Abstract
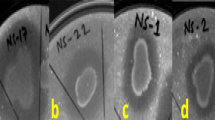
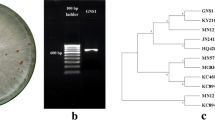
Mulberry bacterial wilt disease, caused by Ralstonia pseudosolanacearum, is a devastating soil-borne disease in the silk-mulberry-related industry. In this study, through high-throughput sequencing, we compared the rhizosphere bacterial composition of the mulberry-resistant cultivar (K10) and susceptible cultivar (G12), confirming Bacillus as a genus-level biomarker for K10. Next, twelve Bacillus spp. isolates, derived from the rhizosphere of K10, were screened for their antagonistic activity against R. pseudosolanacearum. The isolate showing strong antagonism was identified as B. velezensis K0T24 and selected for further analysis. The fermentation supernatant of B. velezensis K0T24 significantly inhibited the growth of R. pseudosolanacearum (82.47%) and the expression of its pathogenic genes. Using B. velezensis K0T24 in mulberry seedlings also increased defense enzyme activities and achieved a control efficacy of up to 55.17% against mulberry bacterial wilt disease. Collectively, our findings demonstrate the potential of B. velezensis K0T24 in suppressing mulberry bacterial wilt disease.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
References
Ahmed W, Yang J, Tan Y, Munir S, Liu Q, Zhang J, Ji G, Zhao Z (2022a) Ralstonia solanacearum, a deadly pathogen: revisiting the bacterial wilt biocontrol practices in tobacco and other Solanaceae. Rhizosphere 21:100479. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rhisph.2022.100479
Ahmed W, Zhou G, Yang J, Munir S, Ahmed A, Liu Q, Zhao Z, Ji G (2022b) Bacillus amyloliquefaciens WS-10 as a potential plant growth-promoter and biocontrol agent for bacterial wilt disease of flue-cured tobacco. Egypt J Biol Pest Control 32:25. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41938-022-00527-5
Albayrak Ç (2019) Bacillus species as biocontrol agents for fungal plant pathogens. In: Islam M, Rahman M, Pandey P, Boehme M, Haesaert G (eds) Bacilli and agrobiotechnology: Phytostimulation and Biocontrol. Bacilli in climate resilient agriculture and bioprospecting. Springer, Cham, pp 239–265
Arkhipova T, Veselov S, Melentiev A, Martynenko E, Kudoyarova G (2005) Ability of bacterium Bacillus subtilis to produce cytokinins and to influence the growth and endogenous hormone content of lettuce plants. Plant Soil 272:201–209. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-004-5047-x
Bakker P, Berendsen R, Doornbos R, Wintermans P, Pieterse C (2013) The rhizosphere revisited: Root microbiomics. Front Plant Sci 4:165. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2013.00165
Bashir O, Khan K, Hakeem K, Mir N, Rather G, Mohiuddin R (2016) Soil microbe diversity and root exudates as important aspects of rhizosphere ecosystem. In: Hakeem K, Akhtar M (eds) Plant, soil and microbes. Springer, Cham, pp 337–357
Blake C, Nordgaard M, Kovács Á (2021) Molecular aspects of plant growth promotion and protection by Bacillus subtilis. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 34:15–25. https://doi.org/10.1094/MPMI-08-20-0225-CR
Caporaso J, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J, Bittinger K, Bushman F, Costello E, Fierer N, Peña A, Goodrich J, Gordon J, Huttley G, Kelley S, Knights D, Koenig J, Ley R, Lozupone C, McDonald D, Muegge B, Pirrung M, Reeder J, Sevinsky J, Turnbaugh P, Walters W, Widmann J, Yatsunenko T, Zaneveld J, Knight R (2010) QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat Methods 7:335–336. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.f.303
Chen M, Wang J, Liu B, Zhu Y, Xiao R, Yang W, Ge C, Chen Z (2020) Biocontrol of tomato bacterial wilt by the new strain Bacillus velezensis FJAT-46737 and its lipopeptides. BMC Microbiol 20:160. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12866-020-01851-2
Dai F, Wang Z, Luo G, Tang C (2016) Transcriptional analysis of different mulberry cultivars in response to Ralstonia solanacearum. Can J for Res 46:152–162. https://doi.org/10.1139/cjfr-2015-0235
Dong Z, Guo Y, Yu C, Zhu Z, Mo R, Deng W, Li Y, Hu X (2021) The dynamics in rhizosphere microbial communities under bacterial wilt resistance by mulberry genotypes. Arch Microbiol 203:1107–1121. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-020-02098-1
