Abstract
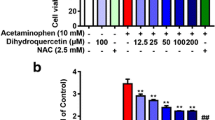
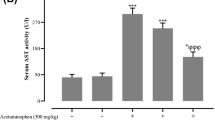
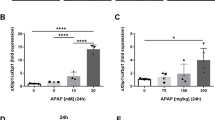
Paracetamol is a commonly used over-the-counter analgesic and antipyretic drug. Nevertheless, an overdose of paracetamol leads to hepatic necrosis that can be lethal. This study aimed to assess the potential hepatoprotective effects of dibenzazepine, a Notch inhibitor, against acute liver injury in rats via interfering with oxidative stress, inflammation, apoptosis, autophagy, and Notch signaling. Silymarin (200 mg/kg, p.o.) or dibenzazepine (2 mg/kg, i.p.) were administered to rats for 5 days before a single hepatotoxic dose of paracetamol (800 mg/kg, i.p.). Pretreatment with silymarin and dibenzazepine significantly mitigated oxidative stress, inflammatory and apoptotic markers induced by paracetamol hepatotoxicity where dibenzazepine showed greater repression of inflammation. Furthermore, dibenzazepine was found to be significantly more efficacious than silymarin in inhibiting Notch signaling as represented by expression of Notch-1 and Hes-1. A significantly greater response was also demonstrated with dibenzazepine pretreatment with regard to the expression of autophagic proteins, Beclin-1 and LC-3. The aforementioned biochemical results were confirmed by histopathological examination. Autophagy and Notch signaling seem to play a significant role in protection provided by dibenzazepine for paracetamol-induced hepatotoxicity in rats, which could explain its superior results relative to silymarin.

Graphical abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Abirami A, Nagarani G, Siddhuraju P (2015) Hepatoprotective effect of leaf extracts from Citrus hystrix and C. maxima against paracetamol-induced liver injury in rats. Food Sci Human Wellness 4:35–41
Ables JL, Breunig JJ, Eisch AJ, Rakic P (2011) Notch just development: Notch signalling in the adult brain. Nat Rev Neurosci 12:269–283
Acharya M, Lau-Cam CA (2010) Comparison of the protective actions of N-acetylcysteine, hypotaurine and taurine against acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in the rat. J Biomed Sci 17:S35–S45
Ackerman Z, Oron-Herman M, Pappo O, Peleg E, Safadi R, Schmilovitz-Weiss H, Grozovski M (2010) Hepatic effects of rosiglitazone in rats with the metabolic syndrome. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 107:663–668
Alam J, Mujahid M, Jahan Y, Bagga P, Rahman MA (2017) Hepatoprotective potential of ethanolic extract of Aquilariaagallocha leaves against paracetamol-induced hepatotoxicity in SD rats. J Tradit Complement Med 7:9–13
Atiba AS, Abbiyesuku FM, Oparinde DP, Niran-Atiba TA, Akindele RA (2016) Plasma malondialdehyde (MDA): an indication of liver damage in women with preeclamsia. Ethiop J Health Sci 26:479–486
Bajt ML, Cover C, Lemasters JJ, Jaeschke H (2006) Nuclear translocation of endonuclease G and apoptosis-inducing factor during acetaminophen-induced liver cell injury. Toxicol Sci 94:217–225
Banchroft JD, Stevens A, Turner DR (1996) Theory and practice of histological techniques, 4th edn. Churchil Livingstone, New York, London, San Francisco, Tokyo
Beutler B (2000) Tlr4: central component of the sole mammalian LPS sensor. Curr Opin Immunol 12:20–26
Blazka ME, Wilmer JL, Holladay SD, Wilson RE, Luster MI (1995) Role of proinflammatory cytokines in acetaminophen hepatotoxicity. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 133:43–52
Borkham-Kamphorst E, van de Leur E, Zimmermann HW, Karlmark KR, Tihaa L, Haas U, Tacke F, Berger T, Mak TW, Weiskirchen R (2013) Protective effects of lipocalin-2 (LCN2) in acute liver injury suggest a novel function in liver homeostasis. Biochim Biophys Acta 1832:660–673
Bray SJ (2006) Notch signalling: a simple pathway becomes complex. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 7:678–689
Chakradhar T, SarathBabu K (2018) Preventive effect of hydroalcoholic extract of Vetiveriazizanoides roots on paracetamol-induced hepatotoxicity in Wistar albino rats. Asian J Pharm Pharmacol 4:70–73
Choi YH, Jin N, Kelly F, Sakthivel SK, Yu T (2016) Elevation of alanine aminotransferase activity occurs after activation of the cell-death signaling initiated by pattern-recognition receptors but before activation of cytolytic effectors in NK or CD8+ T cells in the liver during acute HCV infection. PLoS One 11:e0165533
