Abstract
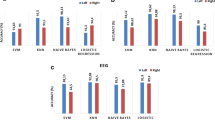
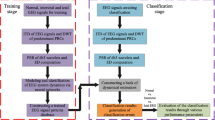
Epileptic seizure is a chronic central nervous system disorder which is characterized by transient event of abnormal and excessive neuronal discharge in the brain. Electroencephalogram (EEG) records the neurological activity in the brain which is commonly used for the identification of epilepsy. However, visual screening of EEG recordings is time consuming, tedious and subjective. Hence, automatic seizure detection becomes urgent in clinical application. Relevant technique in this filed has been developed rapidly with the employment of machine learning and signal processing tools. In this study, we propose a novel method for automatic epileptic EEG identification based upon dual Q-factor signal decomposition derived from tunable Q-factor wavelet transform (TQWT), fast and adaptive multivariate empirical mode decomposition (FA-MVEMD) and neural networks. First, EEG signals are decomposed into high- and low-resonance components using both high-Q-factor and low-Q-factor TQWT jointly. Second, FA-MVEMD decomposes the high- and low-Q-factor components into scale-aligned intrinsic mode components (IMFs). The first two IMFs of the high- and low-Q-factor components are extracted, which contain most of the EEG signals’ energy and are considered to be the predominant IMFs. The properties associated with the nonlinear EEG system dynamics are preserved in the predominant IMFs which demonstrate significant difference in EEG system dynamics between normal (healthy), interictal and ictal EEG signals. Third, neural networks are then used to model, identify and classify EEG system dynamics with the predominant IMFs as the input. Finally, experiments on Bonn EEG database are included to assess the effectiveness of the proposed method. The overall average accuracy for binary classification, ternary classification and five-class classification is reported to be \(98.54\%\), \(99.18\%\) and \(97.84\%\), respectively, by using tenfold cross-validation. In comparison with other state-of-the-art methods, our algorithm illustrates superior performance, which can serve as a potential candidate for the automatic EEG seizure detection in the clinical application.







Similar content being viewed by others

Data Availability
All the datasets used in this manuscript are publicly available datasets (Bonn University database [8], already in the public domain). There is no issue with Ethical approval and Informed consent.
References
U.R. Acharya, S.L. Oh, Y. Hagiwara, J.H. Tan, H. Adeli, Deep convolutional neural network for the automated detection and diagnosis of seizure using EEG signals. Comput. Biol. Med. 100, 270–278 (2018)
U.R. Acharya, S.V. Sree, G. Swapna, R.J. Martis, J.S. Suri, Automated EEG analysis of epilepsy: a review. Knowl. Based Syst. 45, 147–165 (2013)
H. Adeli, Z. Zhou, N. Dadmehr, Analysis of EEG records in an epileptic patient using wavelet transform. J. Neurosci. Methods 123(1), 69–87 (2003)
D. Ahmedt-Aristizabal, C. Fookes, K. Nguyen, S. Sridharan, Deep classification of epileptic signals, in 40th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), pp. 332–335 (2018)
E. Alickovic, J. Kevric, A. Subasi, Performance evaluation of empirical mode decomposition, discrete wavelet transform, and wavelet packed decomposition for automated epileptic seizure detection and prediction. Biomed. Signal Process. 39, 94–102 (2018)
A. Alkan, E. Koklukaya, A. Subasi, Automatic seizure detection in EEG using logistic regression and artificial neural network. J. Neurosci. Methods 148(2), 167–176 (2005)
