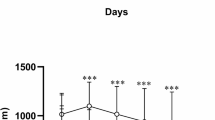
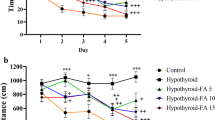
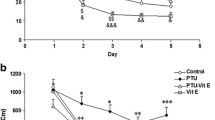
Abstract
Apart from a role as a key regulator of calcium/phosphate homeostasis, vitamin D (Vit D) is suggested to be a potential player in nervous system growth and function. This study aimed to assess the impacts of Vit D administration on memory impairment, oxidative damage, and acetylcholinesterase (AchE) overactivity in hypothyroid juvenile rats. The animals were randomly grouped as (1) Control; (2) Hypothyroid; (3) Hypothyroid-Vit D100, and (4) Hypothyroid-Vit D 500. Propylthiouracil (PTU) was added to their drinking water (0.05%) for 6 weeks, and Vit D (100 or 500 IU/kg) treatment was performed daily by gavage. Morris water maze (MWM) and passive avoidance (PA) tests were performed. The brains were removed under deep anesthesia, then the hippocampal and cortical tissues were separated to assess biochemical parameters. Hypothyroidism was significantly associated with learning and memory impairment in MWM and PA tests. Hypothyroidism was also accompanied by an elevation in AChE activity and malondialdehyde (MDA) content and a reduced level of thiol content and superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity in the brain. Treatment with Vit D recovered hypothyroidism-induced cognitive impairment and improved memory performance in MWM and PA tasks. On the other hand, Vit D alleviated AChE activity and MDA level, whereas increased SOD activity and thiol content in the hippocampal and cortical tissues. In conclusion, these outcomes suggest an association between the oral administrations of Vit D and learning and memory improvement of hypothyroid rats, which was accompanied by decreasing AChE activity and brain tissue oxidative damage.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alberini CM, Travaglia A (2017) Infantile amnesia: a critical period of learning to learn and remember. J Neurosci 37:5783–5795. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0324-17.2017. 28615475
Alrefaie Z, Alhayani A (2015) Vitamin D3 improves decline in cognitive function and cholinergic transmission in prefrontal cortex of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Behav Brain Res 287:156–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2015.03.050. 25835318
Alzoubi Karem H., Gerges Nashaat Z., Aleisa Abdulaziz M., Alkadhi Karim A. (2009) Levothyroxin restores hypothyroidism-induced impairment of hippocampus-dependent learning and memory: Behavioral, electrophysiological, and molecular studies. Hippocampus 19(1):66–78. https://doi.org/10.1002/hipo.20476
Baghcheghi Y, Beheshti F, Shafei MN, Salmani H, Sadeghnia HR, Soukhtanloo M, Anaeigoudari A, Hosseini M (2018) The effects of vitamin E on brain derived neurotrophic factor, tissues oxidative damage and learning and memory of juvenile hypothyroid rats. Metab Brain Dis 33:713–724. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-017-0176-0. 29290043
Baldissarelli J, Santi A, Schmatz R, Abdalla FH, Cardoso AM, Martins CC, Dias GR, Calgaroto NS, Pelinson LP et al (2017) Hypothyroidism enhanced ectonucleotidases and acetylcholinesterase activities in rat synaptosomes can be prevented by the naturally occurring polyphenol quercetin. Cell Mol Neurobiol 37:53–63. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-016-0342-7. 26879755
Beheshti F, Karimi S, Vafaee F, Shafei MN, Sadeghnia HR, Hadjzadeh MAR, Hosseini M (2017a) The effects of vitamin C on hypothyroidism-associated learning and memory impairment in juvenile rats. Metab Brain Dis 32:703–715. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-017-9954-y. 28127705
Beheshti F, Hosseini M, Shafei MN, Soukhtanloo M, Ghasemi S, Vafaee F, Zarepoor L (2017b) The effects of Nigella sativa extract on hypothyroidism-associated learning and memory impairment during neonatal and juvenile growth in rats. Nutr Neurosci 20:49–59. https://doi.org/10.1179/1476830514y.0000000144. 25087773
Bernal J (2007) Thyroid hormone receptors in brain development and function. Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol Metab 3:249–259. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncpendmet0424. 17315033