Dong H, Gao R, Dong Y, Yao Q, Zhu H (2023) Bacillus velezensis RC116 inhibits the pathogens of bacterial wilt and fusarium wilt in tomato with multiple biocontrol traits. Int J Mol Sci 24:8527. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24108527
Fu H, Marian M, Enomoto T, Hieno A, Ina H, Suga H (2020) Biocontrol of tomato bacterial wilt by foliar spray application of a novel strain of endophytic Bacillus sp. Microbes Environ 35:ME20078. https://doi.org/10.1264/jsme2.ME20078
Gong C, Ma X, Song Y, Zhang D, Zhu M, Wang X, Gao S, Gao J, Song C (2023) Characteristics of microbial abundance in rhizosphere and non-rhizosphere soils of permafrost peatland, northeast China. Forests 14:1794. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14091794
Grosu A, Sicuia O, Dobre A, Voaideş C, Cornea C (2015) Evaluation of some Bacillus spp. strains for the biocontrol of Fusarium Graminearum and F. Culmorum in wheat. Agric Agric Sci Proc 6:559–566. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aaspro.2015.08.085
Han X, Shen D, Xiong Q, Bao B, Zhang W, Dai C, Zhao Y, Borriss R, Fan B (2021) The plant-beneficial rhizobacterium Bacillus velezensis FZB42 controls the soybean pathogen Phytophthora sojae due to bacilysin production. Appl Environ Microbiol 87:23. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.01601-21
Hartmann A, Rothballer M, Schmid M (2008) Lorenz Hiltner, a pioneer in rhizosphere microbial ecology and soil bacteriology research. Plant Soil 312:7–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-007-9514-z
Hashem A, Tabassum B, Abd-Allah E (2019) Bacillus subtilis: a plant-growth promoting rhizobacterium that also impacts biotic stress. Saudi J Biol Sci 26:1291–1297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2019.05.004
He P, Cui W, Munir S, He P, Huang R, Li X, Wu Y, Wang Y, Yang J, Tang P, He Y, He P (2023) Fengycin produced by Bacillus subtilis XF-1 plays a major role in the biocontrol of Chinese cabbage clubroot via direct effect and defense stimulation. J Cell Physiol 2023:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.30991
Hikichi Y, Yoshimochi T, Tsujimoto S, Shinohara R, Nakaho K, Kanda A, Kiba A, Ohnishi K (2007) Global regulation of pathogenicity mechanism of Ralstonia solanacearum. Plant Biotechnol 24:149–154. https://doi.org/10.5511/plantbiotechnology.24.149
Hu J, Wei Z, Friman V, Gu S, Wang X, Eisenhauer N, Yang T, Ma J, Shen Q, Xu Y, Jousset A (2016) Probiotic diversity enhances rhizosphere microbiome function and plant disease suppression. mBio 7:e01790–e01716. https://doi.org/10.1128/mBio.01790-16
Hu Y, Li Y, Yang X, Li C, Wang L, Feng J, Chen S, Li X, Yang Y (2021a) Effects of integrated biocontrol on bacterial wilt and rhizosphere bacterial community of tobacco. Sci Rep 11:2653. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-82060-3
Hu Y, Zhao W, Li X, Feng J, Li C, Yang X, Guo Q, Wang L, Chen S, Li Y, Yang Y (2021b) Integrated biocontrol of tobacco bacterial wilt by antagonistic bacteria and marigold. Sci Rep 11:16360. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-95741-w
Huang F (1984) Brief introduction of mulberry bacterial wilt resistant cultivar Kangqing 10. Guangdong Seric 3:12–17 (in Chinese)
Idris A, Li W, Huang F, Lin F, Guan X, Huang T (2024) Impacts of UV radiation on Bacillus biocontrol agents and their resistance mechanisms. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 40:58. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-023-03856-1
Iqbal R, Hyder S (2022) Bacillus spp. as bioagents: uses and application for sustainable agriculture. Biology 11:1763. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11121763
Jabborova D, Enakiev Y, Sulaymanov K, Kadirova D, Ali A, Annapurna K (2021) Plant growth promoting bacteria bacillus subtilis promote growth and physiological parameters of Zingiber officinale Roscoe. Plant Sci Today 8:66–71. https://doi.org/10.14719/pst.2021.8.1.997
Khoso M, Wagan S, Alam I, Hussain A, Ali Q, Saha S, Poudel T, Manghwar H, Liu F (2024) Impact of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) on plant nutrition and root characteristics: current perspective. Plant Stress 11:100341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stress.2023.100341
