Abstract
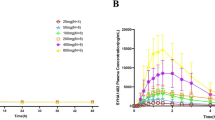
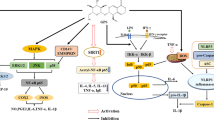
Sinomenine is a bioactive alkaloid isolated from the Chinese medicinal plant Sinomenium acutum (Thunb.) Rehd. et Wils which exhibits significant analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and immunosuppressive effects. Sinomenine hydrochloride (SH) preparations, classified as natural disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs, are currently available for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis and other rheumatic diseases. Our toxicity evaluation demonstrated that the median lethal dose of SH in female Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats was over 11 times greater than that in male SD rats, revealing striking sex-linked differences in the safety profile of SH. The present study was designed to investigate differences in the pharmacokinetics (PKs) and tissue distribution of SH between male and female SD rats after a single oral dose of 25 mg/kg. PK and tissue distribution studies were performed using a validated UPLC-MS/MS method. The results showed that SH-treated SD female rats displayed markedly greater drug exposure, and SH exhibited a longer half-life and slower clearance rate than comparable studies in male rats. Moreover, the tissue distribution study confirmed that the sinomenine concentration in female rats was considerably greater in the internal organs than in male rats. Our study demonstrates, for the first time, significant sex-related differences in the safety profile and PKs of SH, which may be associated with a distinct sex-dependent metabolic mechanism of sinomenine.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- SH:
-
Sinomenine hydrochloride
- nDMARD:
-
Natural disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drug
- RA:
-
Rheumatoid arthritis
- LD50 :
-
Median lethal dose
- SD:
-
Sprague-Dawley
- PK:
-
Pharmacokinetic
- UPLC-MS/MS:
-
Ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry
- ZQFTN:
-
Zhengqing Fengtongning
- ADME:
-
Absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion/elimination
- IS:
-
Internal standard
- HNUCM:
-
Hunan University of Chinese Medicine
- NIH:
-
National Institute of Health
- QC:
-
Quality control
- ESI:
-
Electrospray ionization
- MRM:
-
Multiple-reaction monitoring
- LLOQ:
-
Lower limit of quantification
- S/N:
-
Signal-to-noise
- RE:
-
Relative error
- RSD:
-
Relative standard deviation
- ANOVA:
-
Analysis of variance
- LSD:
-
Least significant difference
- CYP450s:
-
Cytochrome P450
References
Chen T, Doong M, Chang F, Lee S, Wang P (1995) Effects of sex steroid hormones on gastric emptying and gastrointestinal transit in rats. Am J Physiol 268:G171-176
Chen XM, Huang RY, Huang QC, Chu YL, Yan JY (2015) Systemic review and meta-analysis of the clinical efficacy and adverse effects of zhengqing fengtongning combined with methotrexate in rheumatoid arthritis. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2015:910376
Chen J, Zhong B, Wang Y (2017) Agranulocytosis induced by sinomenine hydrochloride. Am J Case Rep 18:959–962
Coşkun T, Sevinç A, Tevetoğlu I, Alican I, Kurtel H, Yeğen B (1995) Delayed gastric emptying in conscious male rats following chronic estrogen and progesterone treatment. Research in experimental medicine. Zeitschrift Fur Die Gesamte Experimentelle Medizin Einschliesslich Experimenteller Chirurgie 195:49–54
Deng F, Ma Y, Liang L, Zhang P, Feng J (2018) The pro-apoptosis effect of sinomenine in renal carcinoma via inducing autophagy through inactivating pi3k/akt/mtor pathway. Biomed Pharmacotherapy = Biomed Pharmacotherapie 97:1269–1274
Farkouh A, Riedl T, Gottardi R, Czejka M, Kautzky-Willer A (2020) Sex-related differences in pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of frequently prescribed drugs: a review of the literature. Adv Ther 37:644–655
