Abstract
Background
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is increasing in incidence and the majority of patients are not candidates for radical therapies. Therefore, interest in minimally invasive therapies in growing.
Methods
A Phase I dose escalation trial was conducted at Indiana University to determine the feasibility and toxicity of stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) for primary HCC. Eligible patients had Child-Turcotte-Pugh’s Class (CTP) A or B, were not candidates for resection, had 1–3 lesions and cumulative tumour diameter less than or equal to 6 cm. Dose escalation started at 36 Gy in 3 fractions (12 Gy/fraction) with a subsequent planned escalation of 2 Gy/fraction/level. Dose-limiting toxicity (DLT) was defined as Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events v3.0 grade 3 or greater toxicity.
Results
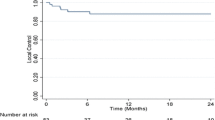
Seventeen patients with 25 lesions were enrolled. Dose was escalated to 48 Gy (16 Gy/fraction) in CTP-A patients without DLT. Two patients with CPC-B disease developed grade 3 hepatic toxicity at the 42-Gy (14 Gy/fraction) level. The protocol was amended for subsequent CTP-B patients to receive a regimen of 5 fractions starting at 40 Gy (8 Gy/fraction) with one patient experiencing progressive liver failure. Four additional patients were enrolled (one died of unrelated causes after an incomplete SBRT course) without DLT. The only factor related to more than one grade 3 or greater liver toxicity or death within 6 months was the CTP score (p=0.03). Six patients underwent a liver transplant. Ten patients are alive without progression with a median FU of 24 months (10–42 months), with local control/stabilisation of the disease of 100%. One and two-year Kaplan-Meier estimates for overall survival are 75% and 60%, respectively.
Conclusions
SBRT is a non-invasive feasible and well tolerated therapy in adequately selected patients with HCC. The preliminary local control and survival are encouraging. A confirmatory Phase II trial is currently open to accrual.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J et al (2005) Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clinic 55:74–108
El-Serag HB, Mason AC (1999) Rising incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma in the United States [see comment]. N Engl J Med 340:745–750
American Cancer Society (2009) Cancer facts and figures. American Cancer Society
Mazzaferro V, Regalia E, Doci R et al (1996) Liver transplantation for the treatment of small hepatocellular carcinomas in patients with cirrhosis. N Engl J Med 334:693–699
Llovet JM, Fuster J, Bruix J (1999) Intention-to-treat analysis of surgical treatment for early heaptocellular carcinoma: resection versus transplantation [see comment]. Hepatology 30:1434–1440
Vilana R, Bruix J, Bru C et al (1992) Tumor size determines the efficacy of percutaneous ethanol injection for the treatment of small hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 16:353–357
Lui L (2002) Radiofrequency ablation of liver cancers. World J Gastroenterol 8:392–399
Llovet JM, Bruix J (2003) Systematic review of randomized trials for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: chemoembolization improves survival. Hepatology 37:429–442
Salem R, Hunter RD (2006) Yttrium-90 microspheres for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: a review. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 66:S83–88
Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V et al (2008) Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma [see comment]. N Engl J Med 359:378–390
Abrams RA, Pajak TF, Haulk TL et al (1998) Survival results among patients with alpha-fetoprotein-positive, unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: analysis of three sequential treatments of the RTOG and Johns Hopkins Oncology Center. Cancer J Sci Am 4:178–184
Stillwagon GB, Order SE, Guse C et al (1989) 194 hepatocellular cancers treated by radiation and chemotherapy combinations: toxicity and response: a Radiation Therapy Oncology Group Study. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 17:1223–1229
Dawson LA, McGinn CJ, Normolle D et al (2000) Escalated focal liver radiation and concurrent hepatic artery fl uorodeoxyuridine for unresectable intrahepatic malignancies. J Clin Oncol 18:2210–2218
Liu M-T, Li S-H, Chu T-C et al (2004) Threedimensional conformal radiation therapy for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma patients who had failed with or were unsuited for transcatheter arterial chemoembolization. Jpn J Clin Oncol 34:532–539
Mornex F, Girard N, Beziat C et al (2006) Feasibility and efficacy of high-dose three-dimensionalconformal radiotherapy in cirrhotic patients with small-size hepatocellular carcinoma non-eligible for curative therapies: mature results of the French Phase II RTF-1 trial. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 66:1152–1158
Park HC, Seong J, Han KH et al (2002) Doseresponse relationship in local radiotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 54:150–155
Lax I, Blomgren H, Naslund I et al (1994) Stereotactic radiotherapy of malignancies in the abdomen. Methodological aspects. Acta Oncol 33:677–683
Blomgren H, Lax I, Goranson H (1998) Radiosurgery for tumors in the body: Clinical experience using a new method. J Radiosurg 1:63–74
