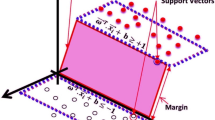
Abstract
The aim of this study is to establish a hybrid model for epileptic seizure detection with genetic algorithm (GA) and particle swarm optimization (PSO) to determine the optimum parameters of support vector machines (SVMs) for classification of EEG data. SVMs are one of the robust machine learning techniques and have been extensively used in many application areas. The kernel parameter’s setting for SVMs in training process effects the classification accuracy. We used GA- and PSO-based approach to optimize the SVM parameters. Compared to the GA algorithm, the PSO-based approach significantly improves the classification accuracy. It is shown that the proposed Hybrid SVM can reach a classification accuracy of up to 99.38% for the EEG datasets. Hence, the proposed Hybrid SVM is an efficient tool for neuroscientists to detect epileptic seizure in EEG.




Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
EEG time series are available under (http://www.meb.unibonn.de/epileptologie/science/physik/eegdata.html).
References
Geva AB, Kerem DH (1999) Brain state identification and forecasting of acute pathology using unsupervised fuzzy clustering of EEG temporal patterns. In: Teodorescu HN, Kandel A, Jain LC (eds) Fuzzy and neuro-fuzzy Systems in Medicine. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL
Bylsma FW, Peyser CE, Folstein SE, Ross C, Brandt J (1994) EEG power spectra in Huntington’s disease: clinical and neuropsychological correlates. Neuropsychologia 32:137–150
D'Alessandro M, Esteller R, Vachtsevanos G, Hinson A, Echauz J, Litt B (2003) Epileptic seizure prediction using hybrid feature selection over multiple intracranial EEG electrode contacts: a report of four patients. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 50:603–615
Geva AB, Kerem DH (1998) Forecasting generalized epileptic seizures from the EEG signal by wavelet analysis and dynamic unsupervised fuzzy clustering. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 45:1205–1216
Preda RO, Vizireanu DN (2011) Robust wavelet-based video watermarking scheme for copyright protection using the human visual system. Journal of Electronic Imaging 20(1):013022–013022
Preda RO, Vizireanu DN (Dec. 2010) A robust digital watermarking scheme for video copyright protection in the wavelet domain. Measurement 43(10):1720–1726
Preda RO, Vizireanu DN (2011) Quantisation-based video watermarking in the wavelet domain with spatial and temporal redundancy. Int J Electron 98(3):393–405
Bigan C (1998) A recursive time-frequency processing method for neural networks recognition of EEG seizures. In: Ifeachor EC, Sperduti A, Starita A (eds) Neural networks and expert systems in medicine and healthcare. World Scientific, Singapore
Bronzino JD (2000) Principles of electroencephalography, The biomedical engineering handbook, Second edn. CRC Press LLC, Boca Raton
Adeli H, Zhou Z, Dadmehr N (2003) Analysis of EEG records in an epileptic patient using wavelet transform. J Neurosci Methods 123:69–87
Subasi A (2007) EEG signal classification using wavelet feature extraction and a mixture of expert model. Expert Syst Appl 32:1084–1093
Subasi A, Gürsoy MI (2010) Comparison of PCA, ICA and LDA in EEG signal classification using DWT and SVM. Expert Syst Appl 37:8659–8666
Harikumar, H., Narayanan, B. S (2003) Fuzzy techniques for classification of epilepsy risk level from EEG signals. Conference on Convergent Technologies for Asia-Pacific Region TENCON, p 209–213
Peker M, Sen B, Delen D (2016) A novel method for automated diagnosis of epilepsy using complex-valued classifiers. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics 20(1):108–118
Islam MK, Rastegarnia A, Yang Z (2016) A wavelet-based artifact reduction from scalp eeg for epileptic seizure detection. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics 20(5):1321–1332
Sharmila A, Geethanjali P (2016) DWT based detection of epileptic seizure from EEG signals using naive Bayes and k-NN classifiers. IEEE Access 4:7716–7727