Kuklinsky-Sobral J, Araújo W, Mendes R, Pizzirani-Kleiner A, Azevedo J (2005) Isolation and characterization of endophytic bacteria from soybean (Glycine max) grown in soil treated with glyphosate herbicide. Plant Soil 273:91–99. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-004-6894-1
Kulkova I, Dobrzyński J, Kowalczyk P, Bełżecki G, Kramkowski K (2023) Plant growth promotion using Bacillus cereus. Int J Mol Sci 24:9759. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24119759
Lee H, Lee S, Choi M, Kwon J, Lee S (2023) A mutation of a putative NDP-Sugar epimerase gene in Ralstonia pseudosolanacearum attenuates exopolysaccharide production and bacterial virulence in tomato plant. Plant Pathol J 39:417–429. https://doi.org/10.5423/PPJ.OA.06.2023.0090
Li J, Zhao Q, Wuriyanghan H, Yang C (2021) Biocontrol bacteria strains Y4 and Y8 alleviate tobacco bacterial wilt disease by altering their rhizosphere soil bacteria community. Rhizosphere 19:100390. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rhisph.2021.100390
Li Z, Bai X, Jiao S, Li Y, Li P, Yang Y, Zhang H, Wei G (2021b) A simplified synthetic community rescues Astragalus mongholicus from root rot disease by activating plant-induced systemic resistance. Microbiome 9:217. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40168-021-01169-9
Liu L, Li X, Li T, Xie Y, Cao Z, Fang P (2022) Bio-organic fertilizer with Bacillus subtilis F2 promotes strawberry plant growth and changes rhizosphere microbial community. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 22:3045–3055. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-022-00866-0
Mansfield J, Genin S, Magori S, Citovsky V, Sriariyanum M, Ronald P, Dow M, Verdier V, Beer S, Machado M, Toth I, Salmond G, Foster G (2012) Top 10 plant pathogenic bacteria in molecular plant pathology. Mol Plant Pathol 13:614–629. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1364-3703.2012.00804.x
Mekonnen H, Kibret M, Assefa F (2023) Isolation and characterization of Ralstonia solanacearum causing wilt disease in tomato. Archives Phytopathol Plant Prot 55:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1080/03235408.2022.2164161
Mendes L, Raaijmakers J, Hollander M, Mendes R, Tsai S (2018) Influence of resistance breeding in common bean on rhizosphere microbiome composition and function. ISME J 12:212–224. https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2017.158
Monteiro F, Genin S, Van-Dijk I, Valls M (2012) A luminescent reporter evidences active expression of Ralstonia solanacearum type III secretion system genes throughout plant infection. Microbiology 158:2107–2116. https://doi.org/10.1099/mic.0.058610-0
Nasiri V, Dalimi A, Ghaffarifar F (2017) LB broth-lyophilized rabbit serum (LLR) as a new and suitable culture medium for cultivation of promastigotes of Leishmania major. J Parasitic Dis 41:247–251. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12639-016-0786-1
Ou T, Gao H, Jiang K, Yu J, Zhao R, Liu X, Zhou Z, Xiang Z, Xie J (2022) Endophytic Klebsiella aerogenes HGG15 stimulates mulberry growth in hydro-fluctuation belt and the potential mechanisms as revealed by microbiome and metabolomics. Front Microbiol 13:978550. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2022.978550
Pal J, Sharma S, Sharma A (2023) Disease suppression, growth promotion and colonization attributes of resident endophytic bacteria against white root rot (Dematophora Necatrix Hartig) of apple. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 117:15. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-3251034/v1
Paray A, Singh M, Mir M, Kaur A (2023) Gram staining: a brief review. Int J Res Rev 10:336–341. https://doi.org/10.52403/ijrr.20230934
Peeters N, Guidot A, Vailleau F, Valls M (2013) Ralstonia solanacearum, a widespread bacterial plant pathogen in the post-genomic era: Ralstonia solanacearum and bacterial wilt disease. Mol Plant Pathol 14:651–662. https://doi.org/10.1111/mpp.12038
Prihatiningsih N, Asnani A, Djatmiko H (2021) Extracellular protease from Bacillus subtilis B315 with antagonistic activity against bacterial wilt pathogen (Ralstonia solanacearum) of Chili. Biodiversitas J Biol Divers 22:1291–1295. https://doi.org/10.13057/biodiv/d220327
