Abstract
Purpose
Retrospective evaluation of stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
Methods
We retrospectively analyzed 36 patients (45 lesions) treated between 2011 and 2017. Twenty-seven had previous treatments. Current treatment consisted of SBRT alone (n = 15) or selective transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) followed by SBRT to the same lesions (n = 21). Eight patients received additional local treatments to different lesions. Liver function was predominantly moderately restricted (Child A: 29, Child B: 6, Child C: 1). Treatment planning was based on 4D-computed tomography, dose/fractionation varied depending on location and size, most commonly 3 fractions of 12.5 Gy (65% isodose) and 5 fractions of 8 Gy (80% isodose).
Results
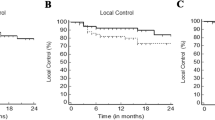
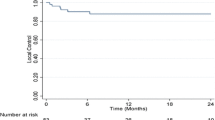
Median follow-up was 15 months. Local recurrence was observed in 3 lesions (7%), resulting in 1‑and 2‑year local control rates of 93%. The only significantly predicting factor was the use of abdominal compression. New hepatic lesions occurred in 19 patients (52%), 1‑ and 2‑year freedom-from-hepatic-failure (FFHF) was 39% and 32%, respectively. Only the number of treated lesions was predictive for FFHF. Sixteen patients have died, resulting in 1‑ and 2‑year overall survival (OS) of 64% and 41%, respectively, significantly impacted by the number of treated lesions and Child–Pugh class. Severe acute and late toxicity (≥grade 3) was observed in 3% and 8%, respectively. 6 patients (17%) received liver transplantation (OLT) after SBRT, of whom 5 showed pathological complete remission.
Conclusion
SBRT (±TACE) in highly pretreated HCC is effective and associated with excellent LC and low toxicity. SBRT may be used as definitive or bridging treatment prior to OLT. Patients with multifocal lesions have significantly decreased 1‑ and 2‑year FFHF and OS.
Zusammenfassung
Ziel
Ziel war die retrospektive Evaluation der Bestrahlungstherapie mittels Körperstereotaxie (SBRT) beim hepatozellulären Karzinom (HCC).
Methoden
Die retrospektive Analyse umfasst 36 Patienten (45 Läsionen), welche zwischen 2011 und 2017 behandelt wurden. Lokale Vorbehandlungen erhielten 27 Patienten. Aktuell wurden 15 Patienten mittels alleiniger SBRT und 21 mittels SBRT nach selektiver transarterieller Chemoembolisation (TACE) der gleichen Läsion behandelt. Bei 8 Patienten erfolgten zusätzlich lokale Behandlungen anderer Läsionen. Die Leberfunktion war überwiegend gering eingeschränkt (Child A: 29, Child B: 6, Child C: 1). Die Therapieplanung erfolgte mittels 4‑D-Computertomographie, die Dosis/Fraktionierung war abhängig von Lokalisation und Größe, üblicherweise 3 × 12,5 Gy (65%-Isodose) oder 5 × 8 Gy (80%-Isodose).
Ergebnisse
Die mediane Nachbeobachtungszeit betrug 15 Monate. Es traten 3 Lokalrezidive auf (7%) auf, die Ein-und 2‑Jahres-Lokalkontrollrate betrug 93%. Der einzige signifikante prädiktive Faktor war die Verwendung einer Bauchpresse. Bei insgesamt 19 Patienten (52%) traten neue hepatische Läsionen auf, das leberspezifische krankheitsfreie Ein- und 2‑Jahres-Intervall (FFHF) betrug 39% bzw. 32%. Lediglich die Zahl der behandelten Läsionen zeigte sich als prädiktiv für das FFHF. Es starben 16 Patienten, das Ein-und 2‑Jahres-Gesamtüberleben (OS) betrug 64% bzw. 41%. Die Anzahl der behandelten Läsionen und die Child-Pugh-Klasse waren signifikant mit dem OS assoziiert. Schwere akute oder späte Nebenwirkungen (≥Grad 3) traten bei 3% bzw. 8% der Patienten auf. Bei 6 Patienten (17%) wurde eine Lebertransplantation nach SBRT durchgeführt, hiervon zeigten 5 eine komplette pathologische Remission.
