Abstract
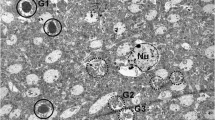
Adrenalectomy-evoked delayed degeneration and death of granule cells in the hippocampal dentate gyrus (DG) of the rat brain were studied by means of electron microscopy and a recently elaborated silver method that selectively stains the “dark”, collapsed neurons in a Golgi-like manner. At the light microscopic level, the silver technique revealed degenerating granule cells located exclusively in the dentate gyrus; other glucocorticoid receptor-containing regions of the brain were not affected. The silver-stained cell bodies were shrunken, most of the dendrites had a beaded appearance, and the stained axons could be traced along their route to the CA3 pyramidal neurons of the hippocampus. The analysis of 2.5 µm thick Epon-embedded sections stained with toluidine blue revealed hyperchromatic, dark granule neurons and their remains and a heavy glial activity in the vicinity of collapsing neuronal profiles. At the ultrastructural level, early and late stages of neuronal degeneration were observed. The early phase was characterized by markedly increased electron density, a massive shrinkage of the whole somato-dendritic domain, vacuolization of mitochondria, swelling of the nucleolus and condensation of the nuclear chromatin. In the late stage, subcellular organelles were hardly recognizable due to the extremely high electron density and dramatic shrinkage of the cytoplasm. These profiles exhibited disintegration of the cellular organelles and loss of their afferents. Concomitantly, disintegration of granule cell dendrites (clasmatodendrosis) and lifting of “dark” mossy fibers from cell bodies and dendrites of CA3 pyramidal neurons were observed. In the latter cells, this partial denervation caused no apparent signs of ultrastructural alterations. Proliferation of astrocytes and microglial cells was also obvious as they engulfed and eliminated the degenerating neuronal elements. Degenerating neurons frequently occurred adjacent neurons with normal morphology. These morphological features indicate that the delayed degeneration of hippocampal granule cells following adrenalectomy might proceed through a cytoskeletal collapse terminating in cell death.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aloe, L. (1989) Adrenalectomy decreases nerve growth factor in young rat hippocampus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 86, 5636–5640.
Andersen, P. (1975) Organization of hippocampal neurons and their interconnections. In: Issacson, R. L., Pribram, K. H. (eds): The Hippocampus. Plenum, New York, pp. 155–175.
Evans, R. M., Arizza, J. F. (1990) A molecular framework for the actions of glucocorticoid hormones in the central nervous system. Neuron 2, 1105–1112.
Finnie, J. W., O’Shea, J. D. (1988) Pathological and pathogenic changes in the central nervous system of guinea pigs given tunicamycin. Acta Neuropathol. 75, 411–421.
Fuxe, K., Wikström, A. C., Okret, S., Aganati, L. F., Härfstrand, F., Yu, Z. Y., Granholm, L., Zoli, M., Vale, W., Gustafsson, J. A. (1985) Mapping of the glucocorticoid receptor immunoreactive neurons in the tel- and diencephalon using monoclonal antibody against rat liver glucocorticoid receptors. Endrocrinology 117, 1803–1812
Fuxe, K., Cintra, A., Härfstrand, A., Aganati, L. F., Kalia, M., Zoli, M., Wikström, A.-S., Okret, S., Aronsson, M., Gusfafsson, J. A. (1987) Central glucocorticoid receptor immuno-reactive neurons: new insights into the endocrine regulation of the brain. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 512, 362–393.
Gallyas, F., Wolff, J. R., Böttcher, H., Záborszky, L. (1980) A reliable and sensitive method to localize terminal degeneration and lysosomes in the central nervous tissue. Stain Technol. 55, 299–306.
Gallyas, F., Guldner, F. H., Zoltay, G., Wolff, J. R. (1990) Golgi-like demonstration of dark neurons with an argyrophil III method for experimental neuropathology. Acta Neuropathol. 79, 620–628.
Gallyas, F., Zoltay, G., Dames, W. (1992) Formation of “dark” argyrophilic neurons of various origin proceeds with a common mechanism of biophysical nature (a novel hypothesis). Acta Neuropathol. 83, 386–393.
Garcia, J. H., Kalimo, H., Kamygo, Y. (1977) Cellular events during partial cerebral ischemia. Electron microscopy of feline cerebral cortex after middle cerebral artery occlusion. Virchows Arch. B. 25, 191–206.
Gould, E., Woolley, C. S., McEwen, B. S. (1990) Short-term glucocorticoid manipulations affect neuronal morphology and survival in the adult dentate gyrus. Neuroscience 37, 367–375.
Hall, E., McCall, H., Chase, R., Yonkers, P., Braughler, M. A. (1987) Nonglucocorticoid steroid analog of methyl-prednisolone duplicates its high-dose pharmacology in models of central nervous system trauma and neuronal membrane damage. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 242, 137–142.
Jaarsma, D., Postema, F., Korf, J. (1992) Time course and distribution of neuronal degeneration in the dentate gyrus of rat after adrenalectomy: A silver impregnation study. Hippocampus 2, 143–150.
Jenkins, L. W., Povliscock, J. T., Lewelt, W., Miller, J. D., Becker, P. D. (1981) The role of postischemic recirculation in the development of ischemic neuronal injury following complete cerebral ischemia. Acta Neuropathol. 55, 205–220.
Kalimo, H., Auer, R. N., Siesjö, B. K. (1985) The temporal evolution of hypoglycemic brain damage III. Light and electron microscopic findings in the rat caudoputamen. Acta Neuropathol. 67, 37–50.
McEwen, B. S., Weiss, J. M., Schwartz, L. S. (1968) Selective retention of corticosterone by limbic structure in the rat brain. Nature 220, 911–912.