H.U. Amin, M.Z. Yusoff, R.F. Ahmad, A novel approach based on wavelet analysis and arithmetic coding for automated detection and diagnosis of epileptic seizure in EEG signals using machine learning techniques. Biomed. Signal Process. 56, 101707 (2020)
R.G. Andrzejak, K. Lehnertz, F. Mormann, C. Rieke, P. David, C.E. Elger, Indications of nonlinear deterministic and finite-dimensional structures in time series of brain electrical activity: dependence on recording region and brain state. Phys. Rev. E 64(6), 061907 (2001)
R.G. Andrzejak, G. Widman, K. Lehnertz, C. Rieke, P. David, C.E. Elger, The epileptic process as nonlinear deterministic dynamics in a stochastic environment: an evaluation on mesial temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsy Res. 44(2–3), 129–140 (2001)
A.T. Azar, S.A. El-Said, Performance analysis of support vector machines classifiers in breast cancer mammography recognition. Neural Comput. Appl. 24, 1163–1177 (2014)
Y. Bai, Z. Liang, X. Li, A permutation Lempel–Ziv complexity measure for EEG analysis. Biomed. Signal Process. 19, 102–114 (2015)
V. Bajaj, R.B. Pachori, Classification of seizure and nonseizure EEG signals using empirical mode decomposition. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 16(6), 1135–1142 (2012)
V. Bajaj, R.B. Pachori, Epileptic seizure detection based on the instantaneous area of analytic intrinsic mode functions of EEG signals. Biomed. Eng. Lett. 3(1), 17–21 (2013)
M. Bandarabadi, C.A. Teixeira, J. Rasekhi, A. Dourado, Epileptic seizure prediction using relative spectral power features. Clin. Neurophysiol. 126(2), 237–248 (2015)
A. Bhardwaj, A. Tiwari, R. Krishna, V. Varma, A novel genetic programming approach for epileptic seizure detection. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 124, 2–18 (2016)
D. Bhati, R.B. Pachori, V.M. Gadre, A novel approach for time-frequency localization of scaling functions and design of three-band biorthogonal linear phase wavelet filter banks. Digit. Signal Process. 69, 309–322 (2017)
D. Bhati, M. Sharma, R.B. Pachori, V.M. Gadre, Time-frequency localized three-band biorthogonal wavelet filter bank using semidefinite relaxation and nonlinear least squares with epileptic seizure EEG signal classification. Digit. Signal Process. 62, 259–273 (2017)
A. Bhattacharyya, R.B. Pachori, A multivariate approach for patient-specific EEG seizure detection using empirical wavelet transform. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 64(9), 2003–2015 (2017)
A. Bhattacharyya, R. Pachori, A. Upadhyay, U.R. Acharya, Tunable-Q wavelet transform based multiscale entropy measure for automated classification of epileptic EEG signals. Appl. Sci. 7(4), 385 (2017)
M. Breakspear, J.A. Roberts, J.R. Terry, S. Rodrigues, N. Mahant, P.A. Robinson, A unifying explanation of primary generalized seizures through nonlinear brain modeling and bifurcation analysis. Cereb. Cortex 16(9), 1296–1313 (2006)
G.D. Cetin, O. Cetin, M.R. Bozkurt, The detection of normal and epileptic EEG signals using ANN methods with matlab-based GUI. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 114(12), 45–50 (2015)
G. Chen, Automatic EEG seizure detection using dual-tree complex wavelet-Fourier features. Expert Syst. Appl. 41(5), 2391–2394 (2014)
S.B. Chen, A. Beigi, A. Yousefpour, F. Rajaee, H. Jahanshahi, S. Bekiros, Y. Chu, Recurrent neural network-based robust nonsingular sliding mode control with input saturation for a non-holonomic spherical robot. IEEE Access 8, 188441–188453 (2020)
O.K. Cura, S.K. Atli, H.S. Ture, A. Akan, Epileptic seizure classifications using empirical mode decomposition and its derivative. Biomed. Eng. Online 19(1), 1–22 (2020)
S. Dilshad, N. Singh, M. Atif, A. Hanif, N. Yaqub, W.A. Farooq, M.T. Masood, Automated image classification of chest X-rays of COVID-19 using deep transfer learning. Results Phys. 28, 104529 (2021)
