Abstract
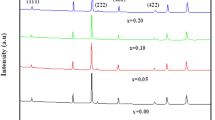
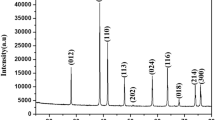
In this present work, antimony-substituted cadmium ferrites with formula CdSbxFe2−xO4 (x = 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5) have been synthesized using the ceramic route. The structural, surface morphological, magnetic and optical properties have been investigated using X-ray diffractometer (XRD), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), scanning electron microscopy, vibrating sample magnetometer and UV–visible spectroscopy, respectively. XRD confirms the single cubic spinel structure of antimony-substituted cadmium ferrites. The lattice parameter increases due to the replacement of Fe+3 (0.64 Å) ions with Sb+3 (0.76 Å). FTIR gives the main vibrational band that lies in the range of 400–600 cm−1 which might be due to the stretching vibration of oxygen and metal ions, confirming the formation of spinel ferrite. The saturation magnetization decreases and coercivity increases as the concentration of non-magnetic antimony ion increases. The optical band gap energy decreases with increasing the concentration of antimony ions.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
A.B. Gadkari, T.J. Shinde, P.N. Vasambekar, Structural analysis of Y+3-doped Mg cd ferrites prepared by oxalate co-precipitation method. Mater. Chem. Phys. 114, 505 (2009)
P. Rabia, K.K. Sharma, P. Kaur, R.K. Kotnala, Effect of Al3+ subtitution on structural cation ditribution, electrical and magnetic properties of CoFe2O4. J. Phys. Chem. Solids. 75, 558–569 (2014)
R. Srivastava, B.C. Yadav, Synthesis techniques, and applications as sensors. Int. J. Green Nanotechnol. Ferrite Mater. 4, 141–154 (2012)
C.J. Brinker, G.W. Scherer, The physics and the chemistry of sol gel processing, in Sol–Gel Science, ed. by G.W. Scherer (Academic Press, London, 1990)
L. Gama, A.P. Diniz, A.C.F.M. Costa, S.M. Bezende, A. Azevedo, D.R. Comejo, Magnetic materials and their application. Phys. B: Conden. Matter 384, 1–2 (2006)
S.E. Jcoba, S. Dukalde, H.R. Bertorella, Rare earth influence on the structural and magnetic properties of NiZn ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2253, 272 (2004)
S. Jan, Magnetic Techniques for the Treatment of Materials (Springer, Berlin, 2004)
A. Lloyd, Applications of hard and soft ferrites. Key Eng. Mater. 122–124, 175–184 (1996)
B. Kulkarni Akshay, N.M. Shridhar, Variation in structural and mechanical properties of Cd-DOPED Co–Zn ferrites. Mater. Sci. Energy Technol. 2, 455–462 (2019)
P.K. Nayak, Synthesis and characterization of cadmium ferrite. J. Mater. Chem. Phys. 112, 24–26 (2008)
B.H. Devmunde, A.V. Raut, S.D. Birajdar, S.J. Shukla, D.R. Shengule, K.M.J. Jadhav, Structural, electrical, dielectric, and magnetic properties of Cd+2 substituted nickel ferrite nanoparticles. J. Nanopart. 2016, 8 (2016)
E. Pervaiz, I.H. Gul, Hydrothermal synthesis, structural and electrical properties of antimony (Sb3+) substituted nickel ferrites. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 27, 881–890 (2014)
E. Pervaiz, I.H. Gul, Enhancement of electrical properties due to Cr3+ substitution in Co-ferrite nanoparticles synthesized by two chemical techniques. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 324, 3695–3703 (2012)
S. Xavier, S. Thankachan, B.P. Jacob, E.M. Mohammed, Cation distribution and magnetic properties of nanocrystalline gallium substituted cobalt ferrite. J. Alloys Compd. 615, 181–187 (2014)
Z. Sam, L. Lin, K. Ashok, Materials Characterization Techniques (Taylor & Francis, London, 2008)
B. Chethan, Y.T. Ravikiran, S.C. Vijayakumari, H.G. Rajprakash, S. Thomas, Nickel Substituted cadmium ferrite as room temperature operable humidity sensor. Sensors Actuators A Phys. 280, 466–474 (2018)