Gandhi M, Aweeka F, Greenblatt RM, Blaschke TF (2004) Sex differences in pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics. Annu Rev Pharm Toxicol 44:499–523
Hogan A, Collins D, Baird A, Winter D (2009) Estrogen and its role in gastrointestinal health and disease. Int J Colorectal Dis 24:1367–1375
Kato R, Yamazoe Y (1992) Sex-specific cytochrome p450 as a cause of sex- and species-related differences in drug toxicity. Toxicol Lett 64:661–667
Kimura T, Higaki K (2002) Gastrointestinal transit and drug absorption. Biol Pharm Bull 25:149–164
Li S, Han J, Wang D, Yang Q, Feng B, Kang W, Yang L, Liu G, Zhao M (2017) Sinomenine attenuates chronic inflammatory pain in mice. Metab Brain Dis 32:211–219
Li Q, Zhou W, Wang Y, Kou F, Lyu C, Wei H (2020) Metabolic mechanism and anti-inflammation effects of sinomenine and its major metabolites n-demethylsinomenine and sinomenine-n-oxide. Life Sci 261:118433
Lin G, Cui Y, Liu X (2003) Gender differences in microsomal metabolic activation of hepatotoxic clivorine in rat. Chem Res Toxicol 16:768–774
Lin G, Tang J, Liu X, Jiang Y, Zheng J (2007) Deacetylclivorine: a gender-selective metabolite of clivorine formed in female sprague-dawley rat liver microsomes. Drug Metab Dispos: Biological Fate Chem 35:607–613
Liu Z, Chan K, Zhou H, Jiang Z, Wong Y, Xu H, Liu L (2005) The pharmacokinetics and tissue distribution of sinomenine in rats and its protein binding ability in vitro. Life Sci 77:3197–3209
Liu R, Che D, Zhao T, Pundir P, Cao J, Lv Y, Wang J, Ma P, Fu J, Wang N, Wang X, Zhang T, Dong X, He L (2017) Mrgprx2 is essential for sinomenine hydrochloride induced anaphylactoid reactions. Biochem Pharm 146:214–223
Liu J, Shao H, Fang S, Cheng Y, Ling P, Chen J (2019) Evaluation of pharmacokinetics and pharmaco-dynamics of sinomenine-hyaluronic acid conjugate after intra-articular administration for osteoarthritis treatment. Drug Des Dev Ther 13:657–665
Lyu C, Zhang Y, Zhou W, Zhang S, Kou F, Wei H, Zhang N, Zuo Z (2016) Gender-dependent pharmacokinetics of veratramine in rats: in vivo and in vitro evidence. AAPS J 18:432–444
Martignoni M, Groothuis G, de Kanter R (2006) Species differences between mouse, rat, dog, monkey and human cyp-mediated drug metabolism, inhibition and induction. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol 2:875–894
Mugford C, Kedderis G (1998) Sex-dependent metabolism of xenobiotics. Drug Metab Rev 30:441–498
Parkinson A, Mudra D, Johnson C, Dwyer A, Carroll K (2004) The effects of gender, age, ethnicity, and liver cirrhosis on cytochrome p450 enzyme activity in human liver microsomes and inducibility in cultured human hepatocytes. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 199:193–209
Raies AB, Bajic VB (2016) In silico toxicology: computational methods for the prediction of chemical toxicity. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Comput Mol Sci 6:147–172
Silva V, Gil-Martins E, Silva B, Rocha-Pereira C, Sousa ME, Remiao F, Silva R (2021) Xanthones as p-glycoprotein modulators and their impact on drug bioavailability. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol 17:441–482
Storelli F, Samer C, Reny JL, Desmeules J, Daali Y (2018) Complex drug-drug-gene-disease interactions involving cytochromes p450: systematic review of published case reports and clinical perspectives. Clin Pharmacokinet 57:1267–1293
Suzuki T, Zhao Y, Nadai M, Naruhashi K, Shimizu A, Takagi K, Takagi K, Hasegawa T (2006) Gender-related differences in expression and function of hepatic p-glycoprotein and multidrug resistance-associated protein (mrp2) in rats. Life Sci 79:455–461