Cohen SD, Khairallah EA (1997) Selective protein arylation and acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity. Drug Metab Rev 29:59–77
Cover C, Liu J, Farhood A, Malle E, Waalkes MP, Bajt ML, Jaeschke H (2006) Pathophysiological role of the acute inflammatory response during acetaminophen hepatotoxicity. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 216:98–107
Deep G, Agarwal R (2007) Chemopreventive efficacy of silymarin in skin and prostate cancer. Integr Cancer Ther 6:130–145
Du K, Ramachandran A, Jaeschke H (2016) Oxidative stress during acetaminophen hepatotoxicity: Sources, pathophysiological role and therapeutic potential. Redox Biol 10:148–156
El Faras AA, Elsawaf AL (2017) Hepatoprotective activity of quercetin against paracetamol-induced liver toxicity in rats. Tanta Med J 45:92–98
Fakurazi S, Hairuszah I, Nanthini U (2008) Moringaoleifera Lam prevents acetaminophen induced liver injury through restoration of glutathione level. Food Chem Toxicol 46:2611–2615
Farghaly HS, Hussein MA (2010) Protective effect of curcumin against paracetamol-induced liver damage. Aust J Basic Appl Sci 4:4266–4274
Fiorotto R, Raizner A, Morell CM, Torsello B, Scirpo R, Fabris L, Strazzabosco M (2013) Notch signaling regulates tubular morphogenesis during repair from biliary damage in mice. J Hepatol 59:124–130
Flora K, Hahn M, Rosen H, Benner K (1998) Milk thistle (Silybum marianum) for the therapy of liver disease. Am J Gastroenterol 93:139–143
Galal RM, Zaki HF, Seif El-Nasr MM, Agha AM (2012) Potential protective effect of honey against paracetamol-induced hepatotoxicity. Arch Iran Med 15:674–680
Geisler F, Strazzabosco M (2015) Emerging roles of Notch signaling in liver disease. Hepatology 61:382–392
Gerondakis S, Grossmann M, Nakamura Y, Pohl T, Grumont R (1999) Genetic approaches in mice to understand Rel/NF-κB and IκB function: transgenics and knockouts. Oncogene 18:6888–6895
Gillessen A, Schmidt HHJ (2020) Silymarin as supportive treatment in liver diseases: a narrative review. Adv Ther 37:1279–1301
Gutiérrez RM, Solís RV (2009) Hepatoprotective and inhibition of oxidative stress in liver of Prostechea michuacana. Rec Nat Prod 3:46–51
Hamza RZ, Al-Harbi MS (2015) Amelioration of paracetamol hepatotoxicity and oxidative stress on mice liver with silymarin and Nigella sativa extract supplements. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed 5:521–531
Hans CP, Koenig SN, Huang N, Cheng J, Beceiro S, Guggilam A, Kuivaniemi H, Partida-Sánchez S, Garg V (2012) Inhibition of Notch1 signaling reduces abdominal aortic aneurysm in mice by attenuating macrophage-mediated inflammation. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 32:3012–3023
Jaeschke H, Bajt ML (2006) Intracellular signaling mechanisms of acetaminophen-induced liver cell death. Toxicol Sci 89:31–41
Jaeschkea H, Bajta M (2010) Mechanisms of acetaminophen hepatotoxicity. Comp Toxicol 9:457–473
Jaeschke H, McGill MR, Williams CD, Ramachandran A (2011) Current issues with acetaminophen hepatotoxicity-A clinically relevant model to test the efficacy of natural products. Life Sci 88:737–745
Jaeschke H, McGill MR, Ramachandran A (2012) Oxidant stress, mitochondria, and cell death mechanisms in drug-induced liver injury: lessons learned from acetaminophen hepatotoxicity. Drug Metab Rev 44:88–106
Jaeschke H (2015) Acetaminophen: dose-dependent drug hepatotoxicity and acute liver failure in patients. Dig Dis 33:464–471
James LP, Mayeux PR, Hinson JA (2003) Acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity. Drug Metab Dispos 31:1499–1506
James LP, Simpson PM, Farrar HC, Kearns GL, Wasserman GS, Blumer JL, Reed MD, Sullivan JE, Hinson JA (2005) Cytokines and toxicity in acetaminophen overdose. J Clin Pharmacol 45:1165–1171
Jia G, Cheng G, Gangahar DM, Agrawal DK (2006) Insulin-like growth factor-1 and TNF-alpha regulate autophagy through c-jun N-terminal kinase and Akt pathways in human atherosclerotic vascular smooth cells. Immunol Cell Biol 84:448–454
Jiang L, Ke M, Yue S, Xiao W, Yan Y, Deng X, , Ying QL Li J, Ke B (2017) Blockade of Notch Signaling Promotes Acetaminophen-Induced Liver Injury. Immunol Res 65: 739-749.