Bernal J, Guadaño-Ferraz A, Morte B (2015) Thyroid hormone transporters–functions and clinical implications. Nat Rev Endocrinol 11:406–417. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrendo.2015.66. 25942657
Bianco AC (2008) Metabolic effects of thyroid hormones-beyond traditional prospects. Thyroid 18:99–100. https://doi.org/10.1089/thy.2007.0411. 18279009
Buell JS, Dawson-Hughes B (2008) Vitamin D and neurocognitive dysfunction: preventing “D”ecline? Mol Aspects Med 29:415–422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mam.2008.05.001. 18579197
Cano-Europa E, Pérez-Severiano F, Vergara P, Ortiz-Butrón R, Ríos C, Segovia J, Pacheco-Rosado J (2008) Hypothyroidism induces selective oxidative stress in amygdala and hippocampus of rat. Metab Brain Dis 23:275–287. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-008-9099-0. 18683039
Carvajal FJ, Inestrosa NC (2011) Interactions of AChE with Aβ aggregates in Alzheimer’s brain: therapeutic relevance of IDN 5706. Front Mol Neurosci 4:19. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2011.00019. 21949501
Chaalal A, Poirier R, Blum D, Laroche S, Enderlin V (2019) Thyroid hormone supplementation estores spatial memory, hippocampal markers of neuroinflammation, plasticity-related signaling molecules, and β-amyloid peptide load in hypothyroid rats. Mol Neurobiol 56:722–735. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-018-1111-z. 29796989
Chiovato L, Magri F, Carlé A (2019) Hypothyroidism in context: where we’ve been and where we’re going. Adv Ther 36:47–58. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12325-019-01080-8. 31485975
Cimadevilla JM, Kaminsky Y, Fenton A, Bures J (2000) Passive and active place avoidance as a tool of spatial memory research in rats. J Neurosci Methods 102:155–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0165-0270(00)00288-0. 11040412
Cruciani S, Santaniello S, Garroni G, Fadda A, Balzano F, Bellu E, Sarais G, Fais G, Mulas M et al (2019) Myrtus polyphenols, from antioxidants to anti-inflammatory molecules: exploring a network involving cytochromes P450 and vitamin D. Molecules 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24081515. 30999678
Dalla C, Shors TJ (2009) Sex differences in learning processes of classical and operant conditioning. Physiol Behav 97:229–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physbeh.2009.02.035. 19272397
DeCarolis NA, Eisch AJ (2010) Hippocampal neurogenesis as a target for the treatment of mental illness: a critical evaluation. Neuropharmacology 58:884–893. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2009.12.013. 20060007
DeLuca GC, Kimball SM, Kolasinski J, Ramagopalan SV, Ebers GC (2013) Review: the role of vitamin D in nervous system health and disease. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 39:458–484. https://doi.org/10.1111/nan.12020. 23336971
Eu WZ, Chen YJ, Chen WT, Wu KY, Tsai CY, Cheng SJ, Carter RN, Huang GJ (2021) The effect of nerve growth factor on supporting spatial memory depends upon hippocampal cholinergic innervation. Transl Psychiatry 11:162. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41398-021-01280-3. 33723225
Farghali M, Ruga S, Morsanuto V, Uberti F (2020) Can brain health be supported by vitamin D-based supplements? A critical review. Brain Sci 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10090660. 32972010
Farrokhi E, Hosseini M, Beheshti F, Vafaee F, Hadjzadeh MA, Dastgheib SS (2014) Brain tissues oxidative damage as a possible mechanism of deleterious effects of propylthiouracil- induced hypothyroidism on learning and memory in neonatal and juvenile growth in rats. Basic Clin Neurosci 5:285–294. 27284393
Fu A, Zhou R, Xu X (2014) The synthetic thyroid hormone, levothyroxine, protects cholinergic neurons in the hippocampus of naturally aged mice. Neural Regen Res 9:864–871. https://doi.org/10.4103/1673-5374.131602. 25206902
Gilbert ME, Rovet J, Chen Z, Koibuchi N (2012) Developmental thyroid hormone disruption: prevalence, environmental contaminants and neurodevelopmental consequences. Neurotoxicology 33:842–852. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuro.2011.11.005. 22138353