McEwen, B. S., De Kloet, E. R., Rostene, W. (1986) Adrenal steroid receptors and action in the nervous system. Physiol. Rev. 66, 1121–1188.
McEwen, B. S., Gould, E. (1990) Adrenal steroids influences on the survival of hippocampal neurons. Biochem. Pharmacol. 40, 2393–2402.
McNeill, T. H., Masters, J. N., Fich, C. B. (1991) Effect of chronic adrenalectomy on neuron loss and distribution of sulfated glycoprotein-2 in the dentate gyrus of prepubertal rats. Exp. Neurol. 111, 140–144.
Mihály, A., Joó, F., Szente, M. (1983) Neuropathological alterations in the neocortex of rats subjected to focal aminopyridine seizures. Acta Neuropathol. 61, 85–94.
Laatsch, R. H., Cowan, W. M. (1966) Electron microscopic studies of the dentate gyrus of the rat. I. Normal structure with special reference to synaptic organization. J. Comp. Neurol. 128, 359–396.
Lin, C.-S., Polsky, K., Nadler, J. V., Crain, B. J. (1990) Selective neocortical and thalamic death in the gerbil after transient ischemia. Neuroscience 35, 289–299.
Liposits, Zs., Sherman, D., Phelix, C., Paull, W. K. (1986) A combined light and electron microscopic immunocytochemical method for the simultaneous localization of multiple tissue antigens. Histochemistry 85, 95–106.
Liposits, Zs., Uht, R. M., Harrison, R. W., Gibbs, F. P., Paull, W. K., Bohn, M. C. (1987) Ultrastructural localization of glucocorticoid receptor (GR) in hypothalamic paraventricular neurons synthesizing corticotorpin releasing factor (CRF). Histochemistry 87, 407–412.
Pittman, R., Oppenheim, R. W. (1979) Cell death of motoneurons in the chick embryo spinal cord. IV. Evidence that a functional neuromuscular interaction is involved in the regulation of naturally occurring cell death and the stabilization of synapses. J. Comp. Neurol. 187, 425–446.
Reul, J. M. H., De Kloet, E. R. (1985) Two receptor systems for glucocorticoids in the rat brain: microdistribution and differential occupation. Endocrinology 117, 2505–2511.
Richter, C. P. (1941) Sodium chloride and dextrose appetite of untreated and treated adrenalectomized rats. Endocrinology 29, 115–125.
Sapolsky, R., Puslinelli, W. (1985) Glucocorticoids potentiate ischemic injury to therapeutic implications. Science 229, 1397–1399.
Sapolsky, R. M., Krey, L. C., McEwen, B. S. (1985) Prolonged glucocorticoid exposure reduces neuron number: implications for aging. J. Neurosci. 5, 1222–1227.
Sapolsky, R., M., Meaney, M. J. (1986) Maturation of the adrenocortical stress response: neuroendocrine control mechanisms and the stress responsive period. Brain Res. Rev. 11, 65–76.
Sapolsky, R. M., Krey, L. C., McEwen, B. S. (1986) The neuroendocrinology of stress and aging: the glucocorticoid cascade hypothesis. Endocr. Rev. 7, 284–301.
Sloviter, R. S., Valiquette, O. G., Abrams, G. M., Ronk, E. C., Sollas, A. I., Paul, L. A., Neubort, S. L. (1989) Selective loss of hippocampal granule cells in the mature rat brain after adrenalectomy. Science 243, 535–538.
Sloviter, R. S., Sollas, A. L., Dean, E., Neubort, S. (1993) Adrenalectomy induced granule cell degeneration in the rat hippocampal dentate gyrus: characterization of an in vivo model of controlled neuronal death. J. Comp. Neurol. 330, 324–336.
Sloviter, R. S., Dean, E., Neubort, S. (1993) Electron microscopic analysis of adrenalectomy-induced hippocampal granule cell degeneration in the rat: apoptosis in the adult central nervous system. J. Comp. Neurol. 33, 337–351.
Söderfeldt, B., Kalimo, H., Olsson, Y., Siesjo, B. K. (1981) Pathogenesis of brain lesion caused by experimental epilepsy. Light and electron microscopic changes in the rat cortex following bicucculine-induced status epilepticus. Acta Neuropathol. 54, 219–231.
Van Eekelen, J. A. M., Jiang, W., De Kloet, E. R., Bohn, M. C. (1988) Distribution of mineralocorticoid and the glucocorticoid receptor mRNAs in the rat hippocampus. J. Neurosci. Res. 21, 88–94.
Vicedomini, J. P., Nonneman, A. J., De Kosky, S. T., Scheff, S. W. (1985) Perinatal glucocorticoids alter dentate gyrus electrophysiology. Brain. Res. Bull. 15, 111–116.
Vicedomini, J. P., Nonnenman, A. J., De Kosky, S. T., Scheff, S. W. (1986) Perinatal glucocorticoids disrupt learning: a sexual dimorphic response. Physiol. Behav. 36, 145–149.
Woolley, C. S., Gould, E., Sakai, R. R., Spencer, R. L., McEwen, B. S. (1991) Effects of aldosterone or RU28362 treatment on adrenalectomy-induced cell death in the dentate gyrus of the adult rat. Brain Res. 554, 312–315.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liposits, Z., Kalló, I., Hrabovszky, E. et al. Ultrastructural Pathology of Degenerating “Dark” Granule Cells in the Hippocampal Dentate Gyrus of Adrenalectomized Rats. BIOLOGIA FUTURA 48, 173–187 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03543188
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03543188