Schlussfolgerung
Die SBRT (±TACE) bei multipel vorbehandeltem HCC ist effektiv, toxizitätsarm und erzielt eine exzellente Lokalkontrolle. Sie eignet sich als definitive Therapiealternative oder als Überbrückung vor Lebertransplantation. Patienten mit multifokalen Herden zeigten ein signifikant reduziertes Ein- und 2‑Jahres-FFHF und -OS.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 4D-CT:
-
four-dimensional computed tomography
- AFP:
-
alpha-fetoprotein
- BCLC:
-
Barcelona Clinical Liver Cancer
- BED:
-
biologically effective dose
- CBCT:
-
cone beam computed tomography
- ccm:
-
cubic centimeters
- CP class:
-
Child–Pugh class
- CT:
-
computed tomography
- CTCAE:
-
Common Toxicity Criteria for Adverse Events
- FFHF:
-
freedom from hepatic failure
- GTV:
-
gross tumor volume
- HCC:
-
hepatocellular carcinoma
- IF:
-
in-field
- IMRT:
-
intensity-modulated radiation therapy
- ITV:
-
internal target volume
- KPS:
-
Karnofsky performance score
- LC:
-
local control
- LR:
-
local recurrence
- MRI:
-
magnetic resonance imaging
- OLT:
-
orthotopic liver transplantation
- OS:
-
overall survival
- pCR:
-
pathologic complete response
- PFS:
-
progression-free survival
- pPR:
-
pathologic partial response
- PTV:
-
planning target volume
- RFA:
-
radiofrequency ablation
- RILD:
-
radiation-induced liver disease
- SBRT:
-
stereotactic body radiation therapy
- SIRT:
-
selective internal radiotherapy
- TACE:
-
transarterial chemoembolization
References
Murray LJ, Dawson LA (2017) Advances in stereotactic body radiation therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Semin Radiat Oncol 27:247–255
Waller LP, Deshpande V, Pyrsopoulos N et al (2015) Hepatocellular carcinoma: a comprehensive review. World J Hepatol 7:2648–2663
Delis SG, Dervenis C (2008) Selection criteria for liver resection in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and chronic liver disease. World J Gastroenterol 14:3452–3460
NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology—hepatobiliary cancers version 2/2019. https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/hepatobiliary.pdf
Kalogeridi MA, Zygogianni A, Kyrgias G et al (2015) Role of radiotherapy in the management of hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review. World J Hepatol 7:101–112
Gerum S, Heinz C, Belka C et al (2018) Stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and oligometastatic disease. Radiat Oncol 13:100
Lawrence TS, Robertson JM, Anscher MS et al (1995) Hepatic toxicity resulting from cancer treatment. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 31:1237–1248
Dawson LA, Normolle D, Balter JM et al (2002) Analysis of radiation-induced liver disease using the Lyman NTCP model. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 53:810–821
Scorsetti M, Comito T, Cozzi L et al (2015) The challenge of inoperable hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC): results of a single-institutional experience on stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT). J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 141:1301–1309
Boda-Heggemann J, Jahnke A, Chan MK et al (2018) Direct dose correlation of MRI morphological alterations of healthy liver tissue after robotic liver surgery. Strahlenther Onkol 194:414–424
Fleckenstein J, Boda-Heggemann J, Siebelist K et al (2018) Non-coplanar VMAT combined with non-uniform dose prescription markedly reduces lung dose in breath-hold lung SBRT. Strahlenther Onkol 194:815–823
Moustakis C, Blanck O, Ebrahimi Tazehmahalleh F et al (2017) Planning benchmark study for SBRT of early stage NSCLC—results of the DERO working group stereotactic radiotherapy. Strahlenther Onkol 193:780–790
Gkika E, Adebahr S, Kirste S et al (2017) Stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) in recurrent or oligometastatic pancreatic cancer. Strahlenther Onkol 193:433–443
Chang JY, Senan S, Paul MA et al (2015) Stereotactic ablative radiotherapy versus lobectomy for operable stage I non-small-cell lung cancer: a pooled analysis of two randomised trials. Lancet Oncol 16:630–637
Blomgren H, Lax I, Näslund I et al (1995) Stereotactic high dose fraction radiation therapy of extracranial tumors using an accelerator. Clinical experience of the first thirty-one patients. Acta Oncol 34:861–870
Gerum S, Roeder F (2019) Stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC): a mini-review. World J Gastrointest Oncol 11:367–376
Lasley FD, Maninna EM, Johnson CS et al (2015) Treatment variables related to liver toxicity in patients with hepatocallular carcinoma, Child-Pugh class A and B enrolled in a phase 1–2 trial of stereotactic body radiation therapy. Pract Radiat Oncol 5:e443–449
Mendez-Romero A, Wunderink W, Hussain SM et al (2006) Stereotactic body radiation therapy for primary and metastatic liver tumors: a single institution phase I–II study. Acta Oncol 45:831–837
Tse RV, Hawkins M, Lockwood G et al (2008) Phase I Study of individualized stereotactic body radiotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma and intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. J Clin Oncol 26:657–664
Cardenes HR, Price TR, Perkins SM et al (2010) Phase I feasibility trial of stereotactic body radiation therapy for primary hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Transl Oncol 12:218–225
Kang JK, Kim MS, Cho CK et al (2012) Stereotactic body radiation therapy for inoperable hepatocellular carcinoma as a local salvage treatment after incomplete transarterial chemoembolization. Cancer 118:5424–5431
