Abstract
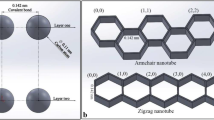
Based on a molecular mechanics coupled with atomistic-based continuum theory, a closed-form formula is presented to examine the elastic properties of single- and double-walled carbon nanotubes subjected to hydrostatic pressure. Following the present model, the effects of the armchair and zigzag CNT structures on the pressure behavior are theoretically investigated. The computational result indicates that the bulk modulus is less sensitive to the chiral structures except for very small tube diameters. Moreover, closed-end nanotubes under hydrostatic pressure exhibit a larger bulking modulus than open ended nanotubes. The cap of the zigzag tubes has a larger effect on the bulk modulus when compared to the armchair tubes, especially in small diameter nanotubes. The predicted strain and the bulk modulus are in good agreement with existing theoretical results.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vaccarini L, Goze C, Henrard L, Hernandez E, Bernier P, Rubio A (2000) Carbon 38:1681
Salvetat JP, Bonard JM, Thomson NH, Kulik AJ, Forro L, Benoit W, Zuppiroli L (1999) Appl. Phys. A: Mater. Sci. Process. 69:255
Wong EW, Sheehan PE, Liebe CM (1997) Science 277:1971
Treacy MMJ, Ebbesen TW, Gibson JM (1996) Nature (London) 381:678
Ruoff RS, Lorents DC (1995) Carbon 33:925
Lau KT, Hui D (2002) Composites: Part B 33:263
Schadler LS, Giannaris SC, Ajayan PM (1998) Appl. Phys. Lett. 73:3842
Krishnan A, Dujardin E, Ebbesen TW, Yianilos PN, Treacy MMJ (1998) Phys. Rev. B 58:14013
Yakobson BI, Brabec CJ, Bernholc J (1996) Phys. Rev. Lett. 76:2511
Lu JP (1997) Phys. Rev. Lett. 79:1297
Dresselhaus MS, Dresselhaus G, Saito R (1995) Carbon 33:883
Zhang P, Huang Y, Geubelle PH, Klein PA, Hwang KC (2002) Int. J. Solids Struct. 39:3893
Natsuki T, Tantrakan K, Endo M (2004) Carbon 42:39
Reich S, Thomsen C, Ordejon P (2002) Phys. Rev. B 65:153407
Li C, Chou TW (2004) Phys. Rev. B 69:073401
Galanov BA, Galanov SB, Gogotsi Y (2002) J. Nanopart. Res. 4:207
Sharma SM, Karmakar S, Sikka SK, Teredesai PV, Sood AK, Govindaraj A, Rao CNR (2001) Phys. Rev. B 63:205417
Tang J, Qin LC, Sasaki T, Yudasaka M, Matsushita A, Iijima S (2000) Phys. Rev. Lett. 85:1887
Venkateswaran UD, Rao AM, Richter E, Menon M, Rinzler A, Smalley RE, Eklund PC (1999) Phys. Rev. B 59:10928
Peters MJ, McNeil LE, Lu JP, Kahn D (2000) Phys. Rev. B 61:5939
Kawasaki S, Matsuoka Y, Yokomae T, Nojima Y, Okino F, Touhara H, Kataura H (2005) Carbon 43:37
Natsuki T, Tantrakarn K, Endo M (2004) Appl. Phys. A: Mater. Sci. Process. 79:117
Shen L, Li J (2000) Phys. Rev. B 69:045414
Cornell WD, Cieplak P, Bayly CI, Gould IR, Merz KM, Ferguson DM, Spellmeyer DC, Fox T, Caldwell JW Kollman PA (1995) J Am Chem Soc 117:5179
He XQ, Kitipornchai S, Liew KM (2005) J. Mech. Phys. Solids 53:303
Zhang XH, Sun DY, Liu ZF, Gong XG (2004) Phys. Rev. B 70:035422
Saito R, Matsuo R, Kimura T, Dresselhaus G, Dresselhaus MS (2001) Chem. Phys. Lett. 384:187
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
PACS
61.46.+w; 62.20.Dc; 62.20.-x; 62.25.+g
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Natsuki, T., Hayashi, T. & Endo, M. Mechanical properties of single- and double-walled carbon nanotubes under hydrostatic pressure. Appl. Phys. A 83, 13–17 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-005-3462-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-005-3462-3