Wang G, Sun Z, Tao R, Li K, Bao G, Yan X (2016) Epileptic seizure detection based on partial directed coherence analysis. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform 20(3):873–879
Hassan AR, Siuly S, Zhang Y (2016) Epileptic seizure detection in EEG signals using tunable-Q factor wavelet transform and bootstrap aggregating. Comput Methods Prog Biomed 137:247–259
Zhang T, Chen W, Li M (2017) AR based quadratic feature extraction in the VMD domain for the automated seizure detection of EEG using random forest classifier. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 31:550–559
Mursalin M, Zhang Y, Chen Y, Chawla NV (2017) Automated epileptic seizure detection using improved correlation-based feature selection with random forest classifier. Neurocomputing 241:204–214
Dhiman R, Saini J (2017) Biogeography based hybrid scheme for automatic detection of epileptic seizures from EEG signatures. Appl Soft Comput 51:116–129
Li M, Chen W, Zhang T (2017) Automatic epileptic EEG detection using DT-CWT-based non-linear features. Biomed Signal Process Control 34:114–125
Andrzejak, R.G., Lehnertz, K., Mormann, F., Rieke, C., David, P., Elger, C.E. (2001) Indications of nonlinear deterministic and finite-dimensional structures in time series of brain electrical activity: dependence on recording region and brain state. Physical Review E 64
Marchant BP (2003) Time–frequency analysis for biosystem engineering. Biosyst Eng 85:261–281
Semmlow JL (2004) Biosignal and biomedical image processing: MATLAB-based applications. Marcel Dekker, Inc., New York
Kandaswamy A, Kumar CS, Ramanathan RP, Jayaraman S, Malmurugan N (2004) Neural classification of lung sounds using wavelet coefficients. Comput Biol Med 34:523–537
Vapnik VN (2000) Nature of statistical learning theory, Second edn. Springer, New York
Joachims, T (1998) Text categorization with support vector machines. Proceedings of European conference on machine learning (ECML). Chemintz, DE, p 137–142
Pontil M, Verri A (1998) Support vector machines for 3D object recognition. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 20:637–646
Yu, G. X., Ostrouchov, G., Geist, A., Samatova, N. F (2003) An SVM-based algorithm for identification of photosynthesis-specific genome features. Second IEEE computer society bioinformatics conference, CA, USA, pp. 235–243
Schlkopf B, Burges C, Smola A (1999) Advances in kernel methods: support vector learning. MIT Press, Cambridge, MA
Schlkopf B, Smola A (2002) Learning with kernels: support vector machines, regularization, optimization and beyond (adaptive computation and machine learning). MIT Press, Cambridge, MA
Cristianini N, Shawe-Taylor J (2000) An introduction to support vector machines: and other kernel-based learning methods. Cambridge University Press, New York
Davis L (ed) (1991) Handbook of genetic algotithms. Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York
Goldberg DE (1989) Genetic algorithms in search, optimization and machine learning. Addison-Wesley, New York
Michalewicz Z (1992) Genetic algorithms + data structures = evolution programs. Springer, Berlin Heideberg New York
Bandyopadhyay, S., Pal, S. K (2007) Classification and learning using genetic algorithms. Springer
Guo XC, Yang JH, Wu CG, Wang CY, Liang YC (2008) A novel LS-SVMs hyper-parameter selection based on particle swarm optimization. Neurocomputing 71:3211–3215
Engelbrecht, A. P. (2007) Computational Intelligence. Wiley
Huang C-L, Dun J-F (2008) A distributed PSO–SVM hybrid system with feature selection and parameter optimization. Appl Soft Comput 8:1381–1391
Ardjani, F., Sadouni, K (2010) Optimization of SVM multiclass by particle swarm (PSO-SVM). I J Modern Education and Computer Science, p 32–38
Hsu, C.-W., Chang, C.-C., Lin, C.-J. (2003) A practical guide to support vector classification
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Subasi, A., Kevric, J. & Abdullah Canbaz, M. Epileptic seizure detection using hybrid machine learning methods. Neural Comput & Applic 31, 317–325 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-017-3003-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-017-3003-y