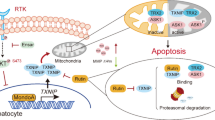
Abstract
Acetaminophen (APAP) overdose is currently the leading cause of acute liver disease, but therapeutic treatment strategies are commonly limited. Although dihydroquercetin (DHQ) is an attractive botanical antioxidant, its protective potential for liver disease remains elusive. The present study investigated the protective effects of DHQ against APAP-induced hepatic cytotoxicity. Primary mouse hepatocytes were treated with different concentrations of DHQ followed by APAP administration. Our data showed that DHQ relieved APAP-induced growth inhibition and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release in a dose-dependent manner, as well as inhibited APAP-induced necrosis and extracellular signal regulated kinase-c-Jun-N-terminal kinase (ERK-JNK) stress. In addition, reactive oxygen species (ROS) accumulation and mitochondria dysfunction were also reversed by DHQ treatment. Further study revealed that DHQ induced phosphorylation of Janus kinase 2/signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (JAK2/STAT3) cascade and thus modulated expression of anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 family proteins. Moreover, DHQ induced autophagy which mediated its protective effects in hepatocytes. The protection was abrogated through pharmacological blockage of autophagy by chloroquine (CQ). These studies demonstrated, for the first time, that DHQ possessed hepatocellular protective effects in the context of APAP-induced cytotoxicity and subsequently revealed that the mechanisms comprised activation of JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway and autophagy. These altogether highlighted the significant therapeutic potential of this agent during acute liver failure and other types of liver diseases.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antoine DJ, Williams DP, Park BK (2008) Understanding the role of reactive metabolites in drug-induced hepatotoxicity: state of the science. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol 4(11):1415–1427. https://doi.org/10.1517/17425255.4.11.1415
Athuraliya TN, Jones AL (2009) Prolonged N-acetylcysteine therapy in late acetaminophen poisoning associated with acute liver failure—a need to be more cautious? Crit Care 13(3):144. https://doi.org/10.1186/cc7800
Baulies A, Ribas V, Núñez S, Torres S, Alarcón-Vila C, Martínez L, Suda J, Ybanez MD, Kaplowitz N, García-Ruiz C, Fernández-Checa (2015) JC lysosomal cholesterol accumulation sensitizes to acetaminophen hepatotoxicity by impairing mitophagy. Sci Rep 5(1):18017. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep18017
Boengler K, Hilfiker-Kleiner D, Drexler H, Heusch G, Schulz R (2008) The myocardial JAK/STAT pathway: from protection to failure. Pharmacol Ther 120(2):172–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2008.08.002
Bunchorntavakul C, Reddy KR (2013) Acetaminophen-related hepatotoxicity. Clin Liver Dis 17(4):587–607. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cld.2013.07.005
Cai W, Yang X, Han S, Guo H, Zheng Z, Wang H, Guan H, Jia Y, Gao J, Yang T, Zhu X, Hu D (2016) Notch1 Pathway Protects against Burn-Induced Myocardial Injury by Repressing Reactive Oxygen Species Production through JAK2/STAT3 Signaling. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2016:5638943. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/5638943
Chen W, Zhang X, Fang J, Zai W, Luan J, Li Y, Wang S, Chen Q, Wang Y, Liang Y, Ju D (2017) Tethering Interleukin-22 to apolipoprotein A-I ameliorates mice from acetaminophen-induced liver injury. Theranostics 7(17):4135–4148. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.20955
Jaeschke H, McGill MR, Ramachandran A (2012) Oxidant stress, mitochondria, and cell death mechanisms in drug-induced liver injury: lessons learned from acetaminophen hepatotoxicity. Drug Metab Rev 44(1):88–106. https://doi.org/10.3109/03602532.2011.602688
Kroll DJ, Shaw HS, Oberlies NH (2007) Milk thistle nomenclature: why it matters in cancer research and pharmacokinetic studies. Integr Cancer Ther 6(2):110–119. https://doi.org/10.1177/1534735407301825
Kuang, H, Tang Z, Zhang C, Wang Z, Li W, Yang C, Wang Q, Yang B, Kong A (2017) Taxifolin activates the Nrf2 anti-oxidative stress pathway in mouse skin epidermal JB6 P+ cells through epigenetic modifications. Int J Mol Sci 18(7). doi:https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18071546
