Abstract
Novel polyetheramine-based hydrogels have been synthesized by reacting difunctional Jeffamine of varying molecular weights (ED600, ED900 and ED2003) with glutaraldehyde (GA) in the presence of trifunctional Jeffamine (T403) as a crosslinker. The prepared hydrogels were characterized by Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy, thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) and differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) techniques. Network properties of the hydrogels were evaluated via swelling investigations. Higher molecular weight of Jeffamine generated hydrogel networks with lower crosslink densities, consequently higher swelling abilities. The crosslink density of the hydrogels increased with increasing GA amount. The prepared hydrogels demonstrated to be pH and temperature responsive depicting decrease in swelling ratios with increasing pH and temperature. The obtained swelling results indicated that the swelling behavior of the hydrogels agreed with the Flory–Rehner equation.
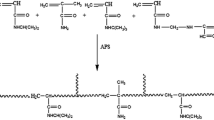
Graphical abstract
Novel polyetheramine crosslinked based water-insoluble hydrogels having imine functional groups in their network structures were prepared via polymerization of difunctional Jeffamine monomers. Investigated influence of different Jeffamine molecular weight synthesized hydrogels depicted suitable swelling, pH and temperature responsive properties.












Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- JED:
-
Jeffamine ED series
- DCE:
-
Dichloro ethane
- PEG:
-
Polyethylene glycol
- POE:
-
Polyoxyethylene
- POP:
-
Polyoxypropylene
- THF:
-
Tetrahydrofuran
- f GA :
-
Mole fraction of glutaraldehyde in the gel
- f JED :
-
Mole fraction of Jeffamine ED in the gel
- f JT :
-
Mole fraction of Jeffamine T403 in the gel
- ∆H endo :
-
Endothermic enthalpy
- ΔH w :
-
Heat of fusion of pure water
- M c :
-
Average molecular weight between two successive crosslinks
- M d :
-
Weights of dry hydrogel after leaching
- M GA :
-
Molecular mass of glutaraldehyde
- M JT :
-
Molecular mass of Jeffamine T403
- M JED :
-
Molecular mass of Jeffamine ED series
- M p :
-
Weights of the hydrogels after preparation
- M s :
-
Weights of hydrogel after swelling
- M o :
-
Molar mass of repeating units
- q v :
-
Equilibrium swelling ratio
- pH pzc :
-
pH point zero charge
- V 1 :
-
Molar volume of solvent
- V 2m :
-
Volume fraction of polymer network in swollen state
- V 2r :
-
Volume fraction of polymer network in relaxed state
- V 2s :
-
Volume fraction of solvent
- V r :
-
Average molar volume of polymer repeating units
- χ :
-
Polymer solvent interaction parameter
- W f :
-
Fraction of the freezing water
- W nf :
-
Fraction of non-freezing bound water
- W ∞ :
-
Equilibrium water content of the hydrogel
References
Krakovský I, Cayuela JC, Serra RS, Salmerón-Sánchez M, Dodda JM (2014) Epoxy networks and thermosensitive hydrogels prepared from α,ω-diamino terminated polyoxypropylene and polyoxyethylene bis (glycidyl ether). Eur Polym J 55:144–152
Krakovský I, Martínez-Haya R, Ferrer GG, Serra RS, Dodda JM (2015) Epoxy networks and hydrogels prepared from α,ω-diamino terminated poly (oxypropylene)-b-poly (oxyethylene)-b-poly (oxypropylene) and polyoxypropylene bis (glycidyl ether). Eur Polym J 62:19–30
Trey SM, Wicks DA (2005) Synthesis and characterization of poly (ethylene glycol) based discrete hydrogels. Polymer 46:568 (preprints)
Saito H, Hoffman AS, Ogawa HI (2007) Delivery of doxorubicin from biodegradable PEG hydrogels having Schiff base linkages. J Bioact Compat Polym 22:589–601
