Abstract
Background
Stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) in pancreatic cancer can be limited by its proximity to organs at risk (OAR). In this analysis, we evaluated the toxicity and efficacy of two different treatment approaches in patients with locally recurrent or oligometastatic pancreatic cancer.
Materials and methods
According to the prescription method, patients were divided in two cohorts (C1 and C2). The planning target volume (PTV) was created through a 4 mm expansion of the internal target volume. In C2, a subvolume was additionally created, a simultaneous integrated protection (SIP), which is the overlap of the PTV with the planning risk volume of an OAR to which we prescribed a reduced dose.
Results
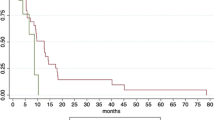
In all, 18 patients were treated (7 with local recurrences, 9 for oligometastases, 2 for both). Twelve of 23 lesions were treated without SIP (C1) and 11 with SIP (C2). The median follow-up was 12.8 months. Median overall survival (OS) was 13.2 (95% confidence interval [CI] 9.8–14.6) months. The OS rates at 6 and 12 months were 87 and 58%, respectively. Freedom from local progression for combined cohorts at 6 and 12 months was 93 and 67% (95% CI 15–36), respectively. Local control was not statistically different between the two groups. One patient in C2 experienced grade ≥3 acute toxicities and 1 patient in C1 experienced a grade ≥3 late toxicity.
Conclusion
The SIP approach is a useful prescription method for abdominal SBRT with a favorable toxicity profile which does not compromise local control and overall survival despite dose sacrifices in small subvolumes.
Zusammenfassung
Hintergrund
Die stereotaktische Strahlentherapie (SBRT) ist bei Pankreaskarzinomen durch die enge Lagebeziehung der Risikoorgane (OAR) zum Zielvolumen erschwert. In dieser Analyse evaluierten wir die Toxizität und die Lokalkontrolle von zwei unterschiedlichen Therapiestrategien bei Patienten mit rezidivierendem oder oligometastatischem Pankreaskarzinom.
Material und Methoden
Die Patienten wurden anhand der Verschreibungsmethode in zwei Kohorten geteilt (C1 und C2). Das Planungszielvolumen (PTV) wurde durch eine Expansion des internen Zielvolumens (ITV) um 4 mm erzeugt. In C2 wurde zusätzlich ein Subvolumen (simultan integrierte Protektion, SIP) definiert, welches durch die Überlappung des PTV mit dem Planungsrisikovolumen (PRV) eines OAR generiert wurde, um die Grenzdosen für das jeweilige OAR einhalten zu können.
Ergebnisse
Insgesamt 18 Patienten wurden behandelt (7 Lokalrezidive, 9 Oligometastasen, 2 kombiniert). Zwölf von 23 Läsionen wurden ohne SIP (C1) und 11 mit SIP (C2) therapiert. Bei einem medianen Follow-up von 12,8 Monaten lag das mediane Überleben bei 13,2 Monaten (95 %-Konfidenzintervall [KI] 9,8–14,6). Das Gesamtüberleben nach 6 und 12 Monaten betrug je 87 % und 58 %. Die Lokalkontrolle für das Gesamtkollektiv betrug nach 6 und 12 Monaten jeweils 93 % und 67 % (95 %-KI 15–36); sie war statistisch nicht unterschiedlich zwischen den beiden Gruppen. Ein Patient in C2 entwickelte eine akute Grad-4-Toxizität und 1 Patient in C1 entwickelte eine Grad-4-Spättoxizität.
