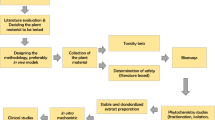
Abstract
In the quest for novel medications, researchers have kept on studying nature to unearth beneficial plant species with medicinal qualities that may cure various diseases and disorders. These medicinal plants produce different bioactive secondary metabolites with immense therapeutic importance. One such valuable secondary metabolite, reserpine (C33H40N2O9), has been used for centuries to cure various ailments like hypertension, cardiovascular diseases, neurological diseases, breast cancer, and human promyelocytic leukaemia. Rauvolfia spp. (family Apocynaceae) is an essential reservoir of this reserpine. The current review thoroughly covers different non-conventional or in vitro–mediated biotechnological methods adopted for pilot-scale as well as large-scale production of reserpine from Rauvolfia spp., including techniques like multiple shoot culture, callus culture, cell suspension culture, precursor feeding, elicitation, synthetic seed production, scale-up via bioreactor, and hairy root culture. This review further analyses the unexplored and cutting-edge biotechnological tools and techniques to alleviate reserpine production.
Key points
• Reserpine, a vital indole alkaloid from Rauvolfia spp., has been used for centuries to cure several ailments.
• Overview of biosynthetic pathways and biotechnological applications for enhanced production of reserpine.
• Probes the research gaps and proposes novel alternative techniques to meet the pharmaceutical industry’s need for reserpine while reducing the over-exploitation of natural resources.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anitha S, Kumari BDR (2006a) Stimulation of reserpine biosynthesis in the callus of Rauvolfia tetraphylla L. by precursor feeding. Afr J Biotechnol 5:659–661
Anitha S, Kumari BDR (2006b) Reserpine accumulation in NaCl treated calli of Rauvolfia tetraphylla L. Sci Asia 32:417–419
Astuti NP, Solichatun S, Susilowati A (2007) Reserpine content of Rauvolfia verticillata callus culture elicited by Pythium sp. Asian J Nat Prod Biochem 5:55–66. https://doi.org/10.13057/biofar/f050202
Baenas N, García-Viguera C, Moreno DA (2014) Elicitation: a tool for enriching the bioactive composition of foods. Molecules 19:13541–13563. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules190913541
Behzadi M, Javanmard AS, Khakdan F, Mohsenzadeh S (2022) Effects of urea supplementation and different substrates on the production of indole alkaloid reserpine in Catharanthus roseus plants. Plant Biosystems 156:1011–1018. https://doi.org/10.1080/11263504.2021.1986587
Bindu S, Rameshkumar K, Kumar B, Singh A, Anilkumar C (2014) Distribution of reserpine in Rauvolfia species from India–HPTLC and LC–MS studies. Ind Crops Prod 62:430–436. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2014.09.018
Cai Z, Wang WH, Yang J, Cai C-T (2009) Growth, photosynthesis and root reserpine concentrations of two Rauvolfia species in response to a light gradient. Ind Crops Prod 30:220–226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2009.03.010
Cigan E, Eggbauer B, Schrittwieser JH, Kroutil W (2021) The role of biocatalysis in the asymmetric synthesis of alkaloids–an update. RSC Adv 11:28223–28270. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1RA04181A
Deshmukh SR, Ashrit DS, Patil BA (2012) Extraction and evaluation of indole alkaloids from Rauwolfia serpentina for their antimicrobial and antiproliferative activities. Int J Pharm Pharm Sci 4:329–334
Dey A, Nandy S, Nongdam P, Tikendra L, Mukherjee A, Mukherjee S, Pandey DK (2020) Methyl jasmonate and salicylic acid elicit indole alkaloid production and modulate antioxidant defence and biocidal properties in Rauvolfia serpentina Benth. ex Kurz. in vitro cultures. South Afr J Bot 135:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sajb.2020.07.020
Faisal M, Alatar AA, Hegazy AK (2013) Molecular and biochemical characterization in Rauvolfia tetraphylla plantlets grown from synthetic seeds following in vitro cold storage. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 169:408–417. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-012-9977-0