Damink LO, Dijkstra P, Van LM, Van WP, Nieuwenhuis P, Feijen J (1995) Glutaraldehyde as a crosslinking agent for collagen-based biomaterials. J Mater Sci Mater Med 6:460–472
Migneault I, Dartiguenave C, Bertrand MJ, Waldron KC (2004) Glutaraldehyde: behavior in aqueous solution, reaction with proteins, and application to enzyme crosslinking. Biotechniques 37:790–806
Hardy P, Nicholls AC, Rydon HN (1969) The nature of glutaraldehyde in aqueous solution. J Chem Soc D 10:565–566
Margel S, Rembaum A (1980) Synthesis and characterization of poly (glutaraldehyde). A potential reagent for protein immobilization and cell separation. Macromolecules 13:19–24
Kawahara J-I, Ohmori T, Ohkubo T, Hattori S, Kawamura M (1992) The structure of glutaraldehyde in aqueous solution determined by ultraviolet absorption and light scattering. Anal Biochem 201:94–98
Liu X, Chen Y, Huang Q, He W, Feng Q, Yu B (2014) A novel thermo-sensitive hydrogel based on thiolated chitosan/hydroxyapatite/beta-glycerophosphate. Carbohydr Polym 110:62–69
Zhou L, Chen M, Guan Y, Zhang Y (2014) Multiple responsive hydrogel films based on dynamic Schiff base linkages. Polym Chem 5:7081–7089
Yildiz U, Kemik ÖF, Hazer B (2010) The removal of heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions by novel pH-sensitive hydrogels. J Hazard Mater 183:521–532
Sun G, Zhang XZ, Chu CC (2007) Formulation and characterization of chitosan-based hydrogel films having both temperature and pH sensitivity. J Mater Sci Mater Med 18:1563–1577
Bader RA, Herzog KT, Kao WJ (2009) A study of diffusion in poly(ethyleneglycol)-gelatin based semi-interpenetrating networks for use in wound healing. Polym Bull 62:381–389
Li M (2014) Thin films of stimuli-responsive hydrogels. Université Pierre et Marie Curie, Paris
Krakovský I, Pleštil J, Almásy L (2006) Structure and swelling behaviour of hydrophilic epoxy networks investigated by SANS. Polymer 47:218–226
Mocanu G, Mihaï D, Dulong V, Picton L, Le Cerf D (2012) New anionic crosslinked multi-responsive pullulan hydrogels. Carbohydr Polym 87:1440–1446
Tang S, Huang L, Shi Z, He W (2015) Water-based synthesis of cationic hydrogel particles: effect of the reaction parameters and in vitro cytotoxicity study. J Mater Chem B 3:2842–2852
Yoshioka H, Mori Y, Shimizu M (2003) Separation and recovery of DNA fragments by electrophoresis through a thermoreversible hydrogel composed of poly (ethylene oxide) and poly (propylene oxide). Anal Biochem 323:218–223
Iannace S, Nicolais L, Huang S (1997) Water sorption of glycol-modified cross-linked gelatin-based hydrogels. J Mater Sci 32:1405–1408
Dulong V, Mocanu G, Picton L, Le Cerf D (2012) Amphiphilic and thermosensitive copolymers based on pullulan and Jeffamine®: synthesis, characterization and physicochemical properties. Carbohydr Polym 87:1522–1531
Lee JH, Bucknall DG (2008) Swelling behavior and network structure of hydrogels synthesized using controlled UV-initiated free radical polymerization. J Polym Sci B: Polym Phys 46:1450–1462
Ranjha NM, Qureshi UF (2014) Preparation and characterization of crosslinked acrylic acid/hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose hydrogels for drug delivery. Int J Pharm Pharmceu Sci 6:400–410
Yildiz U, Hazer B (1998) Free radical crosslinking copolymerization. Gelation behavior of macromonomeric azoinitiators versus macrocrosslinkers. Macromol Chem Phys 199:163–168
Isik B, Kis M (2004) Preparation and determination of swelling behavior of poly(acrylamide-co-acrylic acid) hydrogels in water. J Appl Polym Sci 94:1526–1531
Nassajian MM (2012) Measuring the mesh size of hydrogels. http://infoscience.epfl.ch
