Abstract
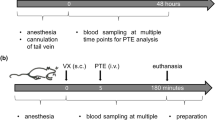
The rapid onset of cholinergic crisis after intoxication with highly toxic organophosphorus compounds calls for pre-clinical administration of effective antidotes as early as possible. For this purpose, i.m. administration of the antidotes by autoinjectors is desired to allow early treatment also in the absence of a physician. Besides atropine, oximes with broad antidotal spectrum are considered valuable adjuncts that should be included in antidotal mixtures. To circumvent the problem of limited stability of the new-generation oximes, dry/wet autoinjectors were developed in which the unstable solid is dissolved by a diluent in an adjacent chamber upon activation of the device. In this study the tolerance, bioavailability and pharmacokinetics of 500 mg HI 6 [1-(((4-(aminocarbonyl) pyridinio)methoxy) methyl)-2-((hydroxyimino)methyl) pyridinium dichloride monohydrate] or 200 mg HLö 7 [1-(((4-(aminocarbonyl) pyridinio)methoxy)methyl)-2,4-bis ((hydroxyimino)methyl)pyridinium dimethanesulfonate] in combination with 2 mg atropine sulfate versus atropine alone, delivered by two dry/wet autoinjector types, were investigated in eight male beagle dogs (16 kg) in a complete cross-over design. The dogs tolerated the six injections with 3-week intervals without any symptoms of discomfort. Nonetheless, CPK activity increased, peaking at 6 h after injection. In contrast to atropine which merely led to a marginal increase, HI 6 plus atropine increased the baseline CPK activity about 10-fold, and HLö 7 plus atropine about 20-fold, regardless of the injector type. The HI 6 autoinjectors from Astra Tech were from an irregular production batch which did not deliver the declared HI 6 dose. The HLö 7 autoinjectors from Astra Tech and both Binjaect autoinjectors from STI functioned well: the bioavailability was complete with tmax values of about 25 min as observed after conventional i.m. injection. The absorption half-time was about 8 min, elimination t1/2 about 50 min, and Vapp 0.26 l/kg. The urinary recovery of unchanged oximes was 70–80%, the renal clearance being the same as for inulin. Unexpectedly, hematocrit and hemoglobin content of blood decreased by about 15% within 2 h and reached pre-treatment values after 6–24 h. This decrease was observed with all three drug treatments and could not be accounted for by blood loss (<4%), thus pointing to an atropine effect. In conclusion, the newly developed dry/wet autoinjectors appear suitable for the administration of atropine and an oxime stored in solid form.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adolph EF (1949) Quantitative relations in the physiological constitutions of mammals. Science 109: 579–585
Albanus L, Jarplid B, Sundwall A (1961) The chronic toxicity of 2-hydroxyiminomethyl-N-methylpyridinium methanesulfonate (P2S), a reactivator of phosphorylated cholinesterase. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol 18: 321–328
Albanus L, Jarplid B, Sundwall A (1964) The toxicity of some cholinesterase-reactivating oximes. Br J Exp Pathol 45: 120–127
Alberts P (1990) A new H-oxime restores rat diaphragm contractility after esterase inhibition in vitro. Eur J Pharmacol 184: 191–194
Andersen AC (1970) The beagle as an experimental dog. Iowa University Press, Ames
Baggot JD, Buckpitt A, Johnson D, Brennan P, Chung H (1993) Bioavailability and disposition kinetics of HI 6 in beagle dogs. Biopharm Drug Dispos 14: 93–105
Boskovic B (1981) The treatment of soman poisoning and its perspectives. Fundam Appl Toxicol 1: 203–213
Boskovic B, Kovacevic V, Jovanovic D (1984) PAM-2 Cl, HI-6, and HGG-12 in soman and tabun poisoning. Fundam Appl Toxicol 4: S106-S115
Cetkovic S, Cvetkovic M, Jandric D, Cosic M, Boskovic B (1984) Effect of PAM-2 Cl, HI-6, and HGG-12 in poisoning by tabun and its thiocholine-like analog in the rat. Fundam Appl Toxicol 4: S116-S123
