Abstract
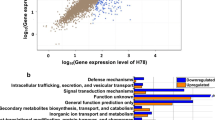
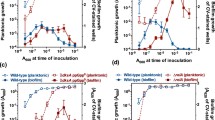
Previously, we identified the uncharacterized predicted membrane protein PA2663 of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 as a virulence factor using a poplar tree model; PA2663 was induced in the poplar rhizosphere and, upon inactivation, it caused 20-fold lower biofilm formation (Attila et al., Microb Biotechnol, 2008). Here, we confirmed that PA2663 is related to biofilm formation by restoring the wild-type phenotype by complementing the PA2663 mutation in trans and investigated the genetic basis of its influence on biofilm formation through whole-transcriptome and -phenotype studies. Upon inactivating PA2663 by transposon insertion, the psl operon that encodes a galactose- and mannose-rich exopolysaccharide was highly repressed (verified by RT-PCR). The inactivation of PA2663 also repressed 13 pyoverdine genes, which eliminated the production of the virulence factor pyoverdine in P. aeruginosa. The inactivation of PA2663 also affected other quorum-sensing-related phenotypes in that it repressed the Pseudomonas quinolone signal (PQS) genes, which abolished PQS production, and repressed lasB, which decreased elastase activity sevenfold. Genes were also induced for motility and attachment (PA0499, PA0993, PA2130, and PA4549) and for small molecule transport (PA0326, PA1541, PA1632, PA1971, PA2214, PA2215, PA2678, and PA3407). Phenotype arrays also showed that PA2663 represses growth on d-gluconic acid, d-mannitol, and N-phthaloyl-l-glutamic acid. Hence, the PA2663 gene product increases biofilm formation by increasing the psl-operon-derived exopolysaccharides and increases pyoverdine synthesis, PQS production, and elastase activity while reducing swarming and swimming motility. We speculate that PA2663 performs these myriad functions as a novel membrane sensor.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Attila C, Ueda, A, Cirillo, SLG, Cirillo, JD, Chen, W, Wood, TK (2008) Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 virulence factors and poplar tree response in the rhizosphere. Microb Biotechnol 1:17–29
Barraud N, Hassett DJ, Hwang SH, Rice SA, Kjelleberg S, Webb JS (2006) Involvement of nitric oxide in biofilm dispersal of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol 188:7344–7353
Breedveld MW, Zevenhuizen LPTM, Zehnder AJB (1991) Osmotically-regulated trehalose accumulation and cyclic β-(1,2)-glucan excretion by Rhizobium leguminosarum biovar trifolii TA-1. Arch Microbiol 156:501–506
Caiazza NC, O'Toole GA (2004) SadB is required for the transition from reversible to irreversible attachment during biofilm formation by Pseudomonas aeruginosa PA14. J Bacteriol 186:4476–4485
Caiazza NC, Merritt JH, Brothers KM, O'Toole GA (2007) Inverse regulation of biofilm formation and swarming motility by Pseudomonas aeruginosa PA14. J Bacteriol 189:3603–3612
Campisano A, Schroeder C, Schemionek M, Overhage J, Rehm BH (2006) PslD is a secreted protein required for biofilm formation by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:3066–3068
Cho EJ, Oh JY, Chang HY, Yun JW (2006) Production of exopolysaccharides by submerged mycelial culture of a mushroom Tremella fuciformis. J Biotechnol 127:129–140
Claassen PA, Kortstee GJ, Oosterveld-van Vliet WM, van Neerven AR (1986) Colonial heterogeneity of Thiobacillus versutus. J Bacteriol 168:791–794
Costerton B (2004) Microbial ecology comes of age and joins the general ecology community. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:16983–16984
de Lorenzo V, Eltis L, Kessler B, Timmis KN (1993) Analysis of Pseudomonas gene products using lacI q/Ptrp-lac plasmids and transposons that confer conditional phenotypes. Gene 123:17–24
Diggle SP, Cornelis P, Williams P, Cámara M (2006) 4-Quinolone signalling in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: old molecules, new perspectives. Int J Med Microbiol 296:83–91