Yildiz U, Hazer B (2000) Dispersion redox copolymerization of methyl methacrylate with macromonomeric azoinitiator as a macrocrosslinker. Polym 41:539–544
Mawad D, Foster JL, Lauto A (2008) Drug-delivery study and estimation of polymer–solvent interaction parameter for bisacrylate ester-modified Pluronic hydrogels. Int J Pharm 360:231–235
Eliassi A, Modarress H, Mansoori GA (1999) Measurement of activity of water in aqueous poly (ethylene glycol) solutions (effect of excess volume on the Flory–Huggins ξ-parameter). J Chem Eng Data 44:52–55
Caykara T, Inam R (2004) Determination of average molecular weight between crosslinks and polymer-solvent interaction parameters of poly(acrylamide-g-ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid) polyelectrolyte hydrogels. J Appl Polym Sci 91:2168–2175
Bajpai S, Saggu SS (2006) Water uptake behavior of poly (methacrylamide-co-N-vinyl-2- pyrrolidone-co-itaconic acid) as pH-sensitive hydrogels: part I. J Macromol Sci A 43:1135–1150
Dhar DN, Taploo C (1982) Schiff-bases and their applications. J Sci Ind Res 41:501–506
Adabiardakani A, Hakimi M, Kargar H (2012) Cinnamaldehyde Schiff base derivatives: a short review. World Appl Program 2:472–476
Chaudhary NK (2012) Synthesis and medicinal use of metal complexes of Schiff bases. Bibechana 9:75–80
Magid AA, Carson K, Harris B, Maryanoff C, Shah R (1996) Reductive amination of aldehydes and ketones with sodium triacetoxyborohydride. Studies on direct and indirect reductive amination procedures. J Org Chem 61:3849–3862
Pei LH, Kurumada K, Tanigaki M, Hiro M, Susa K (2005) Effect of drying on the mesoporous structure of sol-gel derived silica with PPO-PEO-PPO template block copolymer. J Colloid Interface Sci 284:222–227
Macan J, Brnardić I, Ivanković M, Mencer HJ (2005) DSC study of cure kinetics of DGEBA-based epoxy resin with poly (oxypropylene) diamine. J Therm Anal Calorim 81:369–373
Hine J, Craig JC Jr, Underwood JG, Via FA (1970) Kinetics and mechanism of the hydrolysis of N-isobutylidenemethylamine in aqueous solution. J Am Chem Soc 92:5194–5199
Piest M, Zhang X, Trinidad J, Engbersen JF (2011) pH-responsive, dynamically restructuring hydrogels formed by reversible crosslinking of PVA with phenylboronic acid functionalised PPO–PEO–PPO spacers (Jeffamines®). Soft Matter 7:11111–11118
Ngwabebhoh FA, Erdem A, Yildiz U (2016) Synergistic removal of Cu (II) and nitrazine yellow dye using an eco-friendly chitosan-montmorillonite hydrogel: optimization by response surface methodology. J Appl Polym Sci 133:1–4
Yang M, Liu BT, Gao G, Liu X (2010) Poly (maleic anhydride-co-acrylic acid)/poly (ethylene glycol) hydrogels with pH-and ionic-strength-responses. Chin J Polym Sci 28:951–959
Mocanu G, Souguir Z, Picton L, Le Cerf D (2012) Multi-responsive carboxymethyl polysaccharide crosslinked hydrogels containing Jeffamine side-chains. Carbohydr Polym 89:578–585
Acknowledgments
The authors Ahmet Erdem and Asabuwa N. Fahanwi wish to thank the TUBITAK for 2211-D and 2215 fellowship programs and Kocaeli University for the financial support (BAP-2011/60) provided in completing this work. Also great thanks to Physics Department research laboratory for TGA and DSC measurements. Thanks goes to Hunstman for providing the Jeffamine samples used in this research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest for this manuscript.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Erdem, A., Ngwabebhoh, F.A. & Yildiz, U. Synthesis, characterization and swelling investigations of novel polyetheramine-based hydrogels. Polym. Bull. 74, 873–893 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-016-1751-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-016-1751-y