Abstract
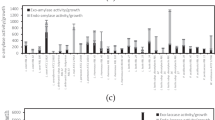
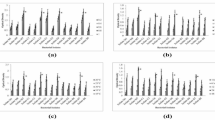
The persistence of Staphylococcus aureus within biofilm can lead to contamination of medical devices and life-threatening infections. Luckily, lactic acid bacteria (LAB) have an inhibitory effect on the growth of these bacteria. This study aims to select LAB strains from fermented vegetables, and analyze their potential inhibition activities against S. aureus. In total, 45 isolates of LAB were successfully isolated from Sichuan pickles, and the CFS of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum LR-14 exerted the strongest inhibitory effect against S. aureus. Moreover, S. aureus cells in planktonic and biofilm states both wrinkled and damaged when treated with the CFS of L. plantarum LR-14. In addition, whole genome sequencing analysis indicates that L. plantarum LR-14 contains various functional genes, including predicted extracellular polysaccharides (EPS) biosynthesis genes, and genes participating in the synthesis and metabolism of fatty acid, implying that L. plantarum LR-14 has the potential to be used as a probiotic with multiple functions.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data used to support the findings of this study are included within the article.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Bellussi L, Passali F, Ralli M, De Vincentiis M, Greco A, Passali D (2019) An overview on upper respiratory tract infections and bacteriotherapy as innovative therapeutic strategy. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 23:27–38. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_201903_17345
Bensch G, Rüger M, Wassermann M, Weinholz S, Reichl U, Cordes C (2014) Flow cytometric viability assessment of lactic acid bacteria starter cultures produced by fluidized bed drying. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98(11):4897–4909. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-5592-z
Bhola J, Bhadekar R (2019) Invitro synergistic activity of lactic acid bacteria against multi-drug resistant staphylococci. BMC Complement Altern Med 19(1):70. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12906-019-2470-3
Dalié DKD, Deschamps AM, Richard-Forget F (2010) Lactic acid bacteria – potential for control of mould growth and mycotoxins: a review. Food Control 21(4):370–380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2009.07.011
Dertli E, Colquhoun I, Gunning A, Bongaerts R, Le Gall G, Bonev B, Mayer M, Narbad A (2013) Structure and biosynthesis of two exopolysaccharides produced by Lactobacillus johnsonii FI9785. J Biol Chem 288(44):31938–31951. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M113.507418
Gao Z, Daliri E, Wang J, Liu D, Chen S, Ye X, Ding T (2019) Inhibitory effect of lactic acid bacteria on foodborne pathogens: a review. J Food Prot 82(3):441–453. https://doi.org/10.4315/0362-028x.Jfp-18-303
Grégori G, Denis M, Sgorbati S, Citterio S (2018) Resolution of viable and membrane-compromised free bacteria in aquatic environments by flow cytometry. Curr Protoc Cytom 85(1):e42. https://doi.org/10.1002/cpcy.42
Huang R, Pan M, Wan C, Shah N, Tao X, Wei H (2016) Physiological and transcriptional responses and cross protection of Lactobacillus plantarum ZDY2013 under acid stress. J Dairy Sci 99(2):1002–1010. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2015-9993
Jiang Y, Zhang J, Zhao X, Zhao W, Yu Z, Chen C, Yang Z (2018) Complete genome sequencing of exopolysaccharide-producing Lactobacillus plantarum K25 provides genetic evidence for the probiotic functionality and cold endurance capacity of the strain. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 82(7):1225–1233. https://doi.org/10.1080/09168451.2018.1453293
Jingjing E, Lili M, Zichao C, Rongze M, Qiaoling Z, Ruiyin S, Zongbai H, Junguo W (2020) Effects of buffer salts on the freeze-drying survival rate of Lactobacillus plantarum LIP-1 based on transcriptome and proteome analyses. Food Chem 326:126849. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.126849