Edgar R, Domrachev M, Lash AE (2002) Gene expression omnibus: NCBI gene expression and hybridization array data repository. Nucleic Acids Res 30:207–210
Ezzell JW Jr., Abshire TG, Little SF, Lidgerding BC, Brown C (1990) Identification of Bacillus anthracis by using monoclonal antibody to cell wall galactose-N-acetylglucosamine polysaccharide. J Clin Microbiol 28:223–231
Filiatrault MJ, Picardo KF, Ngai H, Passador L, Iglewski BH (2006) Identification of Pseudomonas aeruginosa genes involved in virulence and anaerobic growth. Infect Immun 74:4237–4245
Firoved AM, Wood SR, Ornatowski W, Deretic V, Timmins GS (2004) Microarray analysis and functional characterization of the nitrosative stress response in nonmucoid and mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol 186:4046–4050
Friedman L, Kolter R (2004) Two genetic loci produce distinct carbohydrate-rich structural components of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm matrix. J Bacteriol 186:4457–4465
Fux CA, Costerton JW, Stewart PS, Stoodley P (2005) Survival strategies of infectious biofilms. Trends Microbiol 13:34–40
Gallagher LA, McKnight SL, Kuznetsova MS, Pesci EC, Manoil C (2002) Functions required for extracellular quinolone signaling by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol 184:6472–6480
Gillam DE, Bishop PL, Love NG (2005) A study of glutathione-gated potassium efflux in biofilms using potassium microelectrodes. Environ Eng Sci 22:489–495
Hirokawa T, Boon-Chieng S, Mitaku S (1998) SOSUI: classification and secondary structure prediction system for membrane proteins. Bioinformatics 14:378–379
Izano EA, Sadovskaya I, Vinogradov E, Mulks MH, Velliyagounder K, Ragunath C, Kher WB, Ramasubbu N, Jabbouri S, Perry MB, Kaplan JB (2007) Poly-N-acetylglucosamine mediates biofilm formation and antibiotic resistance in Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae. Microb Pathog 43:1–9
Jackson KD, Starkey M, Kremer S, Parsek MR, Wozniak DJ (2004) Identification of psl, a locus encoding a potential exopolysaccharide that is essential for Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 biofilm formation. J Bacteriol 186:4466–4475
Jacobs MA, Alwood A, Thaipisuttikul I, Spencer D, Haugen E, Ernst S, Will O, Kaul R, Raymond C, Levy R, Chun-Rong L, Guenthner D, Bovee D, Olson MV, Manoil C (2003) Comprehensive transposon mutant library of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:14339–14344
Junker LM, Clardy J (2007) High-throughput screens for small-molecule inhibitors of Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm development. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 51:3582–3590
Kaneko Y, Thoendel M, Olakanmi O, Britigan BE, Singh PK (2007) The transition metal gallium disrupts Pseudomonas aeruginosa iron metabolism and has antimicrobial and antibiofilm activity. J Clin Invest 117:877–888
Keshk S, Sameshima K (2006) Influence of lignosulfonate on crystal structure and productivity of bacterial cellulose in a static culture. Enzyme Microb Technol 40:4–8
Kropec A, Maira-Litran T, Jefferson KK, Grout M, Cramton SE, Gotz F, Goldmann DA, Pier GB (2005) Poly-N-acetylglucosamine production in Staphylococcus aureus is essential for virulence in murine models of systemic infection. Infect Immun 73:6868–6876
Kuchma SL, Brothers KM, Merritt JH, Liberati NT, Ausubel FM, O'Toole GA (2007) BifA, a c-di-GMP phosphodiesterase, inversely regulates biofilm formation and swarming motility by Pseudomonas aeruginosa PA14. J Bacteriol 189:8165–8178
Lamont IL, Beare PA, Ochsner U, Vasil AI, Vasil ML (2002) Siderophore-mediated signaling regulates virulence factor production in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99:7072–7077
Lamont IL, Martin LW (2003) Identification and characterization of novel pyoverdine synthesis genes in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microbiology 149:833–842