A.K. Sadoon, Study of the effect of CeO2 on the structural properties of cadmium ferrite. Energy Proc. 156, 561–567 (2019)
M. Shaki, U. Inayat, M.I. Arshad, N.R. Khalid, N.H. Tariq, Influence of zinc and cadmium co-doping on optical and magnetic properties of cobalt ferrites. Ceram. Int. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.11.280
K. Nogi, M. Hosokawa, M. Naito, T. Yokoyama, Nanoparticle Technology Handbook (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2012)
A.K. Nandawar, N.N. Sarkar, D.K. Sahu, Effect of Ni+2 substitution on structural and electrical behaviour of nano-sized cadmium. Mater. Today Proc. 5, 22669–22674 (2018)
F. Zamani, A.H. Taghvaei, Characterization and magnetic properties of nanocrystalline Mg1−xCdxFe2O4 (x = 0.0–0.8) ferrites synthesized by glycine-nitrate autocombustion method. Ceram. Int. 44, 17209–17217 (2018)
S.E. Shirsath, B.G. Toksha, K.M. Jadhav, Mater. Chem. Phys. 117, 163–168 (2009)
N. Mahmoud, Optical and magnetic properties of monophasic cadmium ferrite (CdF2O4) nanostructure prepared by thermal treatment method. J. Magn. Mater. 392, 107–113 (2015)
R. Topkaya, Y. Yafet, Ferrites Magn. Phys. 90, 29 (2016)
M.V.K. Mehar, A. Simhadri, DC electrical properties of antimony substituted lithium ferrites. Int. J. Res. Appl. Sci. Eng. Technol. 3, 2321–9653 (2015)
M. Yokoyama, E. Ohta, Magnetic properties of ultrafine particles and bulk material of cadmium ferrite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 183, 173–180 (1998)
S. Singhal, K. Chandra, Cation distribution and magnetic properties in chromium-substituted nickel ferrites prepared using aerosol route. J. Solid State Chem. 180, 296–300 (2007)
M. Su, K. Shih, L. Kong, Stabilizing cadmium into aluminate and ferrite structures: effectiveness and leaching behavior. J. Environ. Manag. 187, 340–346 (2017)
D.S. Mathew, S.J. Ruey, An overview of the structure and magnetism of spinel ferrite nanoparticles and their synthesis in microemulsions. Chem. Eng. J. 129, 51–65 (2007)
A.M. Fox, Optical Properties of Solids (Oxford University Press, Oxford, 2001), p. 304
A. Datar, B. Ray, S. Datar, V. Mathe, Magnetic force microscopic analysis and the magnetoelectric sensor of PLZT-Spinel ferrite composite films. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 489, 165373 (2019)
S. Jaiswal, J. Kumar, Solid State Sci. 14, 1157–1168 (2012)
O. Caltun, High magnetostrictive doped cobalt ferrite. J. Optoelectron. Adv. Mater. 9(4), 1158 (2007)
A.S. Ponce, High coercivity induced by mechanical milling in cobalt ferrite powders. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 344, 182–187 (2013)
S. Sonal, Investigation of structural, magnetic, electrical and optical properties of chromium substituted cobalt ferrites (CoCrxFe2−xO4, 0 ⩽ x ⩽ 1) synthesized using sol gel auto combustion method. J. Mol. Struct. 1012, 182–188 (2012)
M.N. Ashiq, M.F. Ehsan, Synthesis, structural and electrical characterization of Sb+3 substituted spinel nickel ferrite (NiSbxFe2−xO4) nanoparticles by reverse micelle technique. J. Alloys Compd. 509, 5119–5126 (2011)
C.S. Lakshmi, C.S.L.N. Sridhar, Structural, magnetic and dielectric investigations in antimony doped nano-phased nickle-zinc ferrites. J. Phys. B 459, 97–104 (2015)
M. Kuppan, S. Kaleemulla, N.M. Rao, N.S. Krishna, M.R. Begam, M. Shobana, Structural and magnetic properties of Ni doped SnO2. Adv. Condens. Matter Phys. 2014, 1–5 (2014)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Anjum, S., Ilayas, T. & Mustafa, Z. Influence of antimony substitution on structural, magnetic and optical properties of cadmium spinel ferrite. Appl. Phys. A 126, 227 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-020-3407-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-020-3407-x