Abstract
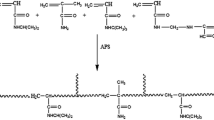
Chemical hydrogel based on poly(γ-glutamic acid) obtained from Bacillus licheniformis (ATCC-9945a) and using urea as a crosslinking agent was synthesized. The hydrogel was characterized by infrared spectroscopy, scanning electron microscopy, thermal analysis and swelling capacity. The crosslinking of the biopolymer was evidenced by changes in the intensities of signals in the infrared spectrum corresponding to amide groups, with respect to the spectrum of the pure biopolymer. Moreover, a porous structure, characteristic of hydrogels, with average pore size of 80 ± 31 μm was confirmed. The hydrogel showed a glass transition temperature of 144.5 °C and a decomposition temperature of 219 °C. The swelling ratio of the hydrogel increased with the increase of contact time with the swelling medium and pH, presenting values at equilibrium of 6.6, 13.4 and 15.3 at pH 3.6, 7.4 and 10, respectively; meanwhile, little influence of temperature on the swelling of the material was observed. Moreover, through the use of mathematical models, it is deduced that the swelling of the hydrogel in the buffer solutions occurs through lower Fickian and Fickian type mechanisms, and in deionized water an anomalous mechanism predominates.
Graphical abstract










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hamidi M, Azadi A, Rafiei P (2008) Hydrogel nanoparticles reviews in drug delivery. Adv Drug Del 60(15):1638–1649. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2008.08.002
Rodríguez DE, Romero-García J, Ramirez-Vargas E, Ledezma-Pérez AS, Arias-Marín E (2006) Synthesis and swelling characteristics of semi-interpenetrating polymer network hydrogels composed of poly(acrylamide) and poly((-glutamic acid). Mater Lett 60:1390–1393. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2005.11.033
Abu Elella MH, Goda ES, Gab-Allah MA, Hong SE, Pandit B, Lee S, Gamal H, Rehman A, Yoon KR (2020) Xanthan gum-derived materials for applications in environment and eco-friendly materials: a review. J Environ Chem Eng. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.104702
Goda ES, Abu Elella MH, Sohail M, Singu BS, Pandit B, El Shafey AM, Aboraia AM, Gamal H, Hong SE, Yoon KR (2021) N-methylene phosphonic acid chitosan/graphene sheets decorated with silver nanoparticles as green antimicrobial agents. Int J Biol Macromol 182:680–688. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.04.024
Akhtar MF, Hanif M, Ranjha NM (2016) Methods of synthesis of hydrogels … A review. Saudi Pharmaceutical Journal 24:554–559. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsps.2015.03.022
Abu Elella MH, Goda ES, Abdallah HM, Shalan AE, Gamal H, Yoon KR (2020) Innovative bactericidal adsorbents containing modified xanthan gum/montmorillonite nanocomposites for wastewater treatment. Int J Biol Macromol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.11.065
Elgamal AM, Abu Elella MH, Saad GR, Abd El-Ghany NA (2022) Synthesis, characterization and swelling behavior of high-performance antimicrobial biocompatible copolymer based on carboxymethyl xanthan. Mater Today Commun 33:104209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2022.104209
Abu Elella MH, Hanna DH, Mohamed RR, Sabaa MW (2021) Synthesis of xanthan gum/trimethyl chitosan interpolyelectrolyte complex as pH-sensitive protein carrier. Polym Bull. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-021-03656-3
Chatterjee S, Chi-leung P (2021) Review of applications and future prospects of stimuli-responsive hydrogel based on thermo-responsive biopolymers in drug delivery systems. Polymers 13:2086–2101. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13132086
Giubertoni G, Burla F, Bakker HJ, Koenderink GH (2020) Connecting the stimuli-responsive rheology of biopolymer hydrogels to underlying hydrogen-bonding interactions. Macromolecules 53:10503–10513. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.macromol.0c01742
Abdel-Aziz MM, Abu Elella MH, Mohamed RR (2019) Green synthesis of quaternized chitosan/silver nanocomposites for targeting mycobacterium tuberculosis and lung carcinoma cells (A-549). Int J Biol Macromol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.09.096
Ngwuluka NC, Abu-Thabit NY, Uwaezuoke OJ, Erebor JO, Ilomuanya MO, Mohamed RR, Ebrahim NA (2021) Natural polymers in micro-and nanoencapsulation for therapeutic and diagnostic applications: part II-polysaccharides and proteins. Nano-and Microencaps-Tech Appl. https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.88590
Ngwuluka NC, Abu-Thabit NY, Uwaezuoke OJ, Erebor JO, Ilomuanya MO, Mohamed RR, Ebrahim NA (2021) Natural polymers in micro-and nanoencapsulation for therapeutic and diagnostic applications: part I: lipids and fabrication techniques. Nano Microencapsul Tech Appl. https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.88590