Jo D, Montgomery C, Yin S, Boyle-Vavra S, Daum R (2011) Improved oxacillin treatment outcomes in experimental skin and lung infection by a methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolate with a vraSR operon deletion. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 55(6):2818–2823. https://doi.org/10.1128/aac.01704-10
Kalaycı Yüksek F, Gümüş D, Gündoğan G, Anğ Küçüker M (2021) Cell-free Lactobacillus sp supernatants modulate Staphylococcus aureus growth, adhesion and invasion to human osteoblast (HOB) cells. Curr Microbiol 78(1):125–132. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-020-02247-1
Kamiloğlu A, Kaban G, Kaya M (2020) Technological properties of autochthonous Lactobacillus plantarum strains isolated from sucuk (Turkish dry-fermented sausage). Braz J Microbiol: [publication of the Brazilian Society for Microbiology] 51(3):1279–1287. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42770-020-00262-9
Kang M, Lim H, Oh J, Lim Y, Wuertz-Kozak K, Harro J, Shirtliff M, Achermann Y (2017) Antimicrobial activity of Lactobacillus salivarius and Lactobacillus fermentum against Staphylococcus aureus. Pathog Dis. https://doi.org/10.1093/femspd/ftx009
Kim E, Chang H, Kim H (2020b) Complete genome sequence of lactobacillus plantarum EM, a putative probiotic strain with the cholesterol-lowering effect and antimicrobial activity. Curr Microbiol 77(8):1871–1882. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-020-02000-8
Kim S, Kang S, Shin D, Oh S, Lee C, Yang Y, Son Y, Yang H, Lee B, An H, Jeong I, Bang W (2020a) Lactobacillus plantarumPotential of cell-free supernatant from NIBR97, including novel bacteriocins, as a natural alternative to chemical Disinfectants. Pharmaceuticals (basel, Switzerland). https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13100266
Klayraung S, Okonogi S (2009) Antibacterial and antioxidant activities of acid and bile resistant strains of Lactobacillus fermentum isolated from Miang. Braz J Microbiol: [publication of the Brazilian Society for Microbiology] 40(4):757–766. https://doi.org/10.1590/s1517-83822009000400005
Lazarevic V, Beaume M, Corvaglia A, Hernandez D, Schrenzel J, François P (2011) Epidemiology and virulence insights from MRSA and MSSA genome analysis. Future Microbiol 6(5):513–532. https://doi.org/10.2217/fmb.11.38
Li S, Huang R, Shah N, Tao X, Xiong Y, Wei H (2014) Antioxidant and antibacterial activities of exopolysaccharides from Bifidobacterium bifidum WBIN03 and Lactobacillus plantarum R315. J Dairy Sci 97(12):7334–7343. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2014-7912
Li W, Lu Y, Xie X, Han Y, Wang N, Sun T, Liu L, Wang Y, Zhuang Z, Gao G, Liu T, Zhao L (2020) CatalpaThe complete chloroplast genome of “Bairihua”, a hybrid variety with multi season flowering. Mitochondrial DNA Part B, Resour 5(3):2760–2762. https://doi.org/10.1080/23802359.2020.1788445
Lin C, Lin M, Lin C, Chiou M, Chen J, Yang K, Wu M (2020) Potential probiotic of Lactobacillus strains isolated from the intestinal tracts of pigs and feces of dogs with antibacterial activity against multidrug-resistant pathogenic bacteria. Arch Microbiol 202(7):1849–1860. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-020-01908-w
Lister J, Horswill A (2014) Staphylococcus aureus biofilms: recent developments in biofilm dispersal. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 4:178. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2014.00178
Luo R, Liu B, Xie Y, Li Z, Huang W, Yuan J, He G, Chen Y, Pan Q, Liu Y, Tang J, Wu G, Zhang H, Shi Y, Liu Y, Yu C, Wang B, Lu Y, Han C, Cheung D, Yiu S, Peng S, Xiaoqian Z, Liu G, Liao X, Li Y, Yang H, Wang J, Lam T, Wang J (2012) SOAPdenovo2: an empirically improved memory-efficient short-read de novo assembler. GigaScience 1(1):18. https://doi.org/10.1186/2047-217x-1-18
Mahdhi A, Leban N, Chakroun I, Bayar S, Mahdouani K, Majdoub H, Kouidhi B (2018) Use of extracellular polysaccharides, secreted by Lactobacillus plantarum and Bacillus spp., as reducing indole production agents to control biofilm formation and efflux pumps inhibitor in Escherichia coli. Microb Pathog 125:448–453. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2018.10.010
