Abstract
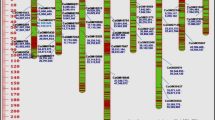
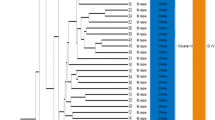
Nuclear RFLPs were used to study the genetic relationships of 2 Portuguese coles, tronchuda cabbage and Galega kale, and 13 otherBrassica oleracea cultivars and 4 nine-chromosome wild brassicas. Cluster and principal coordinates analysis were conducted using RFLP data from 60 probe-enzyme combinations, detecting 277 polymorphic restriction fragments. The results showed that the accessions clustered in five groups: one with all theB. oleracea cultivars except kailan, and the four others isolated with kailan, wildB. oleracea, B. insularis andB. cretica, andB. montana, respectively. Kailan was separated from the other accessions ofB. oleracea cultivars and genetically close to the wildB. oleracea, that was clearly separated from the other nine-chromosome wild brassicas. In theB. oleracea cultivars 3 groupings were clearly individualized: i) including broccolis and cauliflower; ii) with a misture of kales and cabbages originally from Central-North Europe; iii) formed by Portuguese coles. These preliminary results suggest the existence of three major regions of domestication of B. oleracea in Europe: Italy, Central-North Europe and Portugal. Kailan or chinese kale seems to have evolved separately from the otherB. oleracea cultivars in Eastern Asia.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Crisp, P., 1983. The use of an evolutionary scheme for cauliflowers in the screening of genetic resources. Euphytica 31: 725–734.
Crouch, M.L., K.M. Tenbarge, A.E. Simon & R. Ferl, 1983. cDNA clones forBrassica napus seed storage proteins: evidence from nucleotide sequence analysis that both subunits of napin are cleaved from a precursor polypeptide. J. Mol. Appl. Genet. 2: 273–283.
Dias, J.S., M.B. Lima, K.M. Song, A.A. Monteiro, P.H. Williams & T.C. Osborn, 1992. Molecular taxonomy of Portuguese tronchuda cabbage and kale landraces using nuclear RFLPs. Euphytica 58: 221–229.
Dias, J.S., A.A. Monteiro & S. Kresovich, 1994. Genetic diversity and taxonomy of Portuguese Tronchuda cabbage and Galega kale landraces using isozyme analysis. Euphytica 75: 221–230.
Gower, J.C., 1966. Some distance properties of latent root and vector methods used in multivariate analysis. Biometrika 27: 325–338.
Gray, A.R., 1982. Taxonomy and evolution of broccoli (Brassica oleracea var.italica). Econ. Bot. 36: 397–410.
Helm, J., 1963. Morphologisch-taxonomische Gliederung der Kultursippen vonBrassica oleracea L.. Die Kulturpflanze 11: 92–210.
Osborn, T.C., D.C. Alexander & J.F. Fobes, 1987. Identification of restriction fragment length polymorphisms linked to genes controlling soluble solids content in tomato fruit. Theor. Appl. Genet. 73: 350–356.
Rohlf, F.J., 1989. NTSYS-pc. Numerical taxonomy and multivariate analysis system, version 1.5. Exeter Publishing, Ltd., Setauket, New York.
Simon, A.E., K.M. Tenbarge, S.R. Scofield, R.R. Finkelstein & M.L. Crouch, 1985. Nucleotide sequence of a cDNA clone of Brassica napus 12S storage protein shows homology with legumin fromPisum sativum. Plant Mol. Biol. 5: 191–201.
Slocum, M.K., S.S. Figdore, W.C. Kennard, J.Y. Suzuki & T.C. Osborn, 1990. Linkage arrangement of restriction fragment length polymorphism loci inBrassica oleracea. Theor. Appl. Genet. 80: 57–64.
Sneath, P.H.A. & R.R. Sokal, 1973. Numerical taxonomy. The principles and practice of numerical classification. W.F. Freeman, San Francisco, 573p.
Song, K.M., T.C. Osborn & P.H. Williams, 1988.Brassica taxonomy based on nuclear restriction fragment length polymorphisms (RFLPs) 2. Preliminary analysis of subspecies within B. rapa (syn.campestris) andB. oleracea. Theor. Appl. Genet. 76: 593–600.
Song, K.M., T.C. Osborn & P.H. Williams, 1990.Brassica taxonomy based on nuclear restriction fragment length polymorphisms (RFLPs) 3. Genome relationships inBrassica and related genera and the origin ofB. oleracea andB. rapa (syn.campestris). Theor. Appl. Genet. 79: 497–506.
Song, K.M., J.Y., Suzuki, M.K. Slocum, P.H. Williams & T.C. Osborn, 1991. A linkage map ofBrassica rapa (syn.campestris) based on restriction fragment length polymorphism loci. Theor. Appl. Genet. 82: 296–304.
Williams, P.H. & C.B. Hill, 1986. Rapid-cycling populations ofBrassica. Science 232: 1385–1389.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dias, J.S. Genetic relationships of Portuguese coles and other close relatedBrassica genotypes using nuclear RFLPs. Genet Resour Crop Evol 42, 363–369 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02432140
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02432140