Abstract
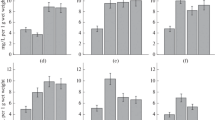
Cholinesterase activity was studied in 2 to 10-week-old pea plants cultivated under artificial illumination. Free and membrane-bound forms of the enzyme were separated by extracting the enzyme from pea shoots with buffers differing in ionic strength. The ratio of the free cholinesterase to the membrane-bound one fluctuated between 1 : 1 and 1 : 2.5. The free cholinesterase was inhibited by neostigmine (0.1mmoll-1) by 50%, the membrane-bound enzyme by 90%. The pH optimum of cholinesterase activity was 8.5, the temperature optimum 37 °C. The enzyme activity was increased by some cations in this order: Mg2+ < < K+. The Km value for the substrate S-acetylthiocholine iodide was 250 μmoll-1, the enzyme activity being inhibited by concentrations higher than 3 mmoll-1 of this substrate.
The activity of the membrane-bound enzyme was demonstrated in the roots, leaves, stems, fruits, seeds and carpels, but could not be reliably detected in the blossoms. The highest activity expressed per fresh matter was found in older leaves and in the fruits, the lowest in the roots and stems. Cholinesterase activity in plant parts markedly varied during the investigated growth period.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ellman, G. L., Countrey, K. D., Andres, V., Feartherstone, R. M.: A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. - Biochem. Pharmacol.7: 88–95, 1961.
Ernst, M., Hartmann, E.: Biochemical characterization of an acetylcholin-hydrolyzing enzyme from bean seedlings. -Plant Physiol.65: 447–450, 1980.
Fluck, R. A., Jaffe, M. J.: The acetylcholine system in plants. - Curr. Adv. Plant Sci.5: 1 to 22, 1974a.
Fluck, R. A., Jaffe, M. J.: Cholinesterases from plant tissues. III. Distribution and subcellular localization inPhaseolus aureus Roxb. - Plant Physiol.53: 752–758, 1974b.
Fluck, R. A., Jaffe, M. J.: The distribution of cholinesterases in plant species. - Phytochemistry13: 2475–2480, 1974c.
Gupta, R., Maheshwari, S. C.: Preliminary characterization of a cholinesterase from roots of Bengal gram -Cicer arietinum L. - Plant Cell Physiol.21 : 1675–1679, 1980.
Hadačová, V., Hofman, J., De Almeida, R. M., Vacková, K., Kutáček, M., Klozová, E.: Choline esterase and choline acetyltransferase in the seeds ofAllium altaicum (Pall). Reyse. - Biol. Plant.23: 220–227, 1981.
Hadačová, V., Vacková, K., Klozová, E., Kutáček, M., Pitterová, K.: Cholinesterase activity in some species of theAllium genus. - Biol. Plant.25 : 209–215, 1983.
Karnovsky, M. J., Roots, L. J.: A direct coloring “thiocholin” method for cholinesterases. - J. Histochem. Cytochem.12: 219–221, 1964.
Kasturi, R.:De novo synthesis of acetylcholinesterase in roots ofPisum sativum. - Phytochemistry17: 647–650, 1978.
Kasturi, R.: Influence of light, phytohormones and acetylcholine on thede novo synthesis of acetylcholinesterase in roots ofPisum sativum..- Ind. J. Biochem. Biophys.l6 : 14–17, 1979.
Kasturi, R., Vasantharajan, V. N.: Properties of acetylcholinesterase fromPisum sativum. - Phytochemistry15: 1345–1347, 1976.
Lees, G. L., Thompson, J. E.: The effects of germination on the subcellular distribution of cholinesterase in cotyledons ofPhaseolus vulgaris. - Physiol. Plant.34: 230–237, 1975.
Lowry, O. H., Rosebrough, N. J., Farr, A. L., Randall, R. J.: Protein measurement with Folin phenol reagent. - J. biol. Chem.193: 265–275, 1951.
Mansfield, D. H. G., Clark, D. G., Taylor, I. E. P.: Partial purification and some properties of a cholinesterase from bush bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) roots. - Biochem. J.175: 769 to 777, 1978.
Miura, G. A., Broomfield, C. A., Lawson, M. A., Worthley, E. G.: Widespread occurrence of cholinesteraae activity in plant leaves. - Physiol. Plant.56: 28–32, 1982.
Riov, J., Jaffe, M. J.: Cholinesterases from plant tissues. I. Purification and characterization of cholinesterase from mung bean roots. - Plant Physiol.51: 520–528, 1973.
Van der Meer, C.: Effect of calcium on choline esterase. - Nature171: 78–79, 1953.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vacková, K., Kutáček, M. & de Almeida, R.M. Some properties of pea cholinesterase and its activity in plant parts at different growth stages. Biol Plant 26, 275–284 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02902909
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02902909