C. Donos, M. Dumpelmann, A. Schulze-Bonhag, Early seizure detection algorithm based on intracranial EEG and random forest classification. Int. J. Neural Syst. 25(05), 1550023 (2015)
X. Gao, X. Yan, P. Gao, X. Gao, S. Zhang, Automatic detection of epileptic seizure based on approximate entropy, recurrence quantification analysis and convolutional neural networks. Artif. Intell. Med. 102, 101711 (2020)
P. Gaur, R.B. Pachori, H. Wang, G. Prasad, A multi-class EEG-based BCI classification using multivariate empirical mode decomposition based filtering and Riemannian geometry. Expert Syst. Appl. 95, 201–211 (2018)
P. Ghaderyan, A. Abbasi, M.H. Sedaaghi, An efficient seizure prediction method using KNN-based undersampling and linear frequency measures. J. Neurosci. Methods 232, 134–142 (2014)
S. Ghosh-Dastidar, H. Adeli, N. Dadmehr, Mixed-band wavelet-chaos-neural network methodology for epilepsy and epileptic seizure detection. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 54(9), 1545–1551 (2007)
L. Guo, D. Rivero, A. Pazos, Epileptic seizure detection using multiwavelet transform based approximate entropy and artificial neural networks. J. Neurosci. Methods 193(1), 156–163 (2010)
V. Gupta, A. Bhattacharyya, R.B. Pachori, Automated identification of epileptic seizures from EEG signals using FBSE-EWT method, in Biomedical Signal Processing. ed. by G. Naik (Springer, Singapore, 2020), pp.157–179
V. Gupta, R.B. Pachori, Epileptic seizure identification using entropy of FBSE based EEG rhythms. Biomed. Signal Process. 53, 101569 (2019)
A.R. Hassan, A. Subasi, Y. Zhang, Epilepsy seizure detection using complete ensemble empirical mode decomposition with adaptive noise. Knowl. Based Syst. 191, 105333 (2020)
N.E. Huang, Z. Shen, S.R. Long, M.C. Wu, H.H. Shih, Q. Zheng, H.H. Liu, The empirical mode decomposition and Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. R. Soc. 454(1971), 903–995 (1998)
A.K. Jaiswal, H. Banka, Local pattern transformation based feature extraction techniques for classification of epileptic EEG signals. Biomed. Signal Process. 34, 81–92 (2017)
V. Joshi, R.B. Pachori, A. Vijesh, Classification of ictal and seizure-free EEG signals using fractional linear prediction. Biomed. Signal Process. 9, 1–5 (2014)
Y. Kaya, M. Uyar, R. Tekin, S. Yildirim, 1D-local binary pattern based feature extraction for classification of epileptic EEG signals. Appl. Math. Comput. 243, 209–219 (2014)
P. Kellaway, The electroencephalographic features of benign centrotemporal (rolandic) epilepsy of childhood. Epilepsia 41(8), 1053–1056 (2000)
O. Kocadagli, R. Langari, Classification of EEG signals for epileptic seizures using hybrid artificial neural networks based wavelet transforms and fuzzy relations. Expert Syst. Appl. 88, 419–434 (2017)
T.S. Kumar, V. Kanhangad, R.B. Pachori, Classification of seizure and seizure-free EEG signals using local binary patterns. Biomed. Signal Process. 15, 33–40 (2015)
S.S. Kumar, N. Kasthuri, EEG seizure classification based on exploiting phase space reconstruction and extreme learning. Clust. Comput. 22(5), 11477–11487 (2019)
S. Lahmiri, Generalized Hurst exponent estimates differentiate EEG signals of healthy and epileptic patients. Phys. A 490, 378–385 (2018)
X. Lang, Q. Zheng, Z. Zhang, S. Lu, L. Xie, A. Horch, H. Su, Fast multivariate empirical mode decomposition. IEEE Access 6, 65521–65538 (2018)
Y. Li, W.G. Cui, H. Huang, Y.Z. Guo, K. Li, T. Tan, Epileptic seizure detection in EEG signals using sparse multiscale radial basis function networks and the Fisher vector approach. Knowl. Based Syst. 164, 96–106 (2019)
