Abstract
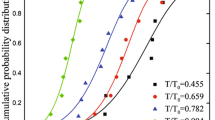
Low-cycle fatigue (LCF) behavior of a lead-free Sn-3.5Ag-0.5Cu solder alloy was investigated at various combinations of strain ratio (R = −1, 0, and 0.5) and tensile hold time (0, 10, and 100 sec). Results showed that the LCF life of the given solder, at each given combination of testing conditions, could be individually described by a Coffin-Manson relationship. An increase of strain ratio from R=−1 to 0 and to 0.5 would cause a significant reduction of LCF life due to a mean strain effect instead of mean stress effect. LCF life was also markedly reduced when the hold time at tensile peak strain was increased from 0 to 100 sec, as a result of additional creep damage generated during LCF loading. With consideration of the effects of strain ratio and tensile hold time, a unified LCF lifetime model was proposed and did an excellent job in describing the LCF lives for all given testing conditions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. McCormack and S. Jin,J. Electron. Mater. 23, 635 (1994).
M. Abtew and G. Selvaduray,Mater. Sci. Eng. R 27, 95 (2000).
D.P. Napp,SAMPE J. 32, 59 (1996).
W.J. Plumbridge,J. Mater. Sci. 31, 2501 (1996).
M. Ohring,Reliability and Failure of Electronic Material and Devices (San Diego: Academic Press, 1998), pp. 492–526.
J.H. Lau,Solder Joint Reliability: Theory and Applications (New York: Van Nostrand Reinhold, 1991).
Y. Kariya and M. Otsuka,J. Electron. Mater. 27, 866 (1998).
Y. Kariya and M. Otsuka,J. Electron. Mater. 27, 1229 (1998).
Y. Kariya, T. Morihata, E. Hazawa, and M. Otsuka,J. Electron. Mater. 30, 1184 (2001).
C. Kanchanomai, S. Yamamoto, Y. Miyashita, Y. Mutoh, and A.J. McEvily,Int. J. Fatigue 24, 57 (2002).
C. Kanchanomai, Y. Miyashita, and Y. Mutoh,J. Electron. Mater. 31, 142 (2002).
C. Kanchanomai, Y. Miyashita, Y. Mutoh, and S.L. Mannan,Mater. Sci. Eng. A 345, 90 (2003).
C. Kanchanomai and Y. Mutoh,Mater. Sci. Eng. A 381, 113 (2004).
C. Kanchanomai and Y. Mutoh,J. Electron. Mater. 33, 329 (2004).
M.R. Harrison, J.H. Vincent, and H.A.H. Steen,Soldering Surf. Mount Technol. 13, 21 (2001).
I.E. Anderson, B.A. Cook, J. Harringa, and R.L. Terpstra,J. Electron. Mater. 31, 1166 (2002).
C.-K. Lin and D.-Y. Chu,J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 16, 355 (2005).
C. Kanchanomai, Y. Miyashita, and Y. Mutoh,J. Electron. Mater. 31, 456 (2002).
J.H.L. Pang, B.S. Xiong, and T.H. Low,Thin Solid Films 462–463, 408 (2004).
K.J. Lau, C.Y. Tang, P.C. Tse, C.L. Chow, S.P. Ng, C.P. Tsui, and B. Rao,Int. J. Fract. 130, 617 (2004).
C. Anderson, Z. Lai, J. Liu, H. Jiang, and Y. Yu,Mater. Sci. Eng. A 394, 20 (2005).
P.-L. Wu, M.-K. Huang, C. Lee, and S.-R. Tzan,Mater. Chem. Phys. 87, 285 (2004).
X. Deng, R.S. Sidhu, P. Johnson, and N. Chawla,Metall. Mater. Trans. A 36A, 55 (2005).
W.W. Lee, L.T. Nguyen, and G.S. Selvaduray,Microelectron. Reliab. 40, 231 (2000).
M.E. Loomans and M.E. Fine,Metall. Mater. Trans. A 31A, 1155 (2000).
K.W. Moon, W.J. Boettinger, U.R. Kattner, F.S. Biancaniello, and C.A. Handwerker,J. Electron. Mater. 29, 1122 (2000).
S.L. Mannan,Bull. Mater. Sci. 16, 561 (1993).
R.E. Read-Hill and R. Abbaschian,Physical Metallurgy Principles, 3rd ed. (Boston: PWS Publishing Company, 1994), pp. 294–298.
L.F. Coffin, Jr.,Trans. ASME 76, 931 (1954).
S.S. Manson,Heat Transfer Symposium (Ann Arbor: University of Michigan Engineering Research Institute, 1953), pp. 9–75.
W. Schutz,Fatigue Life Prediction for Aircraft Structure and Materials, NATO AGARD-LS-62 (Geneva: NATO, 1973), pp. 10-1–10-32.
C.-K. Lin and Y.-L. Pai,Int. J. Fatigue 21, 45 (1999).
J.A. Collins,Failure of Materials in Mechanical Design: Analysis, Prediction, Prevention, 2nd ed. (New York: John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 1993), pp. 401–404.
J.K. Tien, S.V. Nair, and V.C. Nardone,Flow and Fracture at Elevated Temperatures, ed. R. Raj (Philadelphia: Carnes Publication Services, 1983), pp. 179–213.
C. Gandhi,Flow and Fracture at Elevated Temperatures, ed. R. Raj (Philadelphia: Carnes Publication Services, 1983), pp. 83–119.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, CK., Huang, CM. Effects of strain ratio and tensile hold time on low-cycle fatigue of lead-free Sn-3.5Ag-0.5Cu solder. J. Electron. Mater. 35, 292–301 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02692449
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02692449