Gamborg OL, Miller R, Ojima K (1968) Nutrient requirements of suspension cultures of soybean root cells. Exp Cell Res 50:151–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/0014-4827(68)90403-5
Gantait S, Kundu S (2017) Does synthetic seed storage at higher temperature reduce reserpine content of Rauvolfia serpentina (L.) Benth. ex Kurz.? Rend Lincei 28:679–686. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12210-017-0637-8
Gantait S, Kundu S, Ali MN, Sahu NC (2015) Synthetic seed production of medicinal plants: a review on influence of explants, encapsulation agent and matrix. Acta Physiol Plant 37:98. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-015-1847-2
Gantait S, Kundu S, Yeasmin L, Ali MN (2017) Impact of differential levels of sodium alginate, calcium chloride and basal media on germination frequency of genetically true artificial seeds of Rauvolfia serpentina (L.) Benth. ex Kurz. J Appl Res Med Aromat Plants 4:75–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jarmap.2017.01.005
Gantait S, Mukherjee E, Bandyopadhyay P, Bhattacharyya S (2022) M-brigde-and elicitor-assisted enhanced post-storage germination of Rauvolfia serpentina synthetic seeds, their genetic fidelity assessment and reserpine estimation. Ind Crops Prod 180:114732. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2022.114732
Goel MK, Goel S, Banerjee S, Shanker K, Kukreja AK (2010) Agrobacterium rhizogenes-mediated transformed roots of Rauwolfia serpentina for reserpine biosynthesis. Med Aromat Plant Sci Biotechnol 4:8–14
Goel MK, Mehrotra S, Kukreja AK, Shanker K, Khanuja SPS (2009) In vitro propagation of Rauwolfia serpentina using liquid medium, assessment of genetic fidelity of micropropagated plants, and simultaneous quantitation of reserpine, ajmaline, and ajmalicine. In: Jain SM, Saxena PK (eds) Protocols for in vitro cultures and secondary metabolite analysis of aromatic and medicinal plants. Methods Mol Biol 547:17–33. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-60327-287-2_2
Guru A, Dwivedi P, Kaur P, Pandey DK (2022) Exploring the role of elicitors in enhancing medicinal values of plants under in vitro condition. South Afr J Bot 149:1029–1043. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sajb.2021.10.014
Harisaranraj R, Suresh K, Babu SS (2009) Production of reserpine in somatic embryos of Rauwolfia serpentina cultured in bioreactors by the induction of elicitor (methyl Jasmonate). Glob J Biotechnol Biochem 4:143–147
Jahan R, Jannat K, Shoma JF, Khan MA, Shekhar HU, Rahmatullah M (2020) Drug discovery and herbal drug development: a special focus on the anti-diarrheal plants of Bangladesh. In: Sen S, Chakraborty R (eds) Herbal medicine in India: Indigenous knowledge, practice, innovation and its value. Singapore, pp 363–400. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-7248-3_23
Khan ZA, Shahzad SA, Anjum A, Bale AT, Naqvi SAR (2018) Synthetic approaches toward the reserpine. Synth Commun 48:1128–1147. https://doi.org/10.1080/00397911.2018.1434546
Kohli SK, Handa N, Bali S, Arora S, Sharma A, Kaur R, Bhardwaj R (2018) Modulation of antioxidative defense expression and osmolyte content by co-application of 24-epibrassinolide and salicylic acid in Pb exposed Indian mustard plants. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 147:382–393. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.08.051
Kumar S, Singh A, Bajpai V, Srivastava M, Singh BP, Ojha S, Kumar B (2016) Simultaneous determination of bioactive monoterpene indole alkaloids in ethanolic extract of seven Rauvolfia species using UHPLC with hybrid triple quadrupole linear ion trap mass spectrometry. Phytochem Anal 27:296–303. https://doi.org/10.1002/pca.2631
Kurup LB, Vijayan S (2021) Hepatoprotective efficacy of methanolic extract of monochoria vaginalis in acetaminophen induced toxicity in hep G2 cell lines. Materials Today: Proc 41:600–605. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.05.256
Mahadik SM, Sawardekar SV, Kelkar VG, Gokhale NB (2020) In vitro regeneration technique in Rauwolfia serpentina and quantification of reserpine. Int J Chem Stud 8:520–525. https://doi.org/10.22271/chemi.2020.v8.i6h.10827