Lee J, Bansal T, Jayaraman A, Bentley WE, Wood TK (2007) Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli biofilms are inhibited by 7-hydroxyindole and stimulated by isatin. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:4100–4109
Lewenza S, Falsafi RK, Winsor G, Gooderham WJ, McPhee JB, Brinkman FS, Hancock REW (2005) Construction of a mini-Tn5-luxCDABE mutant library in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1: a tool for identifying differentially regulated genes. Genome Res 15:583–589
Liberati NT, Urbach JM, Miyata S, Lee DG, Drenkard E, Wu G, Villanueva J, Wei T, Ausubel FM (2006) An ordered, nonredundant library of Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain PA14 transposon insertion mutants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:2833–2838
Ma L, Jackson KD, Landry RM, Parsek MR, Wozniak DJ (2006) Analysis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa conditional Psl variants reveals roles for the Psl polysaccharide in adhesion and maintaining biofilm structure postattachment. J Bacteriol 188:8213–8221
Ma L, Lu H, Sprinkle A, Parsek MR, Wozniak D (2007) Pseudomonas aeruginosa Psl is a galactose- and mannose-rich exopolysaccharide. J Bacteriol 189:8353–8356
Matsukawa M, Greenberg EP (2004) Putative exopolysaccharide synthesis genes influence Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm development. J Bacteriol 186:4449–4456
Merriman TR, Merriman ME, Lamont IL (1995) Nucleotide sequence of pvdD, a pyoverdine biosynthetic gene from Pseudomonas aeruginosa: PvdD has similarity to peptide synthetases. J Bacteriol 177:252–258
Michel L, González N, Jagdeep S, Nguyen-Ngoc T, Reimmann C (2005) PchR-box recognition by the AraC-type regulator PchR of Pseudomonas aeruginosa requires the siderophore pyochelin as an effector. Mol Microbiol 58:495–509
Moraes TF, Bains M, Hancock REW, Strynadka NCJ (2007) An arginine ladder in OprP mediates phosphate-specific transfer across the outer membrane. Nature Struct Biol 14:85–87
Nicolaus B, Lama L, Panico A, Moriello VS, Romano I, Gambacorta A (2002) Production and characterization of exopolysaccharides excreted by thermophilic bacteria from shallow, marine hydrothermal vents of Flegrean Ares (Italy). Syst Appl Microbiol 25:319–325
Ohman DE, Cryz SJ, Iglewski BH (1980) Isolation and characterization of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO mutant that produces altered elastase. J Bacteriol 142:836–842
Parkins MD, Ceri H, Storey DG (2001) Pseudomonas aeruginosa GacA, a factor in multihost virulence, is also essential for biofilm formation. Mol Microbiol 40:1215–1226
Parvatiyar K, Alsabbagh EM, Ochsner UA, Stegemeyer MA, Smulian AG, Hwang SH, Jackson CR, McDermott TR, Hassett DJ (2005) Global analysis of cellular factors and responses involved in Pseudomonas aeruginosa resistance to arsenite. J Bacteriol 187:4853–4864
Pesci EC, Milbank JBJ, Pearson JP, McKnight S, Kende AS, Greenberg EP, Iglewski BH (1999) Quinolone signaling in the cell-to-cell communication system of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96:11229–11234
Pratt LA, Kolter R (1998) Genetic analysis of Escherichia coli biofilm formation: Roles of flagella, motility, chemotaxis and type I pili. Mol Microbiol 30:285–293
Ren D, Bedzyk LA, Thomas SM, Ye RW, Wood TK (2004) Gene expression in Escherichia coli biofilms. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 64:515–524
Ren D, Zuo R, González Barrios AF, Bedzyk LA, Eldridge GR, Pasmore ME, Wood TK (2005a) Differential gene expression for investigation of Escherichia coli biofilm inhibition by plant extract ursolic acid. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:4022–4034
Ren D, Zuo R, Wood TK (2005b) Quorum-sensing antagonist (5Z)-4-bromo-5-(bromomethylene)-3-butyl-2(5H)-furanone influences siderophore biosynthesis in Pseudomonas putida and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 66:689–695
Rodriguez RL, Tait RC (1983) Recombinant DNA techniques: an introduction. Benjamin/Cummings, Menlo Park, CA
