method. Compos Struct 103:50–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2013.03.018
Belinha J, Dinis LMJS, Nataljorge RM (2013) Analysis of thick plates by the natural radial element method. Int J Mech Sci 76:33–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2013.08.011
Grindeanu I, Chang KH, Choi KK, Chen JS (1998) Design sensitivity analysis of hyperelastic structures using a meshless method. AIAA J 36(4):618–627. https://doi.org/10.2514/2.414
Grindeanu I, Choi KK, Chen J-S, Chang K-H (1999) Shape design optimization of hyperelastic structures using a meshless method. AIAA J 37(8):990–997. https://doi.org/10.2514/3.14273
Grindeanu I, Kim NH, Choi KK, Chen JS (2002) CAD-based shape optimization using a meshfree method. Concurr Eng 10(1):55–66. https://doi.org/10.1106/106329302024056
Kim NH, Choi KK, Botkin ME (2003) Numerical method for shape optimization using meshfree method. Struct Multidiscip Optim 24(6):418–429. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-002-0255-6
Zhang ZQ, Zhou JX, Zhou N, Wang XM, Zhang L (2005) Shape optimization using reproducing kernel particle method and an enriched genetic algorithm. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 194(39–41):4048–4070. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cma.2004.10.004
Zou W, Zhou JX, Zhang ZQ, Li Q (2007) A truly meshless method based on partition of unity quadrature for shape optimization of continua. Comput Mech 39(4):357–365. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00466-006-0032-2
Bobaru F, Mukherjee S (2001) Shape sensivity analysis and shape optimization in planar elasticity using the element-free Galerkin method. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 190(32–33):4319–4337. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0045-7825(00)00321-2
Zhao Z (1991) Shape design sensitivity analysis using the boundary element method—lecture notes in engineering 62. Springer-Verlag, Berlin
Bobaru F, Mukherjee S (2002) Meshless approach to shape optimization of linear thermoelastic solids. Int J Numer Methods Eng 53:765–796. https://doi.org/10.1002/nme.311
Bobaru F, Rachakonda S (2006) E(FG)2: a new fixed-grid shape optimization method based on the element-free galerkin mesh-free analysis: taking large steps in shape optimization. Struct Multidiscip Optim 32:215–228. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-006-0018-x
Juan Z, Shuyao L, Guangyao L (2010) The topology optimization design for continuum structures based on the element free Galerkin method. Eng Anal Bound Elem 34(7):666–672. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enganabound.2010.03.001
Luo Z, Zhang N, Wang Y, Gao W (2012) Topology optimization of structures using meshless density variable approximants. Int J Numer Methods Eng. https://doi.org/10.1002/nme
Zhao F (2014) Topology optimization with meshless density variable approximations and BESO method. Comput Aided Des 56:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cad.2014.06.003
Shobeiri V (2015) The topology optimization design for cracked structures. Eng Anal Bound Elem 58:26–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enganabound.2015.03.002
Wang Y, Luo Z, Wu J, Zhang N (2015) Topology optimization of compliant mechanisms using element-free Galerkin method. Adv Eng Softw 85:61–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advengsoft.2015.03.001
Cui M, Chen H, Zhou J, Wang F (2017) A meshless method for multi-material topology optimization based on the alternating active-phase algorithm. Eng Comput 33(4):871–884. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-017-0503-4
Yang X, Zheng J, Long S (2017) Topology optimization of continuum structures with displacement constraints based on meshless method. Int J Mech Mater Des 13(2):311–320. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10999-016-9337-2
Lin J, Guan Y, Zhao G, Naceur H, Lu P (2017) Topology optimization of plane structures using smoothed particle hydrodynamics method. Int J Numer Methods Eng 110:726–744. https://doi.org/10.1002/nme.5427
Wang K, Zhou S, Nie Z, Kong S (2008) Natural neighbour Petrov-Galerkin Method for shape design sensitivity analysis. Comput Model Eng Sci 26(2):107–121. https://doi.org/10.3970/cmes.2008.026.107
Li S, Atluri SN (2008) The MLPG mixed collocation method for material orientation and topology optimization of anisotropic solids and structures. Comput Model Eng Sci 30(1):37–56. https://doi.org/10.3970/cmes.2008.030.037