Mehrotra S, Srivastava V, Rahman LU, Kukreja AK (2013) Overexpression of a Catharanthus tryptophan decarboxylase (tdc) gene leads to enhanced terpenoid indole alkaloid (TIA) production in transgenic hairy root lines of Rauwolfia serpentina. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 115:377–384. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-013-0369-0
Mehrotra S, Goel MK, Srivastava V, Rahman LU (2015) Hairy root biotechnology of Rauwolfia serpentina: a potent approach for the production of pharmaceutically important terpenoid indole alkaloids. Biotechnol Lett 37:253–263. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-014-1695-y
Mehrotra S, Srivastava V, Goel MK, Kukreja AK (2016) Scale-up of Agrobacterium rhizogenes-mediated hairy root cultures of Rauwolfia serpentina: a persuasive approach for stable reserpine production. In: Jain S (ed) Protocols for in vitro cultures and secondary metabolite analysis of aromatic and medicinal plants, 2nd edn. Methods Mol Biol 1391:241–257. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-3332-7_17
Mukherjee E, Gantait S, Kundu S, Sarkar S, Bhattacharyya S (2019) Biotechnological interventions on the genus Rauvolfia: recent trends and imminent prospects. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 103:7325–7354. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-019-10035-6
Mukherjee E, Sarkar S, Bhattacharyya S, Gantait S (2020) Ameliorated reserpine production via in vitro direct and indirect regeneration system in Rauvolfia serpentina (L.) Benth. ex Kurz. 3 Biotech 10:294. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-020-02285-3
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15:473–497. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-3054.1962.tb08052.x
Nielsen E, Temporiti MEE, Cella R (2019) Improvement of phytochemical production by plant cells and organ culture and by genetic engineering. Plant Cell Rep 38:1199–1215. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-019-02415-z
Nurcahyani N, Solichatun S, Anggarwulan E (2008) The reserpine production and callus growth of Indian snake root (Rauvolfia serpentina (L.) benth. Ex Kurz) culture by addition of Cu2+. Biodiversitas J Biol Divers 9:177–179. https://doi.org/10.13057/biodiv/d090305
Pandit R, Raut K (2022) Efficacy of Rauvolfia tetraphylla leaf extracts against the vector of lymphatic filariasis Culex quinquefasciatus. Eco Env Cons 28:S36–S44. https://doi.org/10.53550/EEC.2022.v28i04s.006
Panwar G, Guru S (2015) Stimulation of reserpine production in the whole plant culture of Rauwolfia serpentina L. by elicitors and precursor feeding. J Plant Biochem Biotechnol 24:49–55. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13562-013-0235-5
Parai D, Banerjee M, Dey P, Mukherjee SK (2020) Reserpine attenuates biofilm formation and virulence of Staphylococcus aureus. Microb Pathog 138:103790. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2019.103790
Qadir SU, Raja V (2021) Herbal medicine: old practice and modern perspectives Phytomedicine. Elsevier, pp 149–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-824109-7.00001-7
Ramu AK, Ali D, Alarifi S, Abuthakir MHS, Abdul BAA (2021) Reserpine inhibits DNA repair, cell proliferation, invasion and induces apoptosis in oral carcinogenesis via modulation of TGF-β signaling. Life Sci 264:118730. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118730
Ratnadewi D (2017) Alkaloids in plant cell cultures. In: Georgiev V, Pavlov A (eds) Alkaloids - alternatives in synthesis, modification and application. IntechOpen, pp 1–23. https://doi.org/10.5772/66288
Ray S, Majumder A, Bandyopadhyay M, Jha S (2014) Genetic transformation of sarpagandha (Rauvolfia serpentina) with Agrobacterium rhizogenes for identification of high alkaloid yielding lines. Acta Physiol Plant 36:1599–1605. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-014-1536-6
Rohela GK, Bylla P, Pendli S, Korra R, Gandu R, Reuben C (2021) High performance liquid chromatography based quantification of reserpine in Rauwolfia tetraphylla L. and enhanced production through precursor feeding. Acta Chromatogr 34:120–129. https://doi.org/10.1556/1326.2021.00888
Roy P (2018) Global pharma and local science: the untold tale of reserpine. Indian J Psychiatry 60:S277