Clement JG (1981) Toxicology and pharmacology of bispyridinium oximes — insight into the mechanism of action vs soman poisoning in vivo. Fundam Appl Toxicol 1: 193–202
Clement JG (1983) Efficacy of mono- and bis-pyridinium oximes versus soman, sarin and tabun poisoning in mice. Fundam Appl Toxicol 3: 533–535
Clement JG, Shiloff JD, Gennings C (1987) Efficacy of a combination of acetylcholine reactivators, HI-6 and obidoxime, against tabun and soman poisoning of mice. Arch Toxicol 61: 70–75
Clement JG, Hansen AS, Boulet CA (1992a) Efficacy of HLö-7 and pyrimidoxime as antidotes of nerve agent poisoning in mice. Arch Toxicol 66: 216–219
Clement JG, Pierce CH, Houle J-M (1992b) Ascending dose tolerance study of the oxime, HI-6, in man. Proc. 4th Int. Symp. Protection Against Chemical Warfare Agents, Stockholm, Sweden
De Jong LPA, Verhagen MAA, Langenberg JP, Hagedorn I, Löffler M (1989) The bispyridinium-dioxime HLö-7. A potent reactivator for acetylcholinesterase inhibited by the stereoisomers of tabun and soman. Biochem Pharmacol 38: 633–640
De Jong LPA, Wolring GZ (1980) Reactivation of acetylcholinesterase inhibited by 1,2,2′-trimethylpropyl methylphosphonofluoridate (soman) with HI-6 and related oximes. Biochem Pharmacol 29: 2379–2387
Dost FH (1968) Grundlagen der Pharmakokinetik. G. Thieme, Stuttgart
Eyer P, Hell W (1985) Chemical stability of the Hagedorn oximes HGG 12 and HI 6. Arch Pharmacol 318: 938–946
Eyer P, Hell W, Kawan A, Klehr H (1986) Studies on the decomposition of the oxime HI 6 in aqueous solution. Arch Toxicol 59: 266–271
Eyer P, Kawan A, Ladstetter B (1987) Formation of cyanide after i.v. administration of the oxime HI 6 to dogs. Arch Toxicol 61: 63–69
Eyer P, Hagedorn I, Ladstetter B (1988) Study on the stability of the oxime HI 6 in aqueous solution. Arch Toxicol 62: 224–226
Eyer P, Ladstetter B, Schäfer W, Sonnenbichler J (1989) Studies on the stability and decomposition of the Hagedorn-oxime HLö 7 in aqueous solution. Arch Toxicol 63: 59–67
Eyer P, hagedorn I, Klimmek R, Lippstreu P, Löffler M, Oldiges H, Spöhrer U, Steidl I, Szinicz L, Worek F (1992) HLö 7 dimethanesulfonate, a potent bispyridinium-dioxime against anticholinesterases. Arch Toxicol 66: 603–621
Federer WT (1955) The latin square design. In: Federer WT (ed) Experimental design. MacMillan, New York, pp 135–165
Fyhr P, Nicklasson M, Gunnvald K, Brodin A (1987) A preformulation study on the kinetics of HI-6 in concentrated solution. Int J Pharm 40: 193–200
Hamilton MG, Lundy PM (1989) HI-6 Therapy of soman and tabun poisoning in primates and rodents. Arch Toxicol 63: 144–149
Inns RH, Leadbeater L (1983) The efficacy of bispyridinium derivatives in the treatment of organophosphate poisoning in the guinea pig. J Pharm Pharmacol 35: 427–433
Kiese M (1959) Oxydation von Anilin zu Nitrosobenzol im Hunde. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Exp Pathol Pharmakol 235: 354–359
Klimmek R, Eyer P (1986) Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of the oxime HI 6 in dogs. Arch Toxicol 59: 272–278
Kumar A, Shukla R, Shukla SB (1986) Evidence for sympathetic augmentation mediated increase in the blood and the plasma volume following vagotomy. Pharmacol Res Commun 18: 935–950
Kusic R, Boskovic B, Vojvodic V, Jovanovic D (1985) HI-6 in man: blood levels, urinary excretion, and tolerance after intramuscular administration of the oxime to healthy volunteers. Fundam Appl Toxicol 5: 89–97
Kusic R, Jovanovic D, Randjelovic S, Joksovic D, Todorovic V, Boskovic B, Jokanovic M, Vojvodic V (1991) HI-6 in man: efficacy of the oxime in poisoning by organophosphorus insecticides. Hum Exp Toxicol 10: 113–118
Lundy PM, Hansen AS, Hand BT, Boulet CA (1992) Comparison of several oximes against poisoning by soman, tabun and GF. Toxicology 72: 99–105.