Rabbee M, Ali S, Choi J, Hwang B, Jeong S, Baek K (2019) Bacillus velezensis: a valuable member of bioactive molecules within plant microbiomes. Molecules 24:1046. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24061046
Rais A, Jabeen Z, Shair F, Hafeez F, Hassan M (2017) Bacillus spp., a biocontrol agent enhances the activity of antioxidant defense enzymes in rice against Pyricularia oryzae. PLoS ONE 12:e0187412. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0187412
Rashid M, Kumar G, Belbase S, Paudel J, Teli B, Bajpai R, Yadav D, Satnami L, Bhutia D, Kumar S, Sarkar A (2022) Detection and diagnosis of important soil-borne diseases: An overview, In: Singh U, Sahu P, Singh H, Sharma P, Sharma S (eds) Rhizosphere Microbes. Microorganisms for Sustainability, Springer, Singapore p93–104
Reasoner D, Geldreich E (1985) A new medium for the enumeration and subculture of bacteria from potable water. Appl Environ Microbiol 49:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.49.1.1-7.1985
Ryu C, Farag M, Hu C, Reddy M, Wei H, Paré P, Kloepper J (2003) Bacterial volatiles promote growth in Arabidopsis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 100:4927–32. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0730845100
Samain E, Duclercq J, Ait Barka E, Eickermann M, Ernenwein C, Mazoyon C, Sarazin V, Dubois F, Aussenac T, Selim S (2023) PGPR-Soil microbial communities’ interactions and their influence on wheat growth promotion and resistance induction against Mycosphaerella Graminicola. Biology 12:1416. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12111416
Samantara K, Bohra A, Mohapatra S, Prihatini R, Asibe F, Singh L, Reyes V, Tiwari A, Maurya A, Croser J, Wani S, Siddique K, Varshney R (2022) Breeding more crops in less time: a perspective on speed breeding. Biology 11:275. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11020275
Santos C, Franco O (2023) Pathogenesis-related proteins (PRs) with enzyme activity activating plant defense responses. Plants 12:2226. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12112226
Santos H, Argolo C, Argôlo-Filho R, Loguercio L (2019) A 16S rDNA PCR-based theoretical to actual delta approach on culturable mock communities revealed severe losses of diversity information. BMC Microbiol 19:74. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12866-019-1446-2
Sawant S, Prabhukarthikeyan S, Mishra M, Parameswaran C, Keerthana U, Senapati A (2023) Induction of defense-related enzymes and enhanced disease resistance in rice against Sarocladium oryzae by Bacillus cereus RBS-57. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 128:102168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmpp.2023.102168
Saxena A, Kumar M, Chakdar H, Anuroopa N, Bagyaraj D (2020) Bacillus species in soil as a natural resource for plant health and nutrition. J Appl Microbiol 128:1583–1594. https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.14506
Seleim M, Bereika M, Ibrahim O, Alqubaie A, Abo-Elyousr K (2023) Effectiveness of Bacillus cereus in controlling potato bacterial wilt caused by Ralstonia solanacearum: greenhouse and field studies with insights into resistance-related enzymes in potatoes. J Plant Dis Prot 131:65–75. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41348-023-00810-z
Senthilkumar M, Amaresan N, Sankaranarayanan A (2021) Spore staining and biochemical characterization of Bacillus. Plant-microbe interactions. Springer Protocols Handbooks. Humana, New York, pp 225–229
Sharma D, Shukla A (2021) Fusarium wilt of cucumber- a review. Int J Economic Plants 8:193–200. https://doi.org/10.23910/2/2021.0423
Shen T, Lei Y, Pu X, Zhang S, Du Y (2021) Identification and application of Streptomyces microflavus G33 in compost to suppress tomato bacterial wilt disease. Appl Soil Ecol 157:103724. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2020.103724
Shen Y, Yang H, Lin Z, Chu L, Pan X, Wang Y, Liu W, Jin P, Miao W (2023) Screening of compound-formulated Bacillus and its effect on plant growth promotion. Front Plant Sci 14:1174583. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2023.1174583
