Abstract
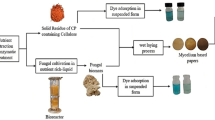
Ten white-rot fungal isolates were evaluated for the decolorization potential of pulp and paper mill effluent. Trametes elegans PP17-06, Pseudolagarobasidium sp. PP17-33, and Microporus sp.2 PP17-20 showed the highest decolorization efficiencies between 42 and 54% in 5 d. To reveal the mechanisms involved in decolorization and assess the long-term performance, PP17-06, which showed the highest decolorization efficiency, was further investigated. It could reduce the ADMI color scale by 63.6% in 10 d. However, extending the treatment period for more than 10 d did not significantly enhance the decolorization efficiencies. The maximum MnP activity of 3.27 U L−1 was observed on the 6 d during the biodegradation. In comparison, laccase activities were low with the maximum activity of 0.38 U L−1 (24 d). No significant LiP activities were monitored during the experiment. Dead fungal biomass showed an optimum decolorization efficiency of 44.18% in 8 d employing the biosorption mechanism. No significant changes in the decolorization efficiency were observed after that, suggesting the equilibrium status was reached. These results revealed that PP17-06 has the potential to decolorize pulp and paper mill effluent by employing both biodegradation and biosorption processes.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Haq I, Mazumder P, Kalamdhad AS (2020) Recent advances in removal of lignin from paper industry wastewater and its industrial applications – a review. Bioresour Technol 312:123636. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123636
Haq I, Raj A (2020) Pulp and paper mill wastewater: ecotoxicological effects and bioremediation approaches for environmental safety. In: Bharagava R, Saxena G (eds) Bioremediation of industrial waste for environmental safety. Springer, Singapore, pp 333–356
Mehmood K, Rehman SKU, Wang J, Farooq F, Mahmood Q, Jadoon AM, Javed MF, Ahmad I (2019) Treatment of pulp and paper industrial effluent using physicochemical process for recycling. Water 11(11):2393. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11112393
Gaur N, Narasimhulu K, Pydi Setty Y (2018) Extraction of ligninolytic enzymes from novel Klebsiella pneumoniae strains and its application in wastewater treatment. Appl Water Sci 8(4):111. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-018-0758-y
Hooda R, Bhardwaj NK, Singh P (2018) Brevibacillus parabrevis MTCC 12105: A potential bacterium for pulp and paper effluent degradation. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 34(2):31. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-018-2414-y
Sachan P, Madan S, Hussain A (2019) Isolation and screening of phenol-degrading bacteria from pulp and paper mill effluent. Appl Water Sci 9(4):100. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-019-0994-9
Sen Sudip K, Raut S, Gaur M, Raut S (2020) Biodegradation of lignin from pulp and paper mill effluent: optimization and toxicity evaluation. J Hazard Toxic Radioact Waste 24(4):04020032. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)HZ.2153-5515.0000522
Singh AK, Yadav P, Bharagava RN, Saratale GD, Raj A (2019) Biotransformation and cytotoxicity evaluation of kraft lignin degraded by ligninolytic Serratia liquefaciens. Front Microbiol 10:2364. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.02364
Zabel RA, Morrell JJ (2020) Chapter Eight - Chemical changes in wood caused by decay fungi. In: Zabel RA, Morrell JJ (eds) Wood microbiology, 2nd edn. Academic Press, Cambridge, pp 215–244
Zainith S, Purchase D, Saratale GD, Ferreira LFR, Bilal M, Bharagava RN (2019) Isolation and characterization of lignin-degrading bacterium Bacillus aryabhattai from pulp and paper mill wastewater and evaluation of its lignin-degrading potential. 3 Biotech 9:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-019-1631-x
Bettin F, Cousseau F, Martins K, Boff NA, Zaccaria S, Moura da Silveira M, Pinheiro Dillon AJ (2019) Phenol removal by laccases and other phenol oxidases of Pleurotus sajor-caju PS-2001 in submerged cultivations and aqueous mixtures. J Environ Manage 236:581–590. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.02.011
Teerapatsakul C, Chitradon L (2016) Physiological regulation of an alkaline-resistant laccase produced by Perenniporia tephropora and efficiency in biotreatment of pulp mill effluent. Mycobiology 44(4):260–268. https://doi.org/10.5941/MYCO.2016.44.4.260
Sigoillot J-C, Berrin J-G, Bey M, Lesage-Meessen L, Levasseur A, Lomascolo A, Record E, Uzan-Boukhris E (2012) Fungal strategies for lignin degradation. Adv Bot Res 61:263–308. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-416023-1.00008-2
Janusz G, Pawlik A, Sulej J, Świderska-Burek U, Jarosz-Wilkołazka A, Paszczyński A (2017) Lignin degradation: microorganisms, enzymes involved, genomes analysis and evolution. FEMS Microbiol Rev 41(6):941–962. https://doi.org/10.1093/femsre/fux049
Fang W, Zhang X, Zhang P, Carol Morera X, van Lier JB, Spanjers H (2020) Evaluation of white rot fungi pretreatment of mushroom residues for volatile fatty acid production by anaerobic fermentation: Feedstock applicability and fungal function. Bioresour Technol 297:122447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.122447