Kandil EA, Sayed RH, Ahmed LA, Abd El Fattah MA, El-Sayeh BM (2018) Modulatory role of Nurr1 activation and thrombin inhibition in the neuroprotective effects of dabigatran etexilate in rotenone-induced Parkinson’s disease in rats. Mol Neurobiol 55:4078–4089
Kaplowitz N (2004) Acetaminophen hepatoxicity: what do we know, what don’t we know, and what do we do next? Hepatology 40:23–26
Kerfoot SM, Kubes P (2005) Local coordination verses systemic disregulation: complexities in leukocyte recruitment revealed by local and systemic activation of TLR4 in vivo. J Leukoc Biol 77:862–867
Kiruthiga P, Shafreen RB, Pandian SK, Devi KP (2007) Silymarin protection against major reactive oxygen species released by environmental toxins: exogenous H2O2 exposure in erythrocytes. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 100:414–419
Kopan R, Ilagan MX (2004) Gamma-secretase: proteasome of the membrane? Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 5:499–504
Kotsafti A, Farinati F, Cardin R, Cillo U, Nitti D, Bortolami M (2012) Autophagy and apoptosis-related genes in chronic liver disease and hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC Gastroenterol 12:118–128
Larson AM (2007) Acetaminophen hepatotoxicity. Clin Liver Dis 11:525–548
Lee WR, Kim SJ, Park JH, Kim KH, Chang YC, Park YY, Lee KG, Han SM, Yeo J, Pak SC (2010) Bee venom reduces atherosclerotic lesion formation via anti-inflammatory mechanism. Am J Chin Med 38:1077–1092
Levine B, Kroemer G (2008) Autophagy in the pathogenesis of disease. Cell 132:27–42
Lien DP, Hoang CK, Hanh NT, Chu DX, Tram PB, Toan HT (2016) Hepatoprotective effect of silymarin on chronic hepatotoxicity in mice induced by carbon tetrachloride. J Pharmacogn Phytochem 5:262–266
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Maniati E, Bossard M, Cook N, Candido JB, Emami-Shahri N, Nedospasov SA, Balkwill FR, Tuveson DA, Hagemann T (2011) Crosstalk between the canonical NF-κB and Notch signaling pathways inhibits Pparγ expression and promotes pancreatic cancer progression in mice. J Clin Invest 121:4685–4699
McGill MR, Sharpe MR, Williams CD, Taha M, Curry SC, Jaeschke H (2012) The mechanism underlying acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in humans and mice involves mitochondrial damage and nuclear DNA fragmentation. J Clin Invest 122:1574–1583
Ni HM, Bockus A, Boggess N, Jaeschke H, Ding WX (2012) Activation of autophagy protects against acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity. Hepatology 55:222–232
Niki E (2009) Peroxidation: physiological levels and dual biological effects. Free Radic Biol Med 47:469–484
Okokon JE, Simeon JO, Umoh EE (2017) Hepatoprotective activity of the extract of Homaliumletestui stem against paracetamol-induced liver injury. Avicenna J Phytomed 7:27–36
Oswald F, Liptay S, Adler G, Schmid RM (1998) NF-kappaB2 is a putative target gene of activated Notch-1 via RBP-Jkappa. Mol Cell Biol 18:2077–2088
Outtz HH, Wu JK, Wang X, Kitajewski J (2010) Notch1 deficiency results in decreased inflammation during wound healing and regulates vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 and inflammatory cytokine expression in macrophages. J Immunol 185:4363–4373
Oztay F, Gezginci-Oktayoglu S, Bayrak BB, Yanardag R, Bolkent S (2010) Cathepsin B inhibition improves lung injury associated to D-galactosamine/tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced liver injury in mice. Mol Cell Biochem 333:65–72