Zheng J, Long S, Xiong Y, Li G (2009) A finite volume meshless local petrov-galerkin method for topology optimization design of the continuum structures. Comput Model Eng Sci 42(1):19–34. https://doi.org/10.3970/cmes.2009.042.019
Li SL, Long SY, Li GY (2010) A topology optimization of moderately thick plates based on the meshless numerical method. Comput Model Eng Sci 60(1):73–94. https://doi.org/10.3970/cmes.2010.060.073
Li S, Atluri SN (2008) Topology-optimization of structures based on the MLPG mixed collocation method. Comput Model Eng Sci 26(1):61–74. https://doi.org/10.3970/cmes.2008.026.061
Zheng J, Long S, Xiong Y, Guangyao L (2008) A topology optimization design for the continuum structure based on the meshless numerical technique. Comput Model Eng Sci 34(2):137–154
Lee S-J, Lee C-K and Bae J-E (2009) Evolution of 2D truss structures using topology optimization technique with meshless method. In: Proc. Int. Assoc. Shell Spat. Struct. Symp., pp 1058–1065
Hardy RL (1990) Theory and applications of the multiquadric-biharmonic method. Comput Math Appl 19(8–9):163–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/0898-1221(90)90272-L
Huang X, Xie YM (2010) Evolutionary topology optimization of continuum structures. WILEY, Hoboken
Conlan-Smith C, James KA (2019) A stress-based topology optimization method for heterogeneous structures. Struct Multidiscip Optim 60(1):167–183. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-019-02207-9
Picelli R, Townsend S, Brampton C, Norato J, Kim HA (2018) Stress-based shape and topology optimization with the level set method. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 329:1–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cma.2017.09.001
Xia L, Zhang L, Xia Q, Shi T (2018) Stress-based topology optimization using bi-directional evolutionary structural optimization method. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 333:356–370. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cma.2018.01.035
Wang H, Liu J, Qian X, Fan X, Wen G (2017) Continuum structural layout in consideration of the balance of the safety and the properties of structures. Lat Am J Solids Struct 14(6):1143–1169. https://doi.org/10.1590/1679-78253679
Biyikli E, To AC (2015) Proportional topology optimization: a new non-sensitivity method for solving stress constrained and minimum compliance problems and its implementation in MATLAB. PLoS One 10(12):1–23. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0145041
Holmberg E, Torstenfelt B, Klarbring A (2013) Stress constrained topology optimization. Struct Multidiscip Optim 48(1):33–47. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-012-0880-7
Verbart A, Langelaar M, Van Dijk N and Van Keulen F (2012) Level set based topology optimization with stress constraints and consistent sensitivity analysis. In: Collect. Tech. Pap. - AIAA/ASME/ASCE/AHS/ASC Struct. Struct. Dyn. Mater. Conf., pp 1–15. https://doi.org/10.2514/6.2012-1358
Le C, Norato J, Bruns T, Ha C, Tortorelli D (2010) Stress-based topology optimization for continua. Struct Multidiscip Optim 41(4):605–620. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-009-0440-y
Ishak MR, Abu Bakar AR, Belhocine A, Taib JM, Omar WZW (2016) Brake torque analysis of fully mechanical parking brake system: Theoretical and experimental approach. Meas J Int Meas Confed 94(June 2017):487–497. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2016.08.026
Rinku A and Ananthasuresh GK (2015) Topology and size Optimization of Modular Ribs in aircraft wings. In: 11th World Congr. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim., pp 1–6
Funding
The authors truly acknowledge the funding provided by Ministério da Ciência, Tecnologia e Ensino Superior—Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia (Portugal), under project funding POCI-01-0145-FEDER-028351 and scholarship RH 028351 UPAL 28/2020. Additionally, the authors acknowledge the funding provided by LAETA, under project UIDB/50022/2020.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gonçalves, D.C., Lopes, J.D.F., Campilho, R.D.S.G. et al. The Radial Point Interpolation Method combined with a bi-directional structural topology optimization algorithm. Engineering with Computers 38, 5137–5151 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-021-01556-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-021-01556-8