Samad N, Manzoor N, Muneer Z, Bhatti SA, Imran I (2021) Reserpine-induced altered neuro-behavioral, biochemical and histopathological assessments prevent by enhanced antioxidant defence system of thymoquinone in mice. Metab Brain Dis 36:2535–2552. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-021-00789-2
Savatagi SB, Srinivas PN, Payyappallimana U (2022) Factors influencing the emergence of self-reliance in primary health care using traditional medicine: a scoping review. Indian J Public Health 66:214
Skurikhin EG, Pershina OV, Ermolaeva LA, Krupin VA, Pakhomova AV, Pan ES, Zeuner MT, Widera D, Khmelevskaya ES, Fisenko VP (2018) Polytherapy with reserpine and glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) improves the symptoms in streptozotocin-induced type-1 diabetic mice by reducing inflammation and inducting beta cell regeneration. Stem Cell Res Ther 8:434. https://doi.org/10.4172/2157-7633.1000434
Soni R, Jaiswal S, Bara JK, Saksena P (2016) The use of Rauwolfia serpentina in hypertensive patients. J Biotechnol Biochem 2:28–32
Subhadhirasakul S, Aimi N, Takayama H, Ponglux D, Sakai S (1994) Hunterioside, first biose bound monoterpenoid indole alkaloid from Hunteria zeylanica. Chem Pharm Bull 42:991–993
Thakur M, Bhattacharya S, Khosla PK, Puri S (2019) Improving production of plant secondary metabolites through biotic and abiotic elicitation. J Appl Res Med Aromat Plants 12:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jarmap.2018.11.004
Tiwari G, Tripathi M, Tiwari S, Tripathi N, Uikey DS, Patel RPK (2021) In vitro production of secondary metabolites reserpine and ajmalicine in Rauvolfia Serpentina (L.) Benth. In: Current aspects in pharmaceutical research and development. BP International, India 4:132–152. https://doi.org/10.9734/bpi/caprd/v4/2136C
Uikey DS, Tiwari G, Tripathi M, Patel R (2014) Secondary metabolite production of reserpine and ajmalicine in Rauvolfia serpentina (L.) Benth. through callus and cell suspension culture. Int J Indig Med Plants 47:1633–1646
Verma K, Paliwal S, Sharma S (2022) Therapeutic potential of reserpine in metabolic syndrome: an evidence based study. Pharmacol Res 186:106531. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106531
Weir MR (2020) Reserpine: a new consideration of an old drug for refractory hypertension. Am J Hypertension 33:708–710. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajh/hpaa069
Xia P, Hu W, Liang T, Yang D, Liang Z (2020) An attempt to establish an Agrobacterium-mediated transient expression system in medicinal plants. Protoplasma 257:1497–1505. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-020-01524-x
Yang L, Wen KS, Ruan X, Zhao YX, Wei F, Wang Q (2018) Response of plant secondary metabolites to environmental factors. Molecules 23:762. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23040762
Zafar N, Mujib A, Ali M, Tonk D, Gulzar B (2017) Aluminum chloride elicitation (amendment) improves callus biomass growth and reserpine yield in Rauvolfia serpentina leaf callus. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 130:357–368. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-017-1230-7
Zafar N, Mujib A, Ali M, Tonk D, Gulzar B, Malik MQ, Mamgain J, Sayeed R (2020) Cadmium chloride (CdCl2) elicitation improves reserpine and ajmalicine yield in Rauvolfia serpentina as revealed by high-performance thin-layer chromatography (HPTLC). 3 Biotech 10:344. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-020-02339-6
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the University e-library assistance from Bidhan Chandra Krishi Viswavidyalaya, West Bengal, India. We are further thankful to the anonymous reviewer(s) and the editor of this article for their critical comments and suggestions on the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
H. S.: writing—original draft preparation. S. G.: conceptualization; writing—original draft preparation, review, and editing. N. M.: writing—review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Swain, H., Gantait, S. & Mandal, N. Developments in biotechnological tools and techniques for production of reserpine. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 107, 4153–4164 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-023-12570-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-023-12570-9