Palabiyik SS, Karakus E, Halici Z, Cadirci E, Bayir Y, Ayaz G, Cinar I (2016) The protective effects of carvacrol and thymol against paracetamol-induced toxicity on human hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines (HepG2). Hum Exp Toxicol 35:1252–1263
Papackova Z, Heczkova M, Dankova H, Sticova E, Lodererova A, Bartonova L, Poruba M, Cahova M (2018) Silymarin prevents acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in mice. PLoS One 13:e0191353
Pan L, Li Y, Jia L, Qin Y, Qi G, Cheng J, Qi Y, Li H, Du J (2012) Cathepsin S deficiency results in abnormal accumulation of autophagosomes in macrophages and enhances Ang II-induced cardiac inflammation. PLoS One 7:e35315
Pasparakis M, Luedde T, Schmidt-Supprian M (2006) Dissection of the NF-κB signalling cascade in transgenic and knockout mice. Cell Death Differ 13:861–872
Piggott K, Deng J, Warrington K, Younge B, Kubo JT, Desai M, Goronzy JJ, Weyand CM (2011) Blocking the NOTCH pathway inhibits vascular inflammation in large-vessel vasculitis. Circulation 123:309–318
Prabu K, Kanchana N, Sadiq AM (2017) Hepatoprotective effect of Ecliptaalba on paracetamol-induced liver toxicity in rats. J Microbiol Biotechnol 1:75–79
Ramasamy K, Agarwal R (2008) Multitargeted therapy of cancer by silymarin. Cancer Lett 269:352–362
Rao AL, Aminabee S, Eswaraiah MC (2018) Evaluation of hepatoprotective activity of Indigoferabarberi in rats against paracetamol-induced hepatic injury. Adv Inv Pha The Medic 1:1–9
Ravikumar B, Berger Z, Vacher C, O’Kane CJ, Rubinsztein DC (2006) Rapamycin pre-treatment protects against apoptosis. Hum Mol Genet 15:1209–1216
Reid AB, Kurten RC, McCullough SS, Brock RW, Hinson JA (2005) Mechanisms of acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity: role of oxidative stress and mitochondrial permeability transition in freshly isolated mouse hepatocytes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 312:509–516
Rumack BH (2004) Acetaminophen misconceptions. Hepatology 40:10–15
Sallie R, Michael Tredger J, Williams R (1991) Drugs and the liver part 1: testing liver function. Biopharm Drug Dispos 12:251–259
Shen C, Chen Y, Liu H, Zhang K, Zhang T, Lin A, Jing N (2008) Hydrogen peroxide promotes Abeta production through JNK-dependent activation of gamma-secretase. J Biol Chem 283:17721–17730
Shi Z, Deng J, Fu S, Wang L, Wang Q, Liu B, Li Y, Deng J (2017) Protective effect of autophagy in neural ischemia and hypoxia: negative regulation of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Int J Mol Med 40:1699–1708
Sivaprasad U, Basu A (2008) Inhibition of ERK attenuates autophagy and potentiates tumour necrosis factor-alpha-induced cell death in MCF-7 cells. J Cell Mol Med 12:1265–1271
Song NJ, Yun UJ, Yang S, Wu C, Seo CR, Gwon AR, Baik SH, Choi Y, Choi BY, Bahn G, Kim S, Kwon SM, Park JS, Baek SH, Park TJ, Yoon K, Kim BJ, Mattson MP, Lee SJ, Jo DG, Park KW (2016) Notch1 deficiency decreases hepatic lipid accumulation by induction of fatty acid oxidation. Sci Rep 6:19377
Struhl K (1998) Histone acetylation and transcriptional regulatory mechanisms. Genes Dev 12:599–606
Swietek K, Juszczyk J (1997) Reduced glutathione concentration in erythrocytes of patients with acute and chronic viral hepatitis. J Viral Hepat 4:139–141
Tai M, Zhang J, Song S, Miao R, Liu S, Pang Q, Liu C (2015) Protective effects of luteolin against acetaminophen-induced acute liver failure in mouse. Int Immunopharmacol 27:164–170
Tiegs G, Wolter M, Wendel A (1989) Tumor necrosis factor is a terminal mediator in galactosamine/endotoxin-induced hepatitis in mice. Biochem Pharmacol 38:627–631
Venkatesan T, Choi YW, Mun SP, Kim YK (2016) Pinusradiata bark extract induces caspase-independent apoptosis-like cell death in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. Cell Biol Toxicol 32:451–464