Schlussfolgerung
Die SIP-Verschreibungsmethode ist eine hilfreiche Strategie bei der SBRT mit einem günstigen Nebenwirkungsprofil. Trotz der Dosisreduktion in kleinen Subvolumina waren die lokale Kontrolle und das Gesamtüberleben identisch.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A (2015) Cancer statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin 65(1):5–29. doi:10.3322/caac.21254
Herman JM, Wild AT, Wang H, Tran PT, Chang KJ, Taylor GE, Donehower RC, Pawlik TM, Ziegler MA, Cai H, Savage DT, Canto MI, Klapman J, Reid T, Shah RJ, Hoffe SE, Rosemurgy A, Wolfgang CL, Laheru DA (2013) Randomized phase III multi-institutional study of TNFerade biologic with fluorouracil and radiotherapy for locally advanced pancreatic cancer: final results. J Clin Oncol 31(7):886–894. doi:10.1200/JCO.2012.44.7516
Ducreux M, Cuhna AS, Caramella C, Hollebecque A, Burtin P, Goéré D, Seufferlein T, Haustermans K, Van Laethem JL, Conroy T, Arnold D (2015) Cancer of the pancreas: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol 26(suppl 5):v56–v68. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdv295
Murphy JD, Christman-Skieller C, Kim J, Dieterich S, Chang DT, Koong AC (2010) A dosimetric model of duodenal toxicity after stereotactic body radiotherapy for pancreatic cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 78(5):1420–1426. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2009.09.075
Brunner TB, Nestle U, Grosu AL, Partridge M (2015) SBRT in pancreatic cancer: what is the therapeutic window? Radiother Oncol 114(1):109–116. doi:10.1016/j.radonc.2014.10.015
Chang DT, Schellenberg D, Shen J, Kim J, Goodman KA, Fisher GA, Ford JM, Desser T, Quon A, Koong AC (2009) Stereotactic radiotherapy for unresectable adenocarcinoma of the pancreas. Cancer 115(3):665–672. doi:10.1002/cncr.24059
Herman JM, Chang DT, Goodman KA, Dholakia AS, Raman SP, Hacker-Prietz A, Iacobuzio-Donahue CA, Griffith ME, Pawlik TM, Pai JS, O’Reilly E, Fisher GA, Wild AT, Rosati LM, Zheng L, Wolfgang CL, Laheru DA, Columbo LA, Sugar EA, Koong AC (2015) Phase 2 multi-institutional trial evaluating gemcitabine and stereotactic body radiotherapy for patients with locally advanced unresectable pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Cancer 121(7):1128–1137. doi:10.1002/cncr.29161
Koong AC, Christofferson E, Le QT, Goodman KA, Ho A, Kuo T, Ford JM, Fisher GA, Greco R, Norton J, Yang GP (2005) Phase II study to assess the efficacy of conventionally fractionated radiotherapy followed by a stereotactic radiosurgery boost in patients with locally advanced pancreatic cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 63(2):320–323. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2005.07.002
Koong AC, Le QT, Ho A, Fong B, Fisher G, Cho C, Ford J, Poen J, Gibbs IC, Mehta VK, Kee S, Trueblood W, Yang G, Bastidas JA (2004) Phase I study of stereotactic radiosurgery in patients with locally advanced pancreatic cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 58(4):1017–1021. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2003.11.004
Pollom EL, Alagappan M, von Eyben R, Kunz PL, Fisher GA, Ford JA, Poultsides GA, Visser BC, Norton JA, Kamaya A, Cox VL, Columbo LA, Koong AC, Chang DT (2014) Single- versus multifraction stereotactic body radiation therapy for pancreatic adenocarcinoma: outcomes and toxicity. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 90(4):918–925. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2014.06.066
Schellenberg D, Kim J, Christman-Skieller C, Chun CL, Columbo LA, Ford JM, Fisher GA, Kunz PL, Van Dam J, Quon A, Desser TS, Norton J, Hsu A, Maxim PG, Xing L, Goodman KA, Chang DT, Koong AC (2011) Single-fraction stereotactic body radiation therapy and sequential gemcitabine for the treatment of locally advanced pancreatic cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 81(1):181–188. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2010.05.006