Thangavel C, Dworakowski W, Shapiro B (2006) Inducibility of male-specific isoforms of cytochrome p450 by sex-dependent growth hormone profiles in hepatocyte cultures from male but not female rats. Drug Metab Dispos: Biological Fate Chem 34:410–419
Tsai T, Wu J (2003) Regulation of hepatobiliary excretion of sinomenine by p-glycoprotein in sprague-dawley rats. Life Sci 72:2413–2426
Vinarov Z, Abdallah M, Agundez JAG, Allegaert K, Basit AW, Braeckmans M, Ceulemans J, Corsetti M, Griffin BT, Grimm M, Keszthelyi D, Koziolek M, Madla CM, Matthys C, McCoubrey LE, Mitra A, Reppas C, Stappaerts J, Steenackers N, Trevaskis NL, Vanuytsel T, Vertzoni M, Weitschies W, Wilson C, Augustijns P (2021) Impact of gastrointestinal tract variability on oral drug absorption and pharmacokinetics: an ungap review. Eur J Pharm Sci 162:105812
Wang Q, Li X (2011) Immunosuppressive and anti-inflammatory activities of sinomenine. Int Immunopharmacol 11:373–376
Wang J, Wei Y, Fei Y, Fang L, Zheng H, Mu C, Li F, Zhang Y (2017) Preparation of mixed monoterpenes edge activated pegylated transfersomes to improve the in vivo transdermal delivery efficiency of sinomenine hydrochloride. Int J Pharm 533:266–274
Wang Y, Jin Y, Yun X, Wang M, Dai Y, Xia Y (2018) Co-administration with simvastatin or lovastatin alters the pharmacokinetic profile of sinomenine in rats through cytochrome p450-mediated pathways. Life Sci 209:228–235
Yan H, Yan M, Li H, Jiang P, Deng Y, Cai H (2015) Pharmacokinetics and penetration into synovial fluid of systemical and electroporation administered sinomenine to rabbits. Biomed Chromatogr: BMC 29:883–889
Yang H, Jiang C, Chen X, He K, Hu Y (2017) Protective effects of sinomenine against lps-induced inflammation in piglets. Microb Pathog 110:573–577
Zhang M, Zhao Y, Jiang K, Han L, Lu X, Wang X, Zuo L, Meng S (2014) Comparative pharmacokinetics study of sinomenine in rats after oral administration of sinomenine monomer and sinomenium acutum extract. Mol (basel, Switzerland) 19:12065–12077
Zhang Y, Han J, Iqbal O, Liang A (2018) Research advances and prospects on mechanism of sinomenin on histamine release and the binding to histamine receptors. Int J Mol Sci 20:70
Zhao X, Peng C, Zhang H, Qin L (2012) Sinomenium acutum: a review of chemistry, pharmacology, pharmacokinetics, and clinical use. Pharm Biol 50:1053–1061
Zhao Q, Yang Z, Cao S, Chang Y, Cao Y, Li J, Yao Z, Wen Y, Huang X, Wu R, Yan Q, Huang Y, Ma X, Han X, Wu Y (2019) Acute oral toxicity test and assessment of combined toxicity of cadmium and aflatoxin b in kunming mice. Food Chem Toxicol: Int J Publ Br Industrial Biological Res Assoc 131:110577
Zhu Q, Sun Y, Zhu J, Fang T, Zhang W, Li JX (2014) Antinociceptive effects of sinomenine in a rat model of neuropathic pain. Sci Rep 4:7270
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China General Program (8227153595), the Science and Technology Innovation Program of Hunan Province (2020SK1020 and XKJ[2021]43-2021RC4035) and was supported by the Hunan Furong Distinguished Scholar Program (XJT[2020]58), Hunan 121 Training Project for Innovative Talents (XRSH[2019]192), Chinese Academy of Engineering Academician Liang Liu’s Workstation of Hunan University of Chinese Medicine (HNUCM) (XKXT[2020]34), and the National First-class Disciple Construction Project of Chinese Medicine of HNUCM (XXKZ[2018]3).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no competing financial interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, H., Zhang, EB., Yi, OY. et al. Sex-related differences in safety profiles, pharmacokinetics and tissue distribution of sinomenine hydrochloride in rats. Arch Toxicol 96, 3245–3255 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-022-03368-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-022-03368-1