Abu Elella MH, Abdel-Aziz MM, Abd El-Ghany NA (2021) Synthesis of a high-performance antimicrobial o-quaternized alginate – a promising potential antimicrobial agent. Cellulose Chem Technol 55(1–2):75–86
Nair P, Navale GR, Dharne MS (2021) Poly-gamma-glutamic acid biopolymer: a sleeping giant with diverse applications and unique opportunities for commercialization. Biomass Convers Biorefinery. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-021-01467-0
Zhang K, Wu J, Zhang W, Sh Yan J, Ding X, Chen L, Cui JY (2018) In situ formation of hydrophobic clusters to enhance mechanical performance of biodegradable poly(L-glutamic acid)/poly(ε-caprolactone) hydrogel towards meniscus tissue engineering. J Mater Chem B 6:7822–7833. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8TB01453A
Nie G, Hong K, Zhang E, Liu N, Wang M, Wang L, Zang Y (2020) Fabrication of a porous chitosan/poly-(γ-glutamic acid) hidrogel with a high absorption capacity by electrostatic contacts. Int J Biol Macromol 159:986–994. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.05.112
Kwiecien I, Niewolik D, Ekere AI, Gupta A, Radecka I (2020) Synthesis of hydrogels made of poly-γ-glutamic acid (γ-PGA) for potential applications as probiotic-delivery vehicles. Appl Sci 10(8):2787. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10082787
Dou Ch, Li Z, Gong J, Li Q, Qiao Ch, Zhang J (2021) Bio-based poly (γ-glutamic acid) hydrogels reinforced with bacterial cellulose nanofibers exhibiting superior mechanical properties and cytocompatibility. Int J Biol Macromol 170:354–365. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.12.148
Yang R, Wang X, Liu S, Zhang W, Wang P, Liu X, Ren Y, Tan X, Chi B (2020) Bioinspired poly (γ-glutamic acid) hydrogels for enhanced chondrogenesis of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Int J Biol Macromol 142:332–344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.09.104
Li Z, He G, Hua J, Wu M, Guo W, Gong J, Zhang J, Qiaoc Ch (2017) Preparation of γ-PGA hydrogels and swelling behaviors in salt solutions with different ionic valence numbers. R S Chem Adv 7:11085–11093. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA26419K
Gonzales D, Fan K, Sevoian M (1996) Synthesis and swelling characterizations of a poly(gamma-glutamic acid) hydrogel. J Polym Sci A Polym Chem 34:2019–2027. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1099-0518(19960730)34:10%3c2019::AIDPOLA19%3e3.0.CO;2-K
Murakami S, Aoki N (2006) Bio-based hydrogels prepared by cross-linking of microbial poly (γ-glutamic acid) with various saccharides. Biomacromol 7:2122–2127. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm0600264
Liu L, Mo H, Wei S, Raftery D (2012) Quantitative analysis of urea in human urine and serum by 1H nuclear magnetic resonance. Analyst 137:595–600. https://doi.org/10.1039/C2AN15780B
Rodríguez-Félix DE, Castillo-Ortega MM, Real-Félix D, Romero-García J, Ledezma-Pérez AS, Rodríguez-Félix F (2011) Synthesis and swelling properties of pH- and temperature sensitive interpenetrating polymer networks composed of poly(acrylamide) and poly(c-glutamic acid). J Appl Polym Sci 119:3531–3537. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.33006
Tasdelen B, Kayaman N, Güven O, Baysal BM (2004) pH-thermoreversible hydrogels. I. Synthesis and characterization of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide/maleic acid) copolymeric hydrogels. Radiat Phys Chem 69:303–310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radphyschem.2003.07.004
Rodríguez-Félix DE, Pérez-Caballero D, del Castillo-Castro T, Castillo-Ortega MM, Garmendía-Diago Y, Alvarado-Ibarra J, Plascencia-Jatomea M, Ledezma-Pérez AS, Burruel-Ibarra SE (2022) Chitosan hydrogels chemically crosslinked with L-glutamic acid and their potential use in drug delivery. Polym Bull. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-022-04152-y
Rodríguez-Rodríguez R, García-Carvajal ZY, Jiménez-Palomar I, Jiménez-Avalos JA, Espinosa-Andrews H (2019) Development of gelatin/chitosan/PVA hydrogels: thermal stability, water state, viscoelasticity, and cytotoxicity assays. J APPL POLYM SCI. https://doi.org/10.1002/APP.47149
Pereira AES, Sandoval-Herrera IE, Zavala-Betancourt SA, Oliveira HC, Ledezma-Pérez AS, Romero J, Fraceto LF (2017) γ-Polyglutamic acid/chitosan nanoparticles for the plant growth regulator gibberellic acid: characterization and evaluation of biological activity. Carbohyd Polym 157:1862–1873. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.11.073