J. Liu, C. Zhang, Y. Zhu, T. Ristaniemi, T. Parviainen, F. Cong, Automated detection and localization system of myocardial infarction in single-beat ECG using Dual-Q TQWT and wavelet packet tensor decomposition. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 184, 105120 (2020)
A.K. Maddirala, R.A. Shaik, Separation of sources from single-channel EEG signals using independent component analysis. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 67(2), 382–393 (2017)
R.J. Martis, J.H. Tan, C.K. Chua, T.C. Loon, S.W.J. Yeo, L. Tong, Epileptic EEG classification using nonlinear parameters on different frequency bands. J. Mech. Med. Biol. 15(03), 1550040 (2015)
A. Mert, A. Akan, Seizure onset detection based on frequency domain metric of empirical mode decomposition. Signal Image Video Process. 12(8), 1489–1496 (2018)
M. Mohammadi, N.A. Khan, A.A. Pouyan, Automatic seizure detection using a highly adaptive directional time-frequency distribution. Multidimens. Syst. Signal Process. 29(4), 1661–1678 (2018)
M. Mursalin, Y. Zhang, Y. Chen, N.V. Chawla, Automated epileptic seizure detection using improved correlation-based feature selection with random forest classifier. Neurocomputing 241, 204–214 (2017)
P. Nagabushanam, S.T. George, S. Radha, EEG signal classification using LSTM and improved neural network algorithms. Soft. Comput. 24, 9981–10003 (2020)
R.B. Pachori, Discrimination between ictal and seizure-free EEG signals using empirical mode decomposition. Res. Lett. Signal Process. 2008, 14 (2008)
R.B. Pachori, V. Bajaj, Analysis of normal and epileptic seizure EEG signals using empirical mode decomposition. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 104(3), 373–381 (2011)
S. Patidar, T. Panigrahi, Detection of epileptic seizure using Kraskov entropy applied on tunable-Q wavelet transform of EEG signals. Biomed. Signal Processs. 34, 74–80 (2017)
R.B. Pachori, S. Patidar, Epileptic seizure classification in EEG signals using second-order difference plot of intrinsic mode functions. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 113(2), 494–502 (2014)
R.B. Pachori, R. Sharma, S. Patidar, Classification of normal and epileptic seizure EEG signals based on empirical mode decomposition, in Complex System Modelling and Control through Intelligent Soft Computations, Studies in Fuzziness and Soft Computing. ed. by Q. Zhu, A.T. Azar (Springer, Cham, 2015), pp.367–388
M. Peker, B. Sen, D. Delen, A novel method for automated diagnosis of epilepsy using complex-valued classifiers. IEEE J. Biomed. Health 20(1), 108–118 (2015)
J.P.M. Pijn, D.N. Velis, M.J. van der Heyden, J. DeGoede, C.W. van Veelen, F.H.L. da Silva, Nonlinear dynamics of epileptic seizures on basis of intracranial EEG recordings. Brain Topogr. 9(4), 249–270 (1997)
K. Polat, S. Gunes, Classification of epileptiform EEG using a hybrid system based on decision tree classifier and fast Fourier transform. Appl. Math. Comput. 187(2), 1017–1026 (2007)
S. Raghu, N. Sriraam, A.S. Hegde, P.L. Kubben, A novel approach for classification of epileptic seizures using matrix determinant. Expert Syst. Appl. 127, 323–341 (2019)
S. Raghu, N. Sriraam, G.P. Kumar, Classification of epileptic seizures using wavelet packet log energy and norm entropies with recurrent Elman neural network classifier. Cogn. Neurodyn. 11(1), 51–66 (2017)
S. Raghu, N. Sriraam, Y. Temel, S.V. Rao, P.L. Kubben, EEG based multi-class seizure type classification using convolutional neural network and transfer learning. Neural Netw. 124, 202–212 (2020)
N. Rehman, D.P. Mandic, Multivariate empirical mode decomposition. Proc. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 466(2117), 1291–1302 (2010)