Sun D, Zhuo T, Hu X, Fan X, Zou H (2017) Identification of a Pseudomonas putida as Biocontrol agent for tomato bacterial wilt disease. Biol Control 114:45–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocontrol.2017.07.015
Sun Y, Su Y, Meng Z, Zhang J, Zheng L, Miao S, Qin D, Ruan Y, Wu Y, Xiong L, Yan X, Dong Z, Cheng P, Shao M, Yu G (2023) Biocontrol of bacterial wilt disease in tomato using Bacillus subtilis strain R31. Front Microbiol 14:1281381. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2023.1281381
Suryadi Y, Susilowati D, Samudra I, Akhdiya A, Kosasih J, Aminah S (2023) Effect of antagonistic bacteria and its formulation to control fusarium wilt disease on shallot. E3S Web Conferences 373(07009). https://doi.org/10.1051/e3sconf/202337307009
Susanti Y, Giyanto G, Sinaga M, Mutaqin K, Tjahjono B (2021) The potential of endophytic bacteria from the root of Eucalyptus pellita as a biocontrol agent against Ralstonia solanacearum. Biodiversitas J Biol Divers 22:3454–3462. https://doi.org/10.13057/biodiv/d220654
Sussanti D, Khairul U, Resti Z (2023) The antagonistic potential of Bacillus spp. against Ralstonia solanacearum causing bacterial wilt disease in ginger (Zingiber officinale). IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science 1160:012044. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/1160/1/012044
Tahir H, Gu Q, Wu H, Niu Y, Huo R, Gao X (2017) Bacillus volatiles adversely affect the physiology and ultra-structure of Ralstonia solanacearum and induce systemic resistance in tobacco against bacterial wilt. Sci Rep 7:40481. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep40481
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28:2731–2739. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msr121
Trivedi P, Leach J, Tringe S, Sa T, Singh B (2020) Plant–microbiome interactions: from community assembly to plant health. Nat Rev Microbiol 18:607–621. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41579-020-0412-1
Tsotetsi T, Nephali L, Malebe M, Tugizimana F (2022) Bacillus for plant growth promotion and stress resilience: what have we learned? Plants 11:2482. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11192482
Vijayan K, Ravikumar G, Tikader A (2018) Mulberry (Morus spp.) breeding for higher fruit production. In: Al-Khayri J, Jain S, Johnson D (eds) Advances in plant breeding strategies: fruits. Springer, Cham, pp 89–130
Wang J, Peng Y, Xie S, Yu X, Bian C, Wu H, Wang Y, Ding T (2023) Biocontrol and molecular characterization of Bacillus velezensis D against tobacco bacterial wilt. Phytopathol Res 5:50. https://doi.org/10.1186/s42483-023-00204-x
Wang J, Qin S, Fan R, Peng Q, Hu X, Yang L, Liu Z, Baccelli I, Migheli Q, Berg G, Chen X, Cernava T (2023b) Plant growth promotion and biocontrol of leaf blight caused by Nigrospora Sphaerica on passion fruit by endophytic Bacillus subtilis strain GUCC4. J Fungi 9:132. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof9020132
Wei Z, Zhang S (2018) NPBSS: a new PacBio sequencing simulator for generating the continuous long reads with an empirical model. BMC Bioinformatics 19:177. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12859-018-2208-0
Wicker E, Grassart L, Coranson-Beaudu R, Mian D, Guilbaud C, Prior P (2007) Ralstonia solanacearum strains from martinique (French West Indies) exhibiting a new pathogenic potential. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:6790–6801. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00841-07
Wu K, Yuan S, Wang L, Shi J, Zhao J, Shen B, Shen Q (2014) Effects of bio-organic fertilizer plus soil amendment on the control of tobacco bacterial wilt and composition of soil bacterial communities. Biol Fertil Soils 50:961–971. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-014-0916-9
Wu H, Lou D, Tu N, Geng T, Lu F, Ji X, Wang S (2020) Rhizosphere Bacterial Community and Diversity at fields of Wilt Resistant or Susceptible Mulberry Trees. Fujian J Agricultural Sci 35(9):1004–1011 (in Chinese)
Xiao X, Lin W, Chen Z, Zou C, Jin H, Zou H (2021) Wide-host vector pBBR1MCS2-Tac-EGFP suitable for the labeling of Ralstonia solanacearum. Chin J Trop Crops 42:1700–1705 (in Chinese)
Xie S, Wu H, Zang H, Wu L, Zhu Q, Gao X (2014) Plant growth promotion by permidine-producing Bacillus subtilis OKB105. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 27:655–663. https://doi.org/10.1094/MPMI-01-14-0010-R