Latchoumycandane C, Goh CW, Ong MM, Boeisterli UA (2007) Mitochondrial protection by the JNK inhibitor leflunomide rescues mice from acetaminophen-induced liver injury. Hepatology 45(2):412–421. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.21475
Lee KK, Imaizumi N, Chamberiand SR, Alder NN, Boelsterli UA (2015) Targeting mitochondria with methylene blue protects mice against acetaminophen-induced liver injury. Hepatology 61(1):326–336. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.27385
Li Y, Zeng X, Wang S, Sun Y, Wang Z, Fan J, Song P, Ju D (2015) Inhibition of autophagy protects against PAMAM dendrimers-induced hepatotoxicity. Nanotoxicology 9(3):344–355. https://doi.org/10.3109/17435390.2014.930533
Lin Z, Wu F, Lin S, Pan X, Jin L, Lu T, Shi L, Wang Y, Xu A, Li X (2014) Adiponectin protects against acetaminophen-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and acute liver injury by promoting autophagy in mice. J Hepatol 61(4):825–831. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2014.05.033
Mahmoud AM, Abd EI-Twab SM (2017) Caffeic acid phenethyl ester protects the brain against hexavalent chromium toxicity by enhancing endogenous antioxidants and modulating the JAK/STAT signaling pathway. Biomed Pharmacother 91:303–311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2017.04.073
McGarry DJ, Chakravarty P, Wolf CR, Henderson CJ (2015) Altered protein S-glutathionylation identifies a potential mechanism of resistance to acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 355(2):137–144. https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.115.227389
McGill MR, Sharpe MR, Williams CD, Taha M, Curry SC, Jaeschke H (2012) The mechanism underlying acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in humans and mice involves mitochondrial damage and nuclear DNA fragmentation. J Clin Invest 122(4):1574–1583. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI59755
Ni HM, Bockus A, Boggess N, Jaeschke H, Ding WX (2012) Activation of autophagy protects against acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity. Hepatology 55(1):222–232. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.24690
Ni HM, McGill MR, Chao X, Du K, Williams JA, Xie Y, Jaeschke H, Ding WX (2016) Removal of acetaminophen protein adducts by autophagy protects against acetaminophen-induced liver injury in mice. J Hepatol 65(2):354–362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2016.04.025
Oi N, Cheng H, Ok Kim M, Lubet RA, Bode AM, Dong Z (2012) Taxifolin suppresses UV-induced EGFR and PI3-K. Cancer Prev Res (Phila) 5(9):1103–1114. https://doi.org/10.1158/1940-6207
Pang C, Zheng Z, Shi L, Sheng Y, Wen H, Wang Z, Ji L (2016) Caffeic acid prevents acetaminophen-induced liver injury by activating the Keap1-Nrf2 antioxidative defense system. Free Radic Biol Med 91:236–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2015.12.024
Polyak SJ, Morishima C, Lohmann V, Pal S, Lee DY, Liu Y, Graf TN, Oberlies NH (2010) Identification of hepatoprotective flavonolignans from silymarin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107(13):5995–5999. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0914009107
Saberi B, Ybanez MD, Johnson HS, Gaarde WA, Han D, Kaplowitz N (2014) Protein kinase C (PKC) participates in acetaminophen hepatotoxicity through c-jun-N-terminal kinase (JNK)-dependent and -independent signaling pathways. Hepatology 59(4):1543–1554. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.26625
Saito C, Zwingmann C, Jaeschke H (2010) Novel mechanisms of protection against acetaminophen hepatotoxicity in mice by glutathione and N-acetylcysteine. Hepatology 51(1):246–254. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.23267
Sun X, Chen RC, Yang ZH, Sun GB, Wang M, Ma XJ, Yang LJ, Sun XB (2014) Taxifolin prevents diabetic cardiomyopathy in vivo and in vitro by inhibition of oxidative stress and cell apoptosis. Food Chem Toxicol 63:221–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2013.11.013
Teselkin YO, Babenkova IV, Kolhir VK, Baginskaya AI, Tjukavkina NA, Kolesnik YA, Selivanova IA, Eichholz AA (2000) Dihydroquercetin as a means of antioxidative defence in rats with tetrachloromethane hepatitis. Phytother Res 14(3):160–162. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1099-1573(200005)14:3<160::AID-PTR555>3.0.CO;2-Y
Theriault A, Wang Q, Van Iderstine SC, Chen B, Franke AA, Adeli K (2000) Modulation of hepatic lipoprotein synthesis and secretion by taxifolin, a plant flavonoid. J Lipid Res 41(12):1969–1979