K. Samiee, P. Kovacs, M. Gabbouj, Epileptic seizure classification of EEG time-series using rational discrete short-time Fourier transform. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 62(2), 541–552 (2014)
I.W. Selesnick, Wavelet transform with tunable Q-factor. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 59(8), 3560–3575 (2011)
I.W. Selesnick, Resonance-based signal decomposition: a new sparsity-enabled signal analysis method. Signal Process. 91(12), 2793–2809 (2011)
A. Sharmila, P. Geethanjali, A review on the pattern detection methods for epilepsy seizure detection from EEG signals. Biomed. Eng./Biomedizinische Technik 64(5), 507–517 (2019)
R.R. Sharma, R.B. Pachori, Time-frequency representation using IEVDHM-HT with application to classification of epileptic EEG signals. IET Sci. Meas. Technol. 12(1), 72–82 (2017)
M. Sharma, R.B. Pachori, A novel approach to detect epileptic seizures using a combination of tunable-Q wavelet transform and fractal dimension. J. Mech. Med. Biol. 17(07), 1740003 (2017)
R. Sharma, R.B. Pachori, Classification of epileptic seizures in EEG signals based on phase space representation of intrinsic mode functions. Expert Syst. Appl. 42(3), 1106–1117 (2015)
M. Sharma, R.B. Pachori, U.R. Acharya, A new approach to characterize epileptic seizures using analytic time-frequency flexible wavelet transform and fractal dimension. Pattern Recogn. Lett. 94, 172–179 (2017)
R. Sharma, R.B. Pachori, P. Sircar, Seizures classification based on higher order statistics and deep neural network. Biomed. Signal Process. 59, 101921 (2020)
R.R. Sharma, P. Varshney, R.B. Pachori, S.K. Vishvakarma, Automated system for epileptic EEG detection using iterative filtering. IEEE Sens. Lett. 2(4), 1–4 (2018)
F. Shayegh, S. Sadri, R. Amirfattahi, K. Ansari-Asl, A model-based method for computation of correlation dimension, Lyapunov exponents and synchronization from depth-EEG signals. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 113(1), 323–337 (2014)
H. Shen, X. Hu, J. Wang, J. Cao, W. Qian, Non-fragile \(H_ {\infty }\) synchronization for Markov jump singularly perturbed coupled neural networks subject to double-layer switching regulation. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/TNNLS
J.L. Song, W. Hu, R. Zhang, Automated detection of epileptic EEGs using a novel fusion feature and extreme learning machine. Neurocomputing 175, 383–391 (2016)
J.L. Starck, M. Elad, D. Donoho, Image decomposition via the combination of sparse representation and a variational approach. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 14(10), 1570–1582 (2005)
A. Subasi, J. Kevric, M.A. Canbaz, Epileptic seizure detection using hybrid machine learning methods. Neural Comput. Appl. 31(1), 317–325 (2019)
P. Swami, T.K. Gandhi, B.K. Panigrahi, M. Tripathi, S. Anand, A novel robust diagnostic model to detect seizures in electroencephalography. Expert Syst. Appl. 56, 116–130 (2016)
M.R. Thirumalaisamy, P.J. Ansell, Fast and adaptive empirical mode decomposition for multidimensional, multivariate signals. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 25(10), 1550–1554 (2018)
L.T. Timothy, B.M. Krishna, U. Nair, Classification of mild cognitive impairment EEG using combined recurrence and cross recurrence quantification analysis. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 120, 86–95 (2017)
A.K. Tiwari, R.B. Pachori, V. Kanhangad, B.K. Panigrahi, Automated diagnosis of epilepsy using key-point-based local binary pattern of EEG signals. IEEE J. Biomed. Health 21(4), 888–896 (2016)
I. Ullah, M. Hussain, H. Aboalsamh, An automated system for epilepsy detection using EEG brain signals based on deep learning approach. Expert Syst. Appl. 107, 61–71 (2018)