Trakul N, Koong AC, Chang DT (2014) Stereotactic body radiotherapy in the treatment of pancreatic cancer. Semin Radiat Oncol 24(2):140–147. doi:10.1016/j.semradonc.2013.11.008
Aitken KL, Hawkins MA (2015) Stereotactic body radiotherapy for liver metastases. Clin Oncol 27(5):307–315. doi:10.1016/j.clon.2015.01.032
Sterzing F, Brunner TB, Ernst I, Baus WW, Greve B, Herfarth K, Guckenberger M (2014) Stereotactic body radiotherapy for liver tumors: principles and practical guidelines of the DEGRO Working Group on Stereotactic Radiotherapy. Strahlenther Onkol 190(10):872–881. doi:10.1007/s00066-014-0714-1
Mahadevan A, Jain S, Goldstein M, Miksad R, Pleskow D, Sawhney M, Brennan D, Callery M, Vollmer C (2010) Stereotactic body radiotherapy and gemcitabine for locally advanced pancreatic cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 78(3):735–742. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2009.08.046
Mahadevan A, Miksad R, Goldstein M, Sullivan R, Bullock A, Buchbinder E, Pleskow D, Sawhney M, Kent T, Vollmer C, Callery M (2011) Induction gemcitabine and stereotactic body radiotherapy for locally advanced nonmetastatic pancreas cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 81(4):e615–622. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2011.04.045
Kumar R, Wild AT, Ziegler MA, Hooker TK, Dah SD, Tran PT, Kang J, Smith K, Zeng J, Pawlik TM, Tryggestad E, Ford E, Herman JM (2013) Stereotactic body radiation therapy planning with duodenal sparing using volumetric-modulated arc therapy vs intensity-modulated radiation therapy in locally advanced pancreatic cancer: A dosimetric analysis. Med Dosim 38(3):243–250. doi:10.1016/j.meddos.2013.02.003
Brunner TB, Nestle U, Adebahr S, Gkika E, Wiehle R, Baltas D, Grosu AL (2016) Simultaneous integrated protection: a new concept for high-precision radiation therapy. Strahlenther Onkol. doi:10.1007/s00066-016-1057-x
Timmerman RD (2008) An overview of hypofractionation and introduction to this issue of seminars in radiation oncology. Semin Radiat Oncol 18(4):215–222. doi:10.1016/j.semradonc.2008.04.001
Hoyer M, Roed H, Sengelov L, Traberg A, Ohlhuis L, Pedersen J, Nellemann H, Kiil Berthelsen A, Eberholst F, Engelholm SA, von der Maase H (2005) Phase-II study on stereotactic radiotherapy of locally advanced pancreatic carcinoma. Radiother Oncol 76(1):48–53. doi:10.1016/j.radonc.2004.12.022
Kavanagh BD, Pan CC, Dawson LA, Das SK, Li XA, Ten Haken RK, Miften M (2010) Radiation dose-volume effects in the stomach and small bowel. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 76(3 Suppl):S101–S107. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2009.05.071
Cattaneo GM, Passoni P, Longobardi B, Slim N, Reni M, Cereda S, di Muzio N, Calandrino R (2013) Dosimetric and clinical predictors of toxicity following combined chemotherapy and moderately hypofractionated rotational radiotherapy of locally advanced pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Radiother Oncol 108(1):66–71. doi:10.1016/j.radonc.2013.05.011
Elhammali A, Patel M, Weinberg B, Verma V, Liu J, Olsen JR, Gay HA (2015) Late gastrointestinal tissue effects after hypofractionated radiation therapy of the pancreas. Radiat Oncol 10:186. doi:10.1186/s13014-015-0489-2
Gurka MK, Kim C, He AR, Charabaty A, Haddad N, Turocy J, Johnson L, Jackson P, Weiner LM, Marshall JL, Collins SP, Pishvaian MJ, Unger K (2014) Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT) Combined With Chemotherapy for Unresected Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma. Am J Clin Oncol. doi:10.1097/COC.0000000000000118