Tian Y, Zhang W, Xia D, Modi P, Liang D, Wei M (2011) Postconditioning inhibits myocardial apoptosis during prolonged reperfusion via a JAK2-STAT3-Bcl-2 pathway. J Biomed Sci 18(1):53. https://doi.org/10.1186/1423-0127-18-53
Ueno T, Komatsu M (2017) Autophagy in the liver: functions in health and disease. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 14(3):170–184. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrgastro.2016.185
Wang L, Zhang S, Cheng H, Lv H, Cheng G, Ci X (2016) Nrf2-mediated liver protection by esculentoside A against acetaminophen toxicity through the AMPK/Akt/GSK3β pathway. Free Radic Biol Med 101:401–412. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2016.11.009
Weidmann AE (2012) Dihydroquercetin: more than just an impurity? Eur J Pharmacol 684(1–3):19–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2012.03.035
Williams JA, Ni HM, Haynes A, Manley S, Li Y, Jaeschke H, Ding WX (2015) Chronic deletion and acute knockdown of Parkin have differential responses to acetaminophen-induced mitophagy and liver injury in mice. J Biol Chem 290(17):10934–10946. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M114.602284
Wu J, Guo W, Lin SZ, Wang ZJ, Kan JT, Chen SY, Zhu YZ (2016) Gp130-mediated STAT3 activation by S-propargyl-cysteine, an endogenous hydrogen sulfide initiator, prevents doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. Cell Death Dis 7(8):e2339. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2016.209
Xie W, Wang M, Chen C, Zhang X, Melzig MF (2016) Hepatoprotective effect of isoquercitrin against acetaminophen-induced liver injury. Life Sci 152:180–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2016.04.002
Xie X, Feng J, Kang Z, Zhang S, Zhang L, Zhang Y, Li X, Tang Y (2017) Taxifolin protects RPE cells against oxidative stress-induced apoptosis. Mol Vis 23:520–528
Yu HC, Qin HY, He F, Wang L, Fu W, Liu D, Guo FC, Liang L, Dou KF, Han H (2011) Canonical notch pathway protects hepatocytes from ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice by repressing reactive oxygen species production through JAK2/STAT3 signaling. Hepatology 54(3):979–988. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.24469
Zhang E, Yin S, Song X, Fan L, Hu H (2016) Glycycoumarin inhibits hepatocyte lipoapoptosis through activation of autophagy and inhibition of ER stress/GSK-3-mediated mitochondrial pathway. Sci Rep 6(1):38138. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep38138
Zhang X, Fan J, Wang S, Li Y, Wang Y, Li S, Luan J, Wang Z, Song P, Chen Q, Tian W, Ju D (2017) Targeting CD47 and autophagy elicited enhanced antitumor effects in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Immunol Res 5(5):363–375. https://doi.org/10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-16-0398
Zhao M, Chen J, Zhu P, Fujino M, Takahara T, Toyama S, Tomita A, Zhao L, Yang Z, Hei M, Zhong L, Zhuang J, Kimura S, Li XK (2015) Dihydroquercetin (DHQ) ameliorated concanavalin A-induced mouse experimental fulminant hepatitis and enhanced HO-1 expression through MAPK/Nrf2 antioxidant pathway in RAW cells. Int Immunopharmacol 28(2):938–944. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2015.04.032
Zu S, Yang L, Huang J, Ma C, Wang W, Zhao C, Zu Y (2012) Micronization of taxifolin by supercritical antisolvent process and evaluation of radical scavenging activity. Int J Mol Sci 13(7):8869–8881. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms13078869
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 81573332 and 81773620) and Special Research Foundation of State Key Laboratory of Medical Genomics and Collaborative Innovation Center of Systems Biomedicine.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All animal care and experiment procedures complied with the Animal Management Rules of China and were approved by the Animal Care Committee of Fudan University.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All applicable international, national, and institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 591 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zai, W., Chen, W., Luan, J. et al. Dihydroquercetin ameliorated acetaminophen-induced hepatic cytotoxicity via activating JAK2/STAT3 pathway and autophagy. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102, 1443–1453 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8686-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8686-6