R. Upadhyay, P.K. Padhy, P.K. Kankar, A comparative study of feature ranking techniques for epileptic seizure detection using wavelet transform. Comput. Electr. Eng. 53, 163–176 (2016)
Y. Wang, Y.M. Chu, Y.A. Khan, Z.Y. Khan, Q. Liu, M.Y. Malik, S.Z. Abbas, A Machine learning-based prediction model for the heart diseases from chance factors through two-variable decision tree classifier. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 41(6), 5985–6002 (2021)
C. Wang, D.J. Hill, Learning from neural control. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 17(1), 130–146 (2006)
C. Wang, D.J. Hill, Deterministic learning and rapid dynamical pattern recognition. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 18(3), 617–630 (2007)
C. Wang, D.J. Hill, Deterministic Learning Theory for Identification, Recognition and Control (CRC Press, Boca Raton, 2009)
Y. Wang, J. Lu, Z. Li, Y. Chu, Fault detection for a class of non-linear networked control systems in the presence of Markov sensors assignment with partially known transition probabilities. IET Control Theory 9(10), 1491–1500 (2015)
M. Wu, T. Wan, X. Wan, Y. Du, J. She, Fast, accurate localization of epileptic seizure onset zones based on detection of high-frequency oscillations using improved wavelet transform and matching pursuit methods. Neural Comput. 29(1), 194–219 (2017)
P.Y. Xiong, H. Jahanshahi, R. Alcaraz, Y.M. Chu, J.F. Gomez-Aguilar, F.E. Alsaadi, Spectral entropy analysis and synchronization of a multi-stable fractional-order chaotic system using a novel neural network-based chattering-free sliding mode technique. Chaos Soliton Fract. 144, 110576 (2021)
Y. Yuan, G. Xun, K. Jia, A. Zhang, A multi-view deep learning framework for EEG seizure detection. IEEE J. Biomed. Health 23(1), 83–94 (2018)
Q. Yuan, W. Zhou, L. Zhang, F. Zhang, F. Xu, Y. Leng, M. Chen, Epileptic seizure detection based on imbalanced classification and wavelet packet transform. Seizure 50, 99–108 (2017)
A. Zahra, N. Kanwal, N. urRehman, S. Ehsan, K.D. McDonald-Maier, Seizure detection from EEG signals using multivariate empirical mode decomposition. Comput. Biol. Med. 88, 132–141 (2017)
W. Zeng, M. Li, C. Yuan, Q. Wang, F. Liu, Y. Wang, Identification of epileptic seizures in EEG signals using time-scale decomposition (ITD), discrete wavelet transform (DWT), phase space reconstruction (PSR) and neural networks. Artif. Intell. Rev. 53(4), 3059–3088 (2020)
T. Zhang, W. Chen, LMD based features for the automatic seizure detection of EEG signals using SVM. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. 25(8), 1100–1108 (2016)
Y. Zhang, W. Zhou, S. Yuan, Q. Yuan, Seizure detection method based on fractal dimension and gradient boosting. Epilepsy Behav. 43, 30–38 (2015)
T.H. Zhao, M.I. Khan, Y.M. Chu, Artificial neural networking (ANN) analysis for heat and entropy generation in flow of non-Newtonian fluid between two rotating disks. Math. Methods Appl. Sci. 2021, 1–19 (2021)
W. Zhou, Y. Liu, Q. Yuan, X. Li, Epileptic seizure detection using lacunarity and Bayesian linear discriminant analysis in intracranial EEG. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 60(12), 3375–3381 (2013)
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This work was funded by the Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province (Grant No. 2022J011146).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zeng, W., Yuan, C. Epileptic EEG Identification Based on Dual Q-Factor Signal Decomposition (DQSD), Fast and Adaptive Multivariate Empirical Mode Decomposition (FA-MVEMD) and Neural Networks. Circuits Syst Signal Process 42, 3552–3588 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-022-02282-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-022-02282-2