Price TR, Perkins SM, Sandrasegaran K et al (2012) Evaluation of response after stereotactic body radiotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer 118:3191–3198
Huang WY, Jen YM, Lee MS et al (2012) Stereotactic body radiation therapy in recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 84:355–361
Bujold A, Massey CA, Kim JJ et al (2013) Sequential phase I and II trials of stereotactic body radiotherapy for locally advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 31:1631–1639
Culleton S, Jiang H, Haddad CR et al (2014) Outcomes following definitive stereotactic body radiotherapy for patients with Child-Pugh B or C hepatocellular carcinoma. Radiother Oncol 111:412–417
Sanuki N, Takeda A, Oku Y et al (2014) Stereotactic body radiotherapy for small hepatocellular carcinoma: a retrospective outcome analysis in 185 patients. Acta Oncol 53:399–404
Su TS, Liang P, Lu HZ et al (2016) Stereotactic body radiation therapy for small primary or recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma in 132 chinese patients. J Surg Oncol 113:181–187
Takeda A, Sanuku N, Tsurugai Y et al (2016) Phase 2 Study of stereotactic body radiotherapy and optional transarterial chemoembolization for solitary hepatocellular carcinoma not amenable to resection and radiofrequency ablation. Cancer 122:2041–2049
Moon DH, Wang AZ, Tepper JE (2018) A prospective study of the safey and efficacy of liver stereotactic body radiotherapy in patients with and without prior liver-directed therapy. Radiother Oncol 126:527–533
Nabavizadeh N, Waller JG, Fain R et al (2018) Safety and efficacy of accelerated hypofractionation and stereotactic body radiation theraoy for hepatocellular carcinoma patients with varying degrees of hepatic impairment. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 100:577–585
Jeong Y, Jung J, Cho B et al (2018) Stereotactic body radiation therapy using a respiratory-gated volumetric-modulated arc therapy technique for small hepatocelluar carcinoma. BMC Cancer 18:416
Chiang CL, Chan MKH, Yeung CSY et al (2019) Combined stereotactic body radio-therapy and trans-arterial chemoembolization as initial treatment in BCLC stage B‑C hepatocellular carcinoma. Strahlenther Onkol 195:254–264
Heinzerling JH, Anderson JF, Papiez L et al (2008) Four-dimensional computed tomography scan analysis of tumor and organ motion at varying levels of abdominal compression during stereotactic treatment of lung and liver. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 70:1571–1578
Marrero JA, Fontana RJ, Barrat A et al (2005) Prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma: comparison of 7 staging systems in an american cohort. Hepatology 41:707–716
Andolino DL, Johnson CS, Maluccio M et al (2011) Stereotactic body radiotherapy for primary hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 81:e447–e453
Mutsaers A, Greenspoon J, Walker-Dilks C et al (2017) Systematic review of patients reported quality of life following stereotactic ablative radiotherapy for primary and metastatic liver cancer. Radiat Oncol 12:110
Rubinstein MM, Kaubisch A, Kinkhabwala M, Reinus J, Liu Q, Chuyy JW (2017) Bridging therapy effectiveness in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma prior to orthotopic liver transplantation. J Gastrointest Oncol 8:1051–1055
Uemura T, Kirichenko A, Bunker M, Vincent M, Machado L, Thai N (2019) Stereotactic body radiation therapy: a new strategy for locoregional treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma while awaiting liver transplantation. World J Surg 43:886–893
O’Connor JK, Trotter J, Davis GL, Dempster J, Klintmalm GB, Goldstein RM (2012) Long-term outcomes of stereotactic body radiation therapy in the treatment of hepatocellular cancer as a bridge to transplantation. Liver Transpl 18:949–954
Moore A, Cohen-Naftaly M, Tobar A, Kundel Y, Benjaminov O, Braun M, Issachar A, Mor E, Sarfaty M, Bragilovski D, Hur BR, Gordon N, Stemmer SM, Allen AM (2017) Stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) for definitive treatment and as a bridge to liver transplantation in early stage inoperable hepatocellular carcinoma. Radiat Oncol 12:163
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SG performed data acquisition and participated in patient treatment, statistical analysis, and in drafting the manuscript. CH participated in treatment of the patients and statistical analysis. FW, PP, ED treated the patients and participated in data acquisition. CB revised the manuscript critically. FR participated in data acquisition, statistical analysis, treatment of the patients, drafting the manuscript and critically reviewed the data and the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
S. Gerum, C. Heinz, C. Belka, F. Walter, P.M. Paprottka, E.N. De Toni, and F. Röder declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical standards
The study was approved by the Ethics committee of the University of Munich (LMU), reference number 617-16. Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gerum, S., Heinz, C., Belka, C. et al. Stereotactic body radiotherapy in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma in a multimodal treatment setting. Strahlenther Onkol 196, 334–348 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00066-019-01540-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00066-019-01540-8
Keywords
- Liver
- Hepatocellular carcinoma
- Stereotactic body radiation therapy
- Orthotopic liver transplantation
- Multimodal treatment