Martí M, Trotonda M, Tormo-Más M, Vergara-Irigaray M, Cheung A, Lasa I, Penadés J (2010) Extracellular proteases inhibit protein-dependent biofilm formation in Staphylococcus aureus. Microbes Infect 12(1):55–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micinf.2009.10.005
Melo T, Dos Santos T, de Almeida M, Junior L, Andrade E, Rezende R, Marques L, Romano C (2016) Inhibition of Staphylococcus aureus biofilm by Lactobacillus isolated from fine cocoa. BMC Microbiol 16(1):250. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12866-016-0871-8
Mirzaei R, Mohammadzadeh R, Mirzaei H, Sholeh M, Karampoor S, Abdi M, Alikhani M, Kazemi S, Ahmadyousefi Y, Jalalifar S, Yousefimashouf R (2020) Role of microRNAs in Staphylococcus aureus infection: potential biomarkers and mechanism. IUBMB Life 72(9):1856–1869. https://doi.org/10.1002/iub.2325
Muhammad Z, Ramzan R, Abdelazez A, Amjad A, Afzaal M, Zhang S, Pan S (2019) Lactobacillus plantarumassessment of the antimicrobial potentiality and functionality of strains isolated from the conventional inner mongolian fermented cheese against foodborne pathogens. Pathogens (basel, Switzerland). https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens8020071
Okonkwo C, Ujor V, Cornish K, Ezeji T (2020) Inactivation of the Levansucrase gene in Paenibacillus polymyxa DSM 365 diminishes exopolysaccharide biosynthesis during 2,3-butanediol fermentation. Appl Environ Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.00196-20
Ołdak A, Zielińska D, Łepecka A, Długosz E, Kołożyn-Krajewska D (2020) Lactobacillus plantarum strains isolated from polish regional cheeses exhibit anti-staphylococcal activity and selected probiotic properties. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins 12(3):1025–1038. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12602-019-09587-w
Onbas T, Osmanagaoglu O, Kiran F (2019) Potential properties of Lactobacillus plantarum F-10 as a bio-control strategy for wound infections. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins 11(4):1110–1123. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12602-018-9486-8
Ong J, Taylor T, Yong C, Khoo B, Sasidharan S, Choi S, Ohno H, Liong M (2020) Lactobacillus plantarum USM8613 aids in wound healing and suppresses staphylococcus aureus infection at wound sites. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins 12(1):125–137. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12602-018-9505-9
Prabhakara R, Foreman O, De Pascalis R, Lee G, Plaut R, Kim S, Stibitz S, Elkins K, Merkel T (2013) Epicutaneous model of community-acquired Staphylococcus aureus skin infections. Infect Immun 81(4):1306–1315. https://doi.org/10.1128/iai.01304-12
Rocha K, Perini H, de Souza C, Schueler J, Tosoni N, Furlaneto M, Furlaneto-Maia L (2019) Inhibitory effect of bacteriocins from enterococci on developing and preformed biofilms of Listeria monocytogenes, Listeria ivanovii and Listeria innocua. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 35(7):96. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-019-2675-0
Schaffer S, Hutchison C, Rouchon C, Mdluli N, Weinstein A, McDaniel D, Frank K (2022) Diverse Enterococcus faecalis strains show heterogeneity in biofilm properties. Res Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resmic.2022.103986
Sharma V, Harjai K, Shukla G (2018) Effect of bacteriocin and exopolysaccharides isolated from probiotic on P. aeruginosa PAO1 biofilm. Folia Microbiol 63(2):181–190. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-017-0545-4
Sharma D, Misba L, Khan A (2019) Antibiotics versus biofilm: an emerging battleground in microbial communities. Antimicrob Resist Infect Control 8:76. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13756-019-0533-3
Silva V, Almeida L, Gaio V, Cerca N, Manageiro V, Caniça M, Capelo J, Igrejas G, Poeta P (2021) Biofilm formation of multidrug-resistant mrsa strains isolated from different types of human infections. Pathogens (basel, Switzerland). https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10080970