Mailman D (1988) Effects of atropine and tetrodotoxin on neurotensin-induced ileal sodium transport in the dog. Br J Pharmacol 94: 121–129
Maksimovic M, Boskovic B, Radovic L, Tadic V, Deljac V, Binenfeld Z (1980) Antidotal effects of bis-pyridinium-2-monooxime carbonyl derivatives in intoxications with highly toxic organophosphorus compounds. Acta Pharm Jugosl 30: 151–160
Oldiges H, Schoene K (1970) Pyridinium- und Imidazoliumsalze als Antidote gegenüber Soman- und Paraoxonvergiftungen bei Mäusen. Arch Toxicol 26: 293–305
Rowland M, Tozer TN (1989) Clinical pharmacokinetics: concepts and applications. Saunders, Philadelphia
Sachs L (1978) Angewandte Statistik. 5. Aufl. Springer-Verlag Berlin, Heidelberg, New York
Schlager JW, Dolzine TW, Stewart JR, Wannarka GL, Shih ML (1991) Operational evaluation of three commercial configurations of atropine/HI-6 wet/dry autoinjectors. Pharm Res 8: 1191–1194
Schoene K, Oldiges H (1973) Die Wirkungen von Pyridiniumsalzen gegenüber Tabun- und Sarinvergiftungen in vivo und in vitro. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther 204: 110–123
Sidell FR, Markis JE, Groff W (1974) Enhancement of drug absorption after administration by an automatic injector. J Pharmacokinet Biopharmaceut 2: 197–210
Siegenthaler W (1970) Wasser- und Elektrolythaushalt. In: Siegenthaler W (ed) Klinische Pathophysiologie. G. Thieme, Stuttgart, pp 178–192
Simons KJ, Briggs CJ (1983) The pharmacokinetics of HI6 in beagle dogs. Biopharm Drug Dispos 4: 375–388
Sundwall A (1961) Minimum concentrations of N-methylpyridinium-2-aldoxime methane sulphonate (P2S) which reverse neuromuscular block. Biochem Pharmacol 8: 413–417
Thiermann H, Spöhrer U, Klimmek R, Eyer P (1994) Operational evaluation of wet/dry autoinjectors containing atropine in solution and powdered HI 6 or HLö 7. Int J Pharm (in press)
Willems JL, Belpaire FM (1992) Anticholinesterase poisoning: an overview of pharmacotherapy. In: Ballantyne B, Marrs T (eds) Clinical and experimental toxicology of organophosphates and carbamates. Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford, pp 536–542.
Wolthuis OL, Berends F, Meeter E (1981a) Problems in the therapy of soman poisoning. Fundam Appl Toxicol 1: 183–192
Wolthuis OL, Vanwersch RAP, van der Wiel HJ (1981b) The efficacy of some bis-pyridinium oximes as antidotes to soman in isolated muscles of several species including man. Eur J Pharmacol 70: 355–369
Worek F, Szinicz L (1993) Atropine and oxime treatment in lethal soman poisoning of anaesthetized guinea-pigs: HLö 7 dimethanesulfonate versus HI 6 dichloride. Pharmacol Toxicol 72: 13–21
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work forms part of the PhD thesis of U. Spöhrer
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Spöhrer, U., Thiermann, H., Klimmek, R. et al. Pharmacokinetics of the oximes HI 6 and HLö 7 in dogs after i.m. injection with newly developed dry/wet autoinjectors. Arch Toxicol 68, 480–489 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002040050100
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002040050100