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning, a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA
Sauer K, Cullen MC, Rickard AH, Zeef LA, Davies DG, Gilbert P (2004) Characterization of nutrient-induced dispersion in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 biofilm. J Bacteriol 186:7312–7326
Sperandio V, Torres AG, Kaper JB (2002) Quorum-sensing Escherichia coli regulators B and C (QseBC): a novel two-component regulatory system involved in the regulation of flagella and motility by quorum sensing in E. coli. Mol Microbiol 43:809–821
Stintzi A, Evans K, Meyer J-M, Poole K (1998) Quorum-sensing and siderophore biosynthesis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: lasR/lasI mutants exhibit reduced pyoverdine biosynthesis. FEMS Microbiol Lett 166:341–345
Stover CK, Pham XQ, Erwin AL, Mizoguchi SD, Warrener P, Hickey MJ, Brinkman FS, Hufnagle WO, Kowalik DJ, Lagrou M, Garber RL, Goltry L, Tolentino E, Westbrock-Wadman S, Yuan Y, Brody LL, Coulter SN, Folger KR, Kas A, Larbig K, Lim R, Smith K, Spencer D, Wong GK, Wu Z, Paulsen IT, Reizer J, Saier MH, Hancock REW, Lory S, Olson MV (2000) Complete genome sequence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PA01, an opportunistic pathogen. Nature 406:959–964
Urata M, Miyakoshi M, Kai S, Maeda K, Habe H, Omori T, Yamane H, Nojiri H (2004) Transcriptional regulation of the ant operon, encoding two-component anthranilate 1,2-dioxygenase, on the carbazole-degradative plasmid pCAR1 of Pseudomonas resinovorans strain CA10. J Bacteriol 186:6815–6823
Visca P, Ciervo A, Orsi N (1994) Cloning and nucleotide sequence of the pvdA gene encoding the pyoverdin biosynthetic enzyme l-ornithine N 5-oxygenase in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol 176:1128–1140
von Heijne G (2006) Membrane-protein topology. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 7:909–918
Waite RD, Paccanaro A, Papakonstantinopoulou A, Hurst JM, Saqi M, Littler E, Curtis MA (2006) Clustering of Pseudomonas aeruginosa transcriptomes from planktonic cultures, developing and mature biofilms reveals distinct expression profiles. BMC Genomics 7:162
Whiteley M, Bangera MG, Bumgarner RE, Parsek MR, Teitzel GM, Lory S, Greenberg EP (2001) Gene expression in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. Nature 413:860–864
Wilhelm S, Gdynia A, Tielen P, Rosenau F, Jaeger KE (2007) The autotransporter esterase EstA of Pseudomonas aeruginosa is required for rhamnolipid production, cell motility, and biofilm formation. J Bacteriol 189:6695–6703
Winsor GL, Lo R, Ho Sui SJ, Ung KSE, Huang S, Cheng D, Ho Ching WK, Hancock REW, Brinkman FSL (2005) Pseudomonas aeruginosa Genome Database and PseudoCAP: facilitating community-based, continually updated, genome annotation. Nucleic Acids Res 33:D338–D343
Yokochi T, Inoue Y, Kimura Y, Kato N (1990) Strong interaction of lipopolysaccharides possessing the mannose homopolysaccharides with complement and its relation to adjuvant action. J Immunol 144:3106–3110
Acknowledgements
We thank Prof. Robert E. W. Hancock and Prof. Colin Manoil for the P. aeruginosa PAO1 transposon mutants, Prof. Frederick M. Ausubel for the P. aeruginosa PA14 transposon mutants, and Prof. Daniel J. Wozniak for providing the P. aeruginosa PAO1 pslAB strain. We thank Dr. Marvin Whiteley for providing the PQS standard and for his assistance with the PQS assay. This research was supported by the NIH (EB003872-01A1) and the NSF (BES-0331416).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Attila, C., Ueda, A. & Wood, T.K. PA2663 (PpyR) increases biofilm formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 through the psl operon and stimulates virulence and quorum-sensing phenotypes. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 78, 293–307 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-007-1308-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-007-1308-y