Hajiluian G, Abbasalizad Farhangi M, Nameni G, Shahabi P, Megari-Abbasi M (2018) Oxidative stress-induced cognitive impairment in obesity can be reversed by vitamin D administration in rats. Nutr Neurosci 21:744–752. https://doi.org/10.1080/1028415x.2017.1348436. 28683595
Hami J, Kheradmand H, Haghir H (2014) Gender differences and lateralization in the distribution pattern of insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor in developing rat hippocampus: an immunohistochemical study. Cell Mol Neurobiol 34:215–226. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-013-0005-x. 24287499
Hii CS, Ferrante A (2016) The non-genomic actions of vitamin D. Nutrients 8:135. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu8030135. 26950144
Hosseini M, Harandizadeh F, Niazamand S, Soukhtanloo M, Mahmoudabady M (2013) Antioxidant effect of Achillea wilhelmsii extract on pentylenetetrazole (seizure model)-induced oxidative brain damage in Wistar rats. Indian J Physiol Pharmacol 57:418–424. 24968581
Hosseini MT, Mohammadpour R, Karami Z, Rajaei H, Sadeghnia RM, Soukhtanloo (2015) Effects of the hydro-alcoholic extract of Nigella sativa on scopolamine-induced spatial memory impairment in rats and its possible mechanism. Chin J Integr Med 21(6):438–444. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-014-1742-5
Jezek P, Hlavatá L (2005) Mitochondria in homeostasis of reactive oxygen species in cell, tissues, and organism. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 37:2478–2503. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocel.2005.05.013. 16103002
Kesby JP, Eyles DW, Burne TH, McGrath JJ (2011) The effects of vitamin D on brain development and adult brain function. Mol Cell Endocrinol 347:121–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mce.2011.05.014. 21664231
Kmieć P, Sworczak K (2015) Vitamin D in thyroid disorders. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes 123:386–393. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0035-1554714. 26171622
Landel V, Annweiler C, Millet P, Morello M, Féron F (2016) Vitamin D, cognition and Alzheimer’s disease: the therapeutic benefit is in the D-tails. J Alzheimers Dis 53:419–444. https://doi.org/10.3233/jad-150943. 27176073
Latimer CS, Brewer LD, Searcy JL, Chen KC, Popović J, Kraner SD, Thibault O, Blalock EM, Landfield PW et al (2014) Vitamin D prevents cognitive decline and enhances hippocampal synaptic function in aging rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 111:E4359-4366. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1404477111. 25267625
Lee JK, Johnson EG, Ghetti S (2017) Hippocampal development: structure, function and implications. In: Hannula DE, Duff MC (eds) The hippocampus from cells to systems: structure, connectivity, and functional contributions to memory and flexible cognition. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 141–166
Lin CI, Chang YC, Kao NJ, Lee WJ, Cross TW, Lin SH (2020) 1,25(OH)(2)D(3) alleviates Aβ(25–35)-induced tau hyperphosphorylation, excessive reactive oxygen species, and apoptosis through interplay with glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor signaling in SH-SY5Y cells. Int J Mol Sci 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21124215. 32545801
Mackawy AM, Al-Ayed BM, Al-Rashidi BM (2013) Vitamin d deficiency and its association with thyroid disease. Int J Health Sci (Qassim) 7:267–275. https://doi.org/10.12816/0006054. 24533019
Madesh M, Balasubramanian KA (1998) Microtiter plate assay for superoxide dismutase using MTT reduction by superoxide. Indian J Biochem Biophys 35:184–188. 9803669
Mansouri F, Ghanbari H, Marefati N, Arab Z, Salmani H, Beheshti F, Hosseini M (2021) Protective effects of vitamin D on learning and memory deficit induced by scopolamine in male rats: the roles of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and oxidative stress. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 394:1451–1466. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-021-02062-w. 33649977