Blomgren H, Lax I, Naslund I et al (1995) Stereotactic high dose fraction radiation therapy of extracranial tumors using an accelerator. Clinical experience of the first thirty-one patients. Acta Oncol 34:861–870
Kelsey CR, Schefter T, Nash SR (2003) Retrospective clinicopathologic correlation of gross tumor size of hepatocellular carcinoma: implications for extracranial stereotactic radiosurgery. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 57:S283
Dawson LA, Eccles C, Bissonnette J-P et al (2005) Accuracy of daily image guidance for hypofractionated liver radiotherapy with active breathing control. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 62:1247–1252
Cancer Therapy Evaluation Program Website: ctep.cancer.gov/forms/CTCAEv3.pdf
Pugh RN, Murray-Lyon IM, Dawson JL et al (1973) Transection of the oesophagus for bleeding oesophageal varices. Br J Surg 60:646–649
Bruix J, Sherman M, Practice Guidelines Committee AAftSoLD (2005) Management of hepatocellular carcinoma [see comment]. Hepatology 42:1208–1236
Henderson MA, Azzouz F, Breen T (2007) Preliminary toxicity analysis of phase I/II trial evaluating stereotactic body radiotherapy for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 69:S297 [Abstract]
Jones D (1994) ICRU Report 50: prescribing, recording and reporting photon beam therapy. Med Phys 21:833–834
ICRU (1999) Report 62: prescribing, recording and reporting photon beam therapy (supplement to ICRU Report 50). International Commission on Radiation Units and Measurements, Bethesda
Therasse P, Arbuck SG, Eisenhauer EA et al (2000) New guidelines to evaluate the response to treatment in solid tumors. European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer, National Cancer Institute of the United States, National Cancer Institute of Canada [see comment]. J Natl Cancer Inst 92:205–216
Kaplan EL, Meier P (1958) Nonparametric estimation from incomplete observations. J Am Stat Assoc 53:457
Timmerman R, Papiez L, McGarry R et al (2003) Extracranial stereotactic radioablation: results of a phase I study in medically inoperable stage I nonsmall cell lung cancer. Chest 124:1946–1955
Timmerman R, McGarry R, Papiez L (2005) Initial report of a prospective phase II trial of stereotactic body radiation therapy for patients with medically inoperable stage I non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 63:S99
Dawson LA, Normolle D, Balter JM et al (2002) Analysis of radiation-induced liver disease using the Lyman NTCP model [see comment] [erratum appears in Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2002;53:1422]. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 53:810–821
Lawrence TS, Ten Haken RK, Kessler ML et al (1992) The use of 3-D dose volume analysis to predict radiation hepatitis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 23:781–788
Lyman JT (1985) Complication probability as assessed from dose-volume histograms. Radiat Res 8:S13–19
Cheng JC-H, Wu JK, Huang CM et al (2002) Radiation-induced liver disease after radiotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: clinical manifestation and dosimetric description. Radiother Oncol 63:41–45
Cheng JC-H, Wu JK, Lee PC (2004) Biological susceptibility of hepatocellular carcinoma patients treated with radiotherapy to radiationinduced liver disease. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 60:1502–1509
Xu Z-Y, Liang S-X, Zhu J et al (2006) Prediction of radiation-induced liver disease by Lyman normal-tissue complication probability model in three-dimensional conformal radiation therapy for primary liver carcinoma [see comment]. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 65:189–195
Herfarth KK, Debus J, Lohr F et al (2001) Stereotactic single-dose radiation therapy of liver tumors: results of a phase I/II trial. J Clin Oncol 19:164–170
Wulf J, Guckenberger M, Haedinger U et al (2006) Stereotactic radiotherapy of primary liver cancer and hepatic metastases. Acta Oncol 45:838–847
Choi BO, Jang HS, Kang KM et al (2006) Fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy in patients with primary hepatocellular carcinoma. Jpn J Clin Oncol 36:154–158
Mendez Romero A, Wunderink W, Hussain SM et al (2006) Stereotactic body radiation therapy for primary and metastatic liver tumors: a single institution phase I/II study. Acta Oncol 45:831–837
Tse RV, Hawkins M, Lockwood G et al (2008) Phase I study of individualized stereotactic body radiotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma and intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. J Clin Oncol 26:657–664
Douglas BG, Fowler JF (1976) The effect of multiple small doses of x rays on skin reactions in the mouse and a basic interpretation. Radiat Res 66:401–426
Park C, Papiez L, Zhang S et al (2008) Universal survival curve and single fraction equivalent dose: useful tools in understanding potency of ablative radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 70:847–852
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cárdenes, H.R., Price, T.R., Perkins, S.M. et al. Phase I feasibility trial of stereotactic body radiation therapy for primary hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Transl Oncol 12, 218–225 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-010-0492-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-010-0492-x