Chuong MD, Springett GM, Freilich JM, Park CK, Weber JM, Mellon EA, Hodul PJ, Malafa MP, Meredith KL, Hoffe SE, Shridhar R (2013) Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy for Locally Advanced and Borderline Resectable Pancreatic Cancer Is Effective and Well Tolerated. Int J Radiat Oncol 86(3):516–522
Polistina F, Costantin G, Casamassima F, Francescon P, Guglielmi R, Panizzoni G, Febbraro A, Ambrosino G (2010) Unresectable Locally Advanced Pancreatic Cancer: A Multimodal Treatment Using Neoadjuvant Chemoradiotherapy (Gemcitabine Plus Stereotactic Radiosurgery) and Subsequent Surgical Exploration. Ann Surg Oncol 17(8):2092–2101
Rwigema JC, Parikh SD, Heron DE, Howell M, Zeh H, Moser AJ, Bahary N, Quinn A, Burton SA (2011) Stereotactic body radiotherapy in the treatment of advanced adenocarcinoma of the pancreas. Am J Clin Oncol 34(1):63–69. doi:10.1097/COC.0b013e3181d270b4
Tozzi A, Comito T, Alongi F, Navarria P, Iftode C, Mancosu P, Reggiori G, Clerici E, Rimassa L, Zerbi A, Fogliata A, Cozzi L, Tomatis S, Scorsetti M (2013) SBRT in unresectable advanced pancreatic cancer: preliminary results of a mono-institutional experience. Radiat Oncol 8(1):148
Didolkar MS, Coleman CW, Brenner MJ, Chu KU, Olexa N, Stanwyck E, Yu A, Neerchal N, Rabinowitz S (2010) Image-Guided Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Locally Advanced Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma Results of First 85 Patients. J Gastrointest Surg 14(10):1547–1559
Goyal K, Einstein D, Ibarra RA, Yao M, Kunos C, Ellis R, Brindle J, Singh D, Hardacre J, Zhang Y, Fabians J, Funkhouser G, Machtay M, Sanabria JR (2012) Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy for Nonresectable Tumors of the Pancreas. J Surg Res 174(2):319–325
Moningi S, Dholakia AS, Raman SP, Blackford A, Cameron JL, Le DT, De Jesus-Acosta AMC, Hacker-Prietz A, Rosati LM, Assadi RK, Dipasquale S, Pawlik TM, Zheng L, Weiss MJ, Laheru DA, Wolfgang CL, Herman JM (2015) The Role of Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy for Pancreatic Cancer: A Single-Institution Experience. Ann Surg Oncol 22(7):2352–2358
Mellon EA, Hoffe SE, Springett GM, Frakes JM, Strom TJ, Hodul PJ, Malafa MP, Chuong MD, Shridhar R (2015) Long-term outcomes of induction chemotherapy and neoadjuvant stereotactic body radiotherapy for borderline resectable and locally advanced pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Acta Oncol 54(7):979–985
Comito T, Cozzi L, Clerici E, Franzese C, Tozzi A, Iftode C, Navarria P, D’Agostino G, Rimassa L, Carnaghi C, Personeni N, Tronconi MC, De Rose F, Franceschini D, Ascolese AM, Fogliata A, Tomatis S, Santoro A, Zerbi A, Scorsetti M (2016) Can Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy Be a Viable and Efficient Therapeutic Option for Unresectable Locally Advanced Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma? Results of a Phase 2 Study. Technol Cancer Res T. doi:10.1177/1533034616650778
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
E. Gkika, S. Adebahr, S. Kirste, T. Schimek-Jasch, R. Wiehle, R. Claus, U. Wittel, U. Nestle, D. Baltas, A.L. Grosu, and T.B. Brunner declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical standards
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Caption Electronic Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gkika, E., Adebahr, S., Kirste, S. et al. Stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) in recurrent or oligometastatic pancreatic cancer. Strahlenther Onkol 193, 433–443 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00066-017-1099-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00066-017-1099-8