Rodríguez-Félix DE, Pérez-Martínez CJ, Castillo-Ortega MM, Pérez-Tello M, Romero-García J, Ledezma-Pérez AS, Del Castillo-Castro T, Rodríguez-Félix F (2012) pH- and temperature-sensitive semi-interpenetrating network hydrogels composed of poly(acrylamide) and poly(γ-glutamic acid) as amoxicillin controlled-release system. Polym Bull 68:197–207. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-011-0549-1
Wang X, Gou C, Gao C et al (2021) Production of a novel nontoxic γ-PGA/casein composite hydrogel using MTG and optimization by response Surface methodology. Grain Oil Sci Technol 4(2):71–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gaost.2021.04.001
Yang N, Wang Y, Zhang Q, Chen L, Zhao Y (2017) γ-Polyglutamic acid mediated crosslinking PNIPAAm-based thermo/pH-responsive hydrogels for controlled drug reléase. Polym Degrad Stab 144:53–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2017.07.028
Ho GH, Ho TI, Hsieh KH, Su YC, Lin PY, Yang J, Yang KH, Yang SC (2006) γ-polyglutamic acid produced by bacillus subtilis (natto): structural characteristics, chemical properties and biological functionalities. J Chin Chem Soc 53:1363–1384. https://doi.org/10.1002/jccs.200600182
Hua J, Li Z, Xia W, Yang N, Gong J, Zhang J, Qiao C (2016) Preparation and properties of EDC/NHS mediated crosslinking poly (gamma-glutamic acid)/epsilon-polylysine hydrogels. Mater Sci Eng, C 61:879–892. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2016.01.001
Kunioka M, Choi HJ (1996) Preparation conditions and swelling equilibria of biodegradable hydrogels prepared from microbial poly(γ-glutamic acid) and poly(ε- lysine). J Environ Polym Degrad 4(2):123–129. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf02074873
Kwiecien I, Niewolik D, Itohowo A, Gupta A, Radecka I (2020) Synthesis of hydrogels made of poly-γ-glutamic acid (γ-pga) for potential applications as probiotic-delivery vehicles. Appl Sci 10(8):2787–2801. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10082787
Wang Y, He G, Li Z, Hua J, Wu M, Gong J, Zhang J, Ban LT, Huang L (2018) Novel biological hydrogel: swelling behaviors study in salt solutions with different ionic valence number. Polymers 10:112. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10020112
Zeng W, Hu WK, Li H, Jing YH, Kang H, Jiang Q, Zhang C (2014) Preparation and characterization of poly(γ-glutamic acid) hydrogels as potential tissue engineering scaffolds. Chin J Polym Sci 32(11):1507–1514. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10118-014-1536-4
González N, Prin JL, Benítez JL, Ramírez A, García A, Ramirez M, Sabino M, de Gáscue BR (2012) Estudio de la cinética de difusión en hidrogeles sintetizados a partir de acrilamida-co-ácido acrílico con turba y almidón vía calentamiento convencional y bajo radiación microondas. Rev LatinAm Metal Mat 32(1):136–144
Benítez JL, Lárez C, Rojas B (2015) Cinética de absorción y transporte del agua en hidrogeles sintetizados a partir de acrilamida y anhídrido maleico. Rev LatinAm Metal Mat 35(2):242–253
Gierszewska-Drużyńska M, Ostrowska-Czubenko J (2012) Mechanism of water diffusion into noncrosslinked and ionically crosslinked chitosan membranes. Prog Chem Appl Chitin Deriv 17:59–66
Caykara T (2004) Effect of maleic acid content on network structure and swelling properties of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-comaleic acid) polyelectrolyte hydrogels. J Appl Polym Sci 92:763–769. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.20032
Tasdelen B, Kayaman-Apohan N, Guven O, Baysal BM (2004) pH-thermoreversible hydrogels. I. Synthesis and characterization of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide/maleic acid) copolymeric hydrogels. Radiat Phys Chem 69:303–310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radphyschem.2003.07.004
Acknowledgements
Y. Garmendía-Diago acknowledges CONACYT (Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología, México) for the financial support provided for her graduate studies during this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YG-D. Methodology, Investigation, Formal Analysis, Data curation, Software, Writing- Original draft preparation, Writing- Reviewing and Editing. DER-F*. Project administration, Conceptualization, Methodology, Investigation, Writing- Reviewing and Editing. DP-C, EB-H. Investigation, Data curation, MMC-O, TDC-C, HSO, JMQ-C, MP-J, FR-F, ASL-P. Investigation, Supervision, Validation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest of any kind when submitting this manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Garmendía-Diago, Y., Rodríguez-Félix, D.E., Pérez-Caballero, D. et al. Synthesis of a novel pH-sensitive hydrogel based on poly(γ-glutamic acid) crosslinked with urea. Polym. Bull. 81, 3725–3741 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-023-04892-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-023-04892-5