Grelska A, Noszczyńska M (2020) White rot fungi can be a promising tool for removal of bisphenol A, bisphenol S, and nonylphenol from wastewater. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 27(32):39958–39976. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10382-2
Zhang A, Wang G, Gong G, Shen J (2017) Immobilization of white rot fungi to carbohydrate-rich corn cob as a basis for tertiary treatment of secondarily treated pulp and paper mill wastewater. Ind Crops Prod 109:538–541. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2017.09.006
Prasongsuk S, Lotrakul P, Imai T, Punnapayak H (2009) Decolourization of pulp mill wastewater using thermotolerant white rot fungi. Sci Asia 35:37–41. https://doi.org/10.2306/scienceasia1513-1874.2009.35.037
Wu J, Xiao Y-Z, Yu H-Q (2005) Degradation of lignin in pulp mill wastewaters by white-rot fungi on biofilm. Bioresour Technol 96(12):1357–1363. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2004.11.019
Costa S, Dedola DG, Pellizzari S, Blo R, Rugiero I, Pedrini P, Tamburini E (2017) Lignin biodegradation in pulp-and-paper mill wastewater by selected white rot fungi. Water 9(12):935. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9120935
Barapatre A, Jha H (2016) Decolourization and biological treatment of pulp and paper mill effluent by lignin-degrading fungus Aspergillus flavus strain F10. J Curr Microbiol Appl Sci 5:19–32. https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2016.505.003
Rybczyńska-Tkaczyk K, Korniłłowicz-Kowalska T (2016) Biosorption optimization and equilibrium isotherm of industrial dye compounds in novel strains of microscopic fungi. Int J Environ Sci Technol 13(12):2837–2846. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-016-1111-3
Maurya NS, Mittal AK, Cornel P, Rother E (2006) Biosorption of dyes using dead macro fungi: effect of dye structure, ionic strength and pH. Bioresour Technol 97(3):512–521. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2005.02.045
Vaithanomsat P, Apiwatanapiwat W, Petchoy O, Chedchant J (2010) Decolorization of reactive dye by white-rot Fungus Datronia sp. KAPI0039. Kasetsart J (Nat Sci) 44:879–890
Thamvithayakorn P, Phosri C, Pisutpaisal N, Krajangsang S, Whalley AJS, Suwannasai N (2019) Utilization of oil palm decanter cake for valuable laccase and manganese peroxidase enzyme production from a novel white-rot fungus, Pseudolagarobasidium sp. PP17-33. 3 Biotech 9(11):417. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-019-1945-8
Argumedo-Delira R, Gómez-Martínez MJ, Uribe-Kaffure R (2021) Trichoderma biomass as an alternative for removal of congo red and malachite green industrial dyes. Appl Sci 11(1):448. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11010448
APHA (2017) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 23rd edn. American Public Health Association, Washington DC
Machado K, Matheus D (2006) Biodegradation of Remazol brilliant blue R by ligninolytic enzymatic complex produced by Pleurotus ostreatus. Braz J Microbiol 37(4):468–473. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1517-83822006000400013
Silva M, Souza V, Santos V, Kamida H, Vasconcellos-Neto J, Góes-Neto A, Koblitz M (2014) Production of manganese peroxidase by Trametes villosa on unexpensive substrate and its application in the removal of lignin from agricultural wastes. Adv Biosci Biotechnol 5:1067–1077. https://doi.org/10.4236/abb.2014.514122
Tien M, Kirk TK (1988) Lignin peroxidase of Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Methods Enzymol 161:238–249. https://doi.org/10.1016/0076-6879(88)61025-1
Raghukumar C, Chandramohan D, Michel FC, Redd CA (1996) Degradation of lignin and decolorization of paper mill bleach plant effluent (BPE) by marine fungi. Biotechnol Lett 18(1):105–106. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00137820
Srinivasan A, Viraraghavan T (2010) Decolorization of dye wastewaters by biosorbents: a review. J Environ Manage 91(10):1915–1929. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2010.05.003
Sagar S, Sharma I, Thakur M, Tripathi A (2020) Decolourization and degradation of Sunset Yellow-FCF and Acid Orange-7 by wild white rot fungi Trametes elegans and Trametes versicolor and their extracellular ligninolytic enzymes. Int J Sci Technol Res 9(1):2255–2271
Dhillon GS, Kaur S, Brar SK (2012) In-vitro decolorization of recalcitrant dyes through an ecofriendly approach using laccase from Trametes versicolor grown on brewer’s spent grain. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 72:67–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2012.05.012
Levin L, Melignani E, Ramo AM (2010) Effect of nitrogen sources and vitamins on ligninolytic enzyme production by some white-rot fungi. Dye decolorization by selected culture filtrates. Bioresour Technol 101(12):4554–4563. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.01.102
Hefnawy MA, Gharieb M, Shaaban MT, Soliman AM (2017) Optimization of culture condition for enhanced decolorization of direct blue dye by Aspergillus flavus and Penicillium canescens. J App Pharm Sci 7:083–092. https://doi.org/10.7324/JAPS.2017.70210
