Abstract
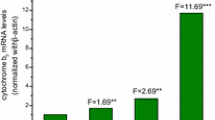
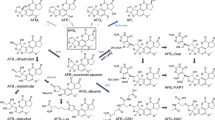
Chronic administration of aflatoxin B1 (AFB1) to rats gives rise to hepatocellular and cholangiocellular carcinomas without affecting Kupffer and endothelial cells. The enzymatic conversion of AFB1 to AFB1-8,9-epoxide is the critical step in the activation of the mycotoxin, while the conversion of AFB1 to aflatoxin M1 (AFM1), catalyzed by the AFB1-9a-hydroxylase, is considered to be a detoxication route for the toxin. In the present study the distribution and inducibility of AFB1-9a-hydroxylase were analyzed in microsomes derived from freshly isolated liver parenchymal (PC) and nonparenchymal cells (i.e. Kupffer +endothelial cells, NPC). AFB1-9a-hydroxylase activity was clearly measurable in NPC and similar to that of PC. In NPC the rate of formation of AFM1 was higher (when incubating with 16 μM AFB1) than or similar (with 128 μM AFB1) to that of AFB1-8,9-epoxide, while in PC it was significantly lower. Taken together, these results suggest that the AFB1-9a-hydroxylase activity might be particularly important in NPC to protect these cells from AFB1 by converting it to a significantly less mutagenic metabolite and by reducing the amount of AFB1 available for epoxidation. Furthermore, it is shown that AFB1-9a-hydroxylase activity is inducible by phenobarbital (only in PC), 3-methylcholanthrene, isosafrole and Aroclor 1254, thus indicating that in rat liver the conversion of AFB1 to AFM1 is catalyzed by members of the cytochrome 1A and 2B families.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Appleton S, Goetchius MP, Campell TC (1982) Linear dose-response curve for the hepatic macromolecular binding of aflatoxin B1 in rats at very low exposures. Cancer Res 42: 3659–3662
Autrup H, Essigmann JM, Croy RG, Trump BF, Wogan GN, Harris CC (1979) Metabolism of aflatoxin B1 and identification of the major aflatoxin B1-DNA adducts formed in cultured human bronchus and colon. Cancer Res 39: 694–698.
Baertschi SW, Raney KD, Stone MP, Harris TM (1988) Preparation of the 8,9-epoxide of the mycotoxin aflatoxin B1: the ultimate carcinogenic species. J Am Chem Soc 110: 7929–7931
Coles B, Meyer DJ, Ketterer B, Stanton CA, Garner RC (1985) Studies on the detoxication of microsomally activated aflatoxin B1 by glutathione and glutathione transferases in vitro. Carcinogenesis 6: 693–697
Croy RG, Wogan GN (1981) Temporal patterns of covalent DNA adducts in rat liver after single and multiple doses of aflatoxin B1 Cancer Res 41: 197–203
Degen GH, Neumann HG (1981) Differences in aflatoxin B1 susceptibility of rat and mouse are correlated with the capability in vitro to inactivate aflatoxin B1-epoxide. Carcinogenesis 2: 299–306
Dunnett CW (1964) New tables for multiple comparisons with a control. Biometrics 6: 482–494
Essigmann JM, Croy RG, Busby WF Jr, Reinhold VN, Büchi G, Wogan GN (1977) Structural identification of the major DNA adduct formed by aflatoxin B1 in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74: 1870–1874
Faletto MB, Gurtoo HL (1989) The effect of inducers of mixedfunction oxidases on hepatic microsome-mediated aflatoxin B1 transformation in C3H/10T1/2 cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 98: 252–262
Faletto MB, Koser PL, Battula N, Townsend GK, Maccubin AE, Gelboin HV, Gurtoo HL (1988) Cytochrome P3-450 cDNA encodes aflatoxin B1-4-hydroxylase. J Biol Chem 263: 12187–12189
Glatt HR, Billings R, Platt KL, Oesch F (1981) Improvement of the correlation of bacterial mutagenicity with carcinogenicity of benzo[a]pyrene and four of its major metabolites by activation with intact liver cells instead of homogenate. Cancer Res 41: 270–277
Gurtoo HL, Dahms RP, Paigen B (1978) Metabolic activation of aflatoxins related to their mutagenicity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 81: 965–972
Hertzog PJ, Smith JRL, Garner RC (1980) A high pressure liquid chromatography study on the removal of DNA-bound aflatoxin B1 in rat liver and in vitro. Carcinogenesis 1: 787–793
Holesky CJ, Eaton DL, Monroe DH, Bellamy GM (1987) Effects of phenobarbital on the biliary excretion of aflatoxin P1-glucuronide and aflatoxin B1-S-glutathione in the rat. Xenobiotica 17: 139–153
IARC (1993) Aflatoxins. In: IARC monographs on the evaluation of carcinogenic risks to humans, vol. 56, IARC Science Publishers, Lyon, pp 245–395
Ishii K, Maeda K, Kamataki T, Kato R (1986) Mutagenic activation of aflatoxin B1 by several forms of purified cytochrome P-450. Mutat Res 174: 85–88
Jennings GS, Oesch F, Steinberg P (1992) In vivo formation of aflatoxin B1-DNA adducts in parenchymal and nonparenchymal cells of rat liver. Carcinogenesis 13: 831–835
Jorgensen KV, Clayton JW, Price RL (1987) Evaluation of aflatoxin B1 mutagenesis: addition of glutathione and glutathione-S-transferase to the Salmonella mutagenicity assay. Environ Mutagen 9: 411–419
Kalengayi MMR, Desmet VJ (1975) Sequential histological and histochemical study of the rat liver during aflatoxin B1-induced carcinogenesis. Cancer Res 35: 2845–2852