Mecocci P, Polidori MC (2012) Antioxidant clinical trials in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. Biochim Biophys Acta 1822:631–638. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2011.10.006. 22019723
Memarpour S, Beheshti F, Baghcheghi Y, Vafaei AA, Hosseini M, Rashidy-Pour A (2020) Neuronal nitric oxide inhibitor 7-nitroindazole improved brain-derived neurotrophic factor and attenuated brain tissues oxidative damage and learning and memory impairments of hypothyroid juvenile rats. Neurochem Res 45:2775–2785. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-020-03128-6. 32930947
Mohammadipour A, Hosseini M, Fazel A, Haghir H, Rafatpanah H, Pourganji M, Bideskan AE (2016) The effects of exposure to titanium dioxide nanoparticles during lactation period on learning and memory of rat offspring. Toxicol Ind Health 32:221–228. https://doi.org/10.1177/0748233713498440. 24081627
Mokhtari-Zaer A, Hosseini M, Salmani H, Arab Z, Zareian P (2020) Vitamin D(3) attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced cognitive impairment in rats by inhibiting inflammation and oxidative stress. Life Sci 253:117703. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117703. 32334010
Pan T, Zhong M, Zhong X, Zhang Y, Zhu D (2013) Levothyroxine replacement therapy with vitamin E supplementation prevents oxidative stress and cognitive deficit in experimental hypothyroidism. Endocrine 43:434–439. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-012-9801-1. 23001627
Paprocki J, Sutkowy P, Piechocki J, Woźniak A (2021) Association between vitamin D supplements, oxidative stress biomarkers, and hyperbaric therapy in patients with sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2021:8895323. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/8895323. 33777323
Patel AJ, Smith RM, Kingsbury AE, Hunt A, Balázs R (1980) Effects of thyroid state on brain development: muscarinic acetylcholine and GABA receptors. Brain Res 198:389–402. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-8993(80)90752-0. 7407604
Patel AJ, Hayashi M, Hunt A (1987) Selective persistent reduction in choline acetyltransferase activity in basal forebrain of the rat after thyroid deficiency during early life. Brain Res 422:182–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-8993(87)90556-7. 3676781
Petschner P, Balogh N, Adori C, Tamasi V, Kumar S, Juhasz G, Bagdy G (2018) Downregulation of the vitamin D receptor regulated gene set in the hippocampus after MDMA treatment. Front Pharmacol 9:1373. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2018.01373. 30559663
Rastegar-Moghaddam SH, Mohammadipour A, Hosseini M, Bargi R, Ebrahimzadeh-Bideskan A (2019) Maternal exposure to atrazine induces the hippocampal cell apoptosis in mice offspring and impairs their learning and spatial memory. Toxin Rev 38:298–306. https://doi.org/10.1080/15569543.2018.1466804
Rivas M, Naranjo JR (2007) Thyroid hormones, learning and memory. Genes Brain Behav 6 Suppl 1:40–44. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1601-183X.2007.00321.x. 17543038
Sepidarkish M, Farsi F, Akbari-Fakhrabadi M, Namazi N, Almasi-Hashiani A, Maleki Hagiagha A, Heshmati J (2019) The effect of vitamin D supplementation on oxidative stress parameters: a systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials. Pharmacol Res 139:141–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2018.11.011. 30447293
Siebert C, Pierozan P, Kolling J, Dos Santos TM, Sebotaio MC, Marques EP, Biasibetti H, Longoni A, Ferreira F et al (2017) Vitamin D(3) reverses the hippocampal cytoskeleton imbalance but not memory deficits caused by ovariectomy in adult Wistar rats. Neuromolecular Med 19:345–356. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-017-8449-7. 28689355
Smith JW, Evans AT, Costall B, Smythe JW (2002) Thyroid hormones, brain function and cognition: a brief review. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 26:45–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0149-7634(01)00037-9.11835983