Souza ÉS, Souza JVB, Silva FT, Paiva TCB (2014) Treatment of an ECF bleaching effluent with white-rot fungi in an air-lift bioreactor. Environ Earth Sci 72(4):1289–1294. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3048-5
Souza JV, Silva ES, Silva FT, Paiva TC (2005) Fungal treatment of a delignification effluent from a nitrocellulose industry. Bioresour Technol 96(17):1936–1942. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2005.01.027
Kreetachat T, Chaisan O, Vaithanomsat P (2016) Decolorization of pulp and paper mill effluents using wood rotting fungus Fibrodontia sp. RCK783S. Int J Environ Sci Dev 7:321–324. https://doi.org/10.7763/IJESD.2016.V7.792
Neoh CH, Yahya A, Adnan R, Majid ZA, Ibrahim Z (2013) Optimization of decolorization of palm oil mill effluent (POME) by growing cultures of Aspergillus fumigatus using response surface methodology. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20(5):2912–2923. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-012-1193-5
Neoh CH, Lam CY, Lim CK, Yahya A, Ibrahim Z (2013) Decolorization of palm oil mill effluent using growing cultures of Curvularia clavata. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21(6):4397–4408. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-2350-1
Wang N, Chu Y, Wu F, Zhao Z, Xu X (2017) Decolorization and degradation of Congo red by a newly isolated white rot fungus, Ceriporia lacerata, from decayed mulberry branches. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 117:236–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2016.12.015
Fang W, Zhang P, Zhang X, Zhu X, van Lier JB, Spanjers H (2018) White rot fungi pretreatment to advance volatile fatty acid production from solid-state fermentation of solid digestate: efficiency and mechanisms. Energy 162:534–541. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2018.08.082
Pazarlıoǧlu NK, Sariişik M, Telefoncu A (2005) Laccase: production by Trametes versicolor and application to denim washing. Process Biochem 40(5):1673–1678. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2004.06.052
Pedroza A, Mosqueda R, Alonso-Vante N, Rodriguez Vazquez R (2007) Sequential treatment via Trametes versicolor and UV/TiO2/RuxSey to reduce contaminants in waste water resulting from the bleaching process during paper production. Chemosphere 67:793–801. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.10.015
Ramsay JA, Mok WHW, Luu YS, Savage M (2005) Decoloration of textile dyes by alginate-immobilized Trametes versicolor. Chemosphere 61(7):956–964. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.03.070
Sahoo D, Gupta R (2005) Evaluation of ligninolytic microorganisms for efficient decolorization of a small pulp and paper mill effluent. Process Biochem 40:1573–1578. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2004.05.013
Levin L, Forchiassin F, Ramo AM (2002) Copper induction of lignin-modifying enzymes in the white-rot fungus Trametes trogii. Mycologia 94(3):377–383. https://doi.org/10.2307/3761771
Kabbout R, Taha S (2014) Biodecolorization of textile dye effluent by biosorption on fungal biomass materials. Phys Procedia 55:437–444. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phpro.2014.07.063
Apiwatanapiwat W, Siriacha P, Vaithanomsat P (2005) Screening of fungi for decolorization of wastewater from pulp and paper industry. Kasetsart J (Nat Sci) 40:215–221
Chen C-L, Chang H-M, Kirk TK (1983) Carboxylic acids produced through oxidative cleavage of aromatic rings during degradation of lignin in spruce wood by Phanerochaete chrysosporium. J Wood Chem Technol 3(1):35–57
Torres JM, Cardenas C, Moron L, Guzman A, Dela Cruz TE (2012) Dye decolorization activities of marine-derived fungi isolated from Manila bay and Calatagan bay, Philippines. Philipp J Sci 140:133–143
Yeddou-Mezenner N (2010) Kinetics and mechanism of dye biosorption onto an untreated antibiotic waste. Desalination 262(1):251–259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2010.06.023
Kang Y, Xu X, Pan H, Tian J, Tang W, Liu S (2018) Decolorization of mordant yellow 1 using Aspergillus sp. TS-A CGMCC 12964 by biosorption and biodegradation. Bioengineered 9(1):222–232. https://doi.org/10.1080/21655979.2018.1472465
Yonten V, Ince M, Tanyol M, Yildirim N (2016) Adsorption of bisphenol A from aqueous solutions by Pleurotus eryngii immobilized on Amberlite XAD-4 using as a new adsorbent. Desalin Water Treat 57(47):22362–22369. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2015.1130659
Acknowledgment
We would like to acknowledge for the financial supports from King Mongkut’s University of Technology North Bangkok (KMUTNB-65-IP-03; KMUTNB-66-KNOW-18; KMUTNB-FF-65-67).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest in publishing the manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ridtibud, S., Suwannasai, N., Sawasdee, A. et al. Screening of White-Rot Fungi Isolates for Decolorization of Pulp and Paper Mill Effluent and Assessment of Biodegradation and Biosorption Processes. Curr Microbiol 80, 350 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-023-03464-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-023-03464-0