Wang L, Huang QH, Li YX, Huang YF, Xie JH, Xu LQ, Dou YX, Su ZR, Zeng HF, Chen JN (2018) Protective effects of silymarin on triptolide-induced acute hepatotoxicity in rats. Mol Med Rep 17:789–800
Wu X, Fleming A, Ricketts T, Pavel M, Virgin H, Menzies FM, Rubinsztein DC (2016) Autophagy regulates Notch degradation and modulates stem cell development and neurogenesis. Nat Commun 7:10533
Yang X, Schnackenberg LK, Shi Q, Salminen WF (2014) Hepatic toxicity biomarkers. In: G.R (Ed.), Biomarkers in Toxicology. Elsevier Inc., NY, USA, pp. 241-259.
Yilmaz I, Cetin A, Bilgic Y (2015) Hepatoprotective effects of apricot against acetaminophen-induced acute hepatotoxicity in rats. Am J Pharmacol Sci 3:44–48
Yoon E, Babar A, Choudhary M, Kutner M, Pyrsopoulos N (2016) Acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity: a comprehensive update. J Clin Transl Hepatol 4:131–142
Zhang Y, Zhang F, Wang K, Liu G, Yang M, Luan Y, Zhao Z (2016) Protective effect of allyl methyl disulfide on acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in mice. Chem Biol Interact 249:71–77
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Prof. Dr. A. Bakear (Pathology Department, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Cairo University, Cairo, Egypt) for his assistance in the histopathological examinations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LAA, RHA, SKH, and MFE conceived and designed research. RHA, AMG, and SKH conducted experiments. LAA, RHA, AMG, and MFE analyzed data. RHA and LAA wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. All data were generated at National Organization for Drug Control and Research (NODCAR, Giza, Egypt), and no paper mill was used.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
All procedures performed in this study were conducted in accordance with the regulations approved by the Ethics Committee at Faculty of Pharmacy, Cairo University (permit number: 2385). The investigation complied with the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals published by the US National Institutes of Health (NIH Publication No. 85-23, revised 2011).
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(XLSX 26 kb)
Supplementary figure 1
Representative images for scores of hepatic damage; (A) No damage, score 0 revealing normal histological structure of the portal vein (pv), bile duct (bd) and the surrounding hepatocytes (h). (B) mild damage with score 1, showing few inflammatory cells infiltration in the portal area (arrow). (C) moderate damage with score 2, showing dilation and congestion in the portal vein (pv) with moderate inflammatory cells infiltration in the portal area (arrow). (D) severe damage with score 3, demonstrating hyperplasia in the bile duct (hbd), diffuse Kupffer cells (k), focal lymphoid cells aggregation (lym) and marked inflammatory cells infiltration in the portal area (arrow) (JPG 3025 kb)
Supplementary figure 2
Full-scanned images of western blots presented in Fig. 4 (JPG 753 kb)
Supplementary figure 3
Full-scanned images of western blots presented in Fig. 5 (JPG 777 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmed, L.A., Abd El-Rhman, R.H., Gad, A.M. et al. Dibenzazepine combats acute liver injury in rats via amendments of Notch signaling and activation of autophagy. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 394, 337–348 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-020-01977-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-020-01977-0