Xu W, Yang Q, Yang F, Xie X, Goodwin P, Deng X, Tian B, Yang L (2022) Evaluation and genome analysis of Bacillus subtilis YB-04 as a potential biocontrol agent against Fusarium wilt and growth promotion agent of cucumber. Front Microbiol 13:885430. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2022.885430
Yao J, Allen C (2006) Chemotaxis is required for virulence and competitive fitness of the bacterial wilt pathogen Ralstonia solanacearum. J Bacteriol 188:3697–3708. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.188.10.3697-3708.2006
Yasmin S, Zaka A, Imran A, Zahid M, Yousaf S, Rasul G, Arif M, Mirza M (2016) Plant growth promotion and suppression of bacterial leaf blight in rice by inoculated bacteria. PLoS ONE 11:e0160688. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0160688
Yuan S, Wang L, Wu K, Shi J, Wang M, Yang X, Shen Q, Shen B (2014) Evaluation of Bacillus-fortified organic fertilizer for controlling tobacco bacterial wilt in greenhouse and field experiments. Appl Soil Ecol 75:86–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2013.11.004
Yuan J, Raza W, Shen Q (2018) Root exudates dominate the colonization of pathogen and plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria. In: Giri B, Prasad R, Varma A (eds) Root Biology. Soil Biology. Springer, Cham, pp 167–180
Yuan T, Qazi I, Li J, Yang P, Yang H, Zhang X, Liu W, Liu J (2023a) Analysis of changes in bacterial diversity in healthy and bacterial wilt mulberry samples using metagenomic sequencing and culture-dependent approaches. Front Plant Sci 14:1206691. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2023.1206691
Yuan T, Qazi I, Yang P, Zhang X, Li J, Liu J (2023b) Analysis of endophytic bacterial flora of mulberry cultivars susceptible and resistant to bacterial wilt using metagenomic sequencing and culture-dependent approach. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 39:163. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-023-03599-z
Zhang L, Xu J, Xu J, Zhang H, He L, Feng J (2014) TssB is essential for virulence and required for type VI secretion system in Ralstonia solanacearum. Microb Pathog 74:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2014.06.006
Zhang N, Wang Z, Shao J, Xu Z, Liu Y, Xun W, Miao Y, Shen Q, Zhang R (2023) Biocontrol mechanisms of Bacillus: improving the efficiency of green agriculture. Microb Biotechnol 16:2250–2263. https://doi.org/10.1111/1751-7915.14348
Acknowledgements
We thank Prof. Wei Ding for providing us with the greenhouse facility and Prof. Tongbao Liu for his critical reading of the manuscript and helpful suggestions. We also thank for the lab classmates Yupan Qu, Keyao Zhang, Yan Li and Wenqi Yang for assisting in some experiments.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32371713 and 32102300), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (SWU-KQ22082) and the Natural Science Foundation of Chongqing Municipality (CSTB2022NSCQ-MSX0536).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Wenlian Jiao: Conceptualization, Investigation, Data curation, Writing -original draft, Formal analysis, Visualization. Ju Wen: Investigation, Writing -original draft, Formal analysis, Visualization. Na Li: Investigation, Formal analysis. Ting Ou: Methodology, Visualization. Changyu Qiu: Resources. Yutong Ji: Investigation, Formal analysis. Kai Lin: Investigation, Formal analysis. Xiaojiao Liu: Conceptualization, Methodology, Project administration, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing - review & editing, Visualization. Jie Xie: Conceptualization, Project administration, Funding acquisition, Resources, Supervision, Writing - review & editing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Communicated by Yusuf Akhter.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Xiaojiao Liu and Jie Xie contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jiao, W., Wen, J., Li, N. et al. The biocontrol potentials of rhizospheric bacterium Bacillus velezensis K0T24 against mulberry bacterial wilt disease. Arch Microbiol 206, 213 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-024-03935-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-024-03935-3