Kitada M, Taneda M, Die H, Komori M, Itahashi K, Nagao M, Kamataki J (1989) Mutagenic activation of aflatoxin B1 by P-450 HFLa in human fetal livers. Mutat Res 227: 53–58
Koser PL, Faletto MB, Maccubbin AE, Gurtoo HL (1988) The genetics of aflatoxin B1 metabolism. Association of the induction of aflatoxin B1-4-hydroxylase with the transcriptional activation of cytochrome P3-450 gene. J Biol Chem 263: 12584–12595
Lafranconi WM, Glatt HR, Oesch F (1986) Xenobiotic metabolizing enzymes of rat liver nonparenchymal cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 84: 500–511
Metcalfe SA, Neal GE (1983) Some studies on the relationship between the cytotoxicity of aflatoxin B1 to rat hepatocytes and metabolism of the toxin. Carcinogenesis 4: 1013–1019
Metcalfe SA, Colley PJ, Neal GE (1981) A comparison of the effects of pretreatment with phenobarbitone and 3-methylcholanthrene on the metabolism of aflatoxin B1 by rat liver microsomes and isolated hepatocytes in vitro. Chem-Biol Interact 35: 145–157
Monroe DH, Eaton DL (1987) Comparative effects of butylated hydroxyanisole on hepatic in vivo DNA binding and in vitro biotransformation of aflatoxin B1 in the rat and mouse. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 34: 128–142
Newberne PM, Butler WH (1969) Acute and chronic effects of aflatoxin B1 on the liver of domestic and laboratory animals: a review. Cancer Res 29: 236–250
Newberne PM, Wogan GN (1968) Sequential morphologic changes in aflatoxin B1 carcinogenesis in the rat. Cancer Res 28: 770–781
Oesch F, Arand M, Coughtrie MW, Burchell B, Steinberg P (1992) The distribution of UDP-glucuronosyltransferase in rat liver parenchymal and nonparenchymal cells. Biochem Pharmacol 43: 731–737
Ramsdell HS, Eaton DL (1990) Species susceptibility to aflatoxin B1 carcinogenesis: comparative kinetics of microsomal biotransformation. Cancer Res 50: 615–620
Schlemper B, Harrison J, Garner RC, Oesch F, Steinberg P (1991) DNA binding, adduct characterisation and metabolic activation of aflatoxin B1 catalysed by isolated rat liver parenchymal, Kupffer and endothelial cells. Arch Toxicol 65: 633–639
Shimada T, Guengerich FP (1989) Evidence for cytochrome P-450 NF, the nifedipine oxidase, being the principal enzyme involved in the bioactivation of aflatoxins in human liver. Proc Natl Acad USA 86: 462–465
Shimada T, Nakamura S, Omaoka S, Funae Y (1987) Genotoxic and mutagenic activation of aflatoxin B1 by constitutive forms of cytochrome P-450 in rat liver microsomes. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 91: 13–21
Steinberg P, Lafranconi WM, Wolf CR, Waxman DJ, Oesch F, Friedberg T (1987) Xenobiotic metabolizing enzymes are not restricted to parenchymal cells in rat liver. Mol Pharmacol 32: 463–470
Steinberg P, Schladt L, Dienes HP, Timms C, Oesch F (1988) Microsomal and cytosolic epoxide hydrolases, the peroxisomal fatty acid β-oxidation system and catalase: activities, distribution and induction in rat liver parenchymal and nonparenchymal cells. Eur J Biochem 176: 39–45
Steinberg P, Schramm H, Thomas H, Schladt L, Robertson LW, Oesch F (1989) The distribution, induction and isoenzyme profile of glutathione transferase and glutathione peroxidase in isolated rat liver parenchymal, Kupffer and endothelial cells. Biochem J 264: 737–744
Stresser DM, Bailey GS, Williams DE (1994) Indole-3-carbinol and β-naphthoflavone induction of aflatoxin B1 metabolism and cytochromes P-450 associated with bioactivation and detoxincation of aflatoxin B1 in the rat. Drug Metab Dispos 22: 383–391
Thomas PE, Reik LM, Ryan DE, Levin W (1983) Induction of two immunochemically related rat liver cytochrome P-450 isozymes, cytochromes P-450c and P-450d, by structurally diverse xenobiotics. J Biol Chem 258: 4590–4598
Wild CP, Garner RC, Montesano R, Tursi F (1986) Aflatoxin B1 binding to plasma albumin and liver DNA upon chronic administration to rats. Carcinogenesis 7: 853–858
Wogan GN (1973) Aflatoxin carcinogenesis. In: Busch H (ed) Methods in cancer research. Academic Press, New York, p 309
Wogan GN, Newberne PM (1967) Dose-dependent characteristics of aflatoxin B1 carcinogenesis in the rat. Cancer Res 27: 2370–2376
Wong JJ, Hsieh DPH (1976) Mutagenicity of aflatoxins related to their metabolism and carcinogenic potential. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 73: 2241–2244
Wong ZA, Hsieh DPH (1980) The comparative metabolism and toxicokinetics of aflatoxin B1 in the monkey, rat and mouse. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 55: 115–125
Yoshizawa H, Uchimaru R, Kamataki T, Kato R, Ueno Y (1982) Metabolism and activation of aflatoxin B1 by reconstituted cytochrome P-450 system of rat liver. Cancer Res 42: 1120–1124
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gemechu-Hatewu, M., Platt, K.L., Oesch, F. et al. Distribution and induction of aflatoxin B1-9a-hydroxylase activity in rat liver parenchymal and non-parenchymal cells. Arch Toxicol 70, 553–558 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002040050312
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002040050312