Taylor PN, Albrecht D, Scholz A, Gutierrez-Buey G, Lazarus JH, Dayan CM, Okosieme OE (2018) Global epidemiology of hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism. Nat Rev Endocrinol 14:301–316. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrendo.2018.18.29569622
Tian A, Ma H, Cao X, Zhang R, Wang X, Wu B (2015) Vitamin D improves cognitive function and modulates Th17/T reg cell balance after hepatectomy in mice. Inflammation 38:500–509. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-014-9956-4.24958015
Travaglia A, Steinmetz AB, Miranda JM, Alberini CM (2018) Mechanisms of critical period in the hippocampus underlie object location learning and memory in infant rats. Learn Mem 25:176–182. https://doi.org/10.1101/lm.046946.117.29545389
Vara H, Martínez B, Santos A, Colino A (2002) Thyroid hormone regulates neurotransmitter release in neonatal rat hippocampus. Neuroscience 110:19–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0306-4522(01)00541-3.11882369
Veilleux-Lemieux D, Castel A, Carrier D, Beaudry F, Vachon P (2013) Pharmacokinetics of ketamine and xylazine in young and old Sprague-Dawley rats. J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci 52:567–570. 24041212
Villanueva I, Alva-Sánchez C, Pacheco-Rosado J (2013) The role of thyroid hormones as inductors of oxidative stress and neurodegeneration. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2013:218145. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/218145. 24386502
Wang F, Zeng X, Zhu Y, Ning D, Liu J, Liu C, Jia X, Zhu D (2015) Effects of thyroxine and donepezil on hippocampal acetylcholine content, acetylcholinesterase activity, synaptotagmin-1 and SNAP-25 expression in hypothyroid adult rats. Mol Med Rep 11:775–782. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2014.2825.25371181
Wimalawansa SJ (2019) Vitamin D deficiency: effects on oxidative stress, epigenetics, gene regulation, and aging. Biology (Basel) 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology8020030. 31083546
Wrzosek M, Łukaszkiewicz J, Wrzosek M, Jakubczyk A, Matsumoto H, Piątkiewicz P, Radziwoń-Zaleska M, Wojnar M, Nowicka G (2013) Vitamin D and the central nervous system. Pharmacol Rep 65:271–278. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1734-1140(13)71003-x. 23744412
Acknowledgements
The reported data in the current manuscript were obtained from a PhD thesis (NO: 1611-A and 981317 ).
Funding
We would like to extend our honest thanks to the Vice Chancellor for Research and Technology, Mashhad University of Medical Sciences, Mashhad, Iran, for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Seyed Hamidreza Rastegar-Moghaddam, Fatemeh Alipour, Arezoo Rajabian, Mahmoud Hosseini, Alireza Ebrahimzadeh bideskan.
MH and AE conceived and designed research. HR, FA, and AR conducted experiments. HR and MH analyzed data. HR, FA, AR, and MH wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the manuscript, all data were generated in-house, and that no paper mill was used.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
The animal procedures were carried out in accordance with the standards of the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals, and the Committee on Animal Research at Mashhad University of Medical Sciences (IR.MUMS.MEDICAL.REC.1399.116) approved the study protocol.
Consent to participate
Related to “Authors include a statement in the manuscript that informed consent was obtained for experimentation with human subjects. The privacy rights of human subjects must always be observed.” the authors state that they did not use human subjects in this study.
Consent to publish
The authors state that they did not use human subjects in this study.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rastegar-Moghaddam, S.H., Hosseini, M., Alipour, F. et al. The effects of vitamin D on learning and memory of hypothyroid juvenile rats and brain tissue acetylcholinesterase activity and oxidative stress indicators. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 395, 337–351 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-021-02195-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-021-02195-y