Srivastava N, Ellepola K, Venkiteswaran N, Chai L, Ohshima T, Seneviratne C (2020) Lactobacillus plantarum 108 inhibits streptococcus mutans and Candida albicans mixed-species biofilm formation. Antibiotics (basel, Switzerland). https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9080478
Tai K, Kamdar K, Yamaki J, Le V, Tran D, Tran P, Selsted M, Ouellette A, Wong-Beringer A (2015) Microbicidal effects of α- and θ-defensins against antibiotic-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Innate Immun 21(1):17–29. https://doi.org/10.1177/1753425913514784
Tam K, Torres V (2019) Staphylococcus aureus secreted toxins and extracellular enzymes. Microbiol Spectr. https://doi.org/10.1128/microbiolspec.GPP3-0039-2018
Truc L, Ngoc A, Hong T, Thanh T, Kim H, Kim L, Truong G, Quoc P, Ngoc T (2019) Vibrio parahaemolyticusselection of lactic acid bacteria (LAB) antagonizing : the pathogen of acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease (AHPND) in whiteleg shrimp (). Biology. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology8040091
Wallis J, Krömker V, Paduch J (2019) Biofilm challenge: lactic acid bacteria isolated from bovine udders versus Staphylococci. Foods (Basel, Switzerland). https://doi.org/10.3390/foods8020079
Wang J, Zhao X, Yang Y, Zhao A, Yang Z (2015) Characterization and bioactivities of an exopolysaccharide produced by Lactobacillus plantarum YW32. Int J Biol Macromol 74:119–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2014.12.006
Wang J, Yang C, Fang S, Lu J, Quan C (2016) Inhibition of biofilm in Bacillus amyloliquefaciens Q-426 by diketopiperazines. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 32(9):143. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-016-2106-4
Wang Y, Wang F, Zhang X, Cen C, Fu L (2020) Transcription factors FabR and FadR regulate cold adaptability and spoilage potential of Shewanella baltica. Int J Food Microbiol 331:108693. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2020.108693
Wong C, Khoo B, Sasidharan S, Piyawattanametha W, Kim S, Khemthongcharoen N, Ang M, Chuah L, Liong M (2015) Inhibition of Staphylococcus aureus by crude and fractionated extract from lactic acid bacteria. Beneficial Microbes 6(1):129–139. https://doi.org/10.3920/bm2014.0021
Zheng Z, Cao F, Wang W, Yu J, Chen C, Chen B, Liu J, Firrman J, Renye J, Ren D (2020a) Probiotic characteristics of Lactobacillus plantarum E680 and its effect on hypercholesterolemic mice. BMC Microbiol 20(1):239. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12866-020-01922-4
Zheng J, Wittouck S, Salvetti E, Franz C, Harris H, Mattarelli P, O’Toole P, Pot B, Vandamme P, Walter J, Watanabe K, Wuyts S, Felis G, Gänzle M, Lebeer S (2020b) LactobacillusA taxonomic note on the genus : description of 23 novel genera, emended description of the genus Beijerinck 1901, and union of and. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 70(4):2782–2858. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.004107
Funding
This work was financially supported by the National Science Foundation for Young Scientists of China (Grant No. 32001663), the Sichuan Province Science and Technology Innovation Seedling Project (2021081), Chunhui Project of Ministry of Education of China, and the Open Research Fund of Comprehensive Health Promotion Center of Xihua University (jkgl2018-033).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SY, SG, XC, XD, MT and YT: performed the experiments, analyzed data and wrote the manuscript. JW: reviewed and edited the manuscript. LL and YR: designed this study, supervised all experiments and reviewed the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
All authors agree to publish.
Additional information
Communicated by Erko Stackebrandt.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, S., Liu, L., Wang, J. et al. Antimicrobial activity against Staphylococcus aureus and genome features of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum LR-14 from Sichuan pickles. Arch Microbiol 204, 637 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-022-03232-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-022-03232-x