Abstract
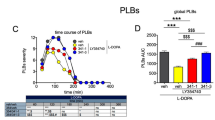
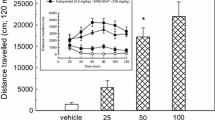
In rats with unilateral 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA) lesions of the medial forebrain bundle, pretreatment with the D1 DA antagonists, SCH 23390 (7-chloro-8-hydroxy-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-3-methyl-1-phenyl-1H-3-benzazepine) and A66359 (1-[2-bromo-4, 5-dimethoxybenzyl]-7-hydroxy-6-methoxy-2-methyl-1,2,3,4 tetrahydroisoquinoline), but not the D2 DA antagonist raclopride inhibited the contralateral circling induced by the benzazepine D1 DA agonists SKF 38393 (7-H, 3-H analogue of SCH 23390), SKF 80723 (7-H, 3-H, 6-Br analogue) and SKF 83959 (7-H, 6-Cl, 3′-CH3 analogue). In MPTP (1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine) treated common marmosets, administration of SKF 80723 and SKF 83959 increased locomotor activity and reversed the motor disability. Grooming and oral activities were also increased. Pretreatment with SCH 23390 and A66359 inhibited all the behavioural changes induced by both D1 DA agonists. In general, higher doses of A66359 and more especially SCH 23390 were needed to inhibit SKF 83959 and SKF 80723 induced increases in oral activity and grooming than locomotor activity. Raclopride pretreatment did not affect SKF 83959 and SKF 80723 induced oral activity and grooming, though it reduced the duration of the locomotor changes induced by the D1 DA agonists. These findings demonstrate that the behavioural effects of benzazepine D1 DA agonists in the 6-OHDA lesioned rat and MPTP-treated marmoset are mediated by D1 DA receptor sites, although in the primate, stimulation of D2 DA receptors by endogenous DA may be necessary in facilitating the antiparkinsonian effects of D1 DA agonists. The differential sensitivities of locomotor/motor disability and oral/grooming behaviours to antagonism by D1 DA antagonists may indicate the involvement of multiple D1 DA receptor subtypes in mediating benzazepine D1 DA agonist induced behaviours in the MPTP-treated marmoset.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnt J (1985a) Behavioural stimulation is induced by separate dopamine D1 and D2 receptors in reserpine-pretreated but not in normal rats. Eur J Pharmacol 113:79–88
Arnt J (1985b) Hyperactivity induced by stimulation of separate dopamine D1 and D2 receptors in rats with bilateral 6-OHDA lesions. Life Sci 37:717–723
Arnt J, Hyttel J (1984) Differential inhibition by dopamine D1 and D2 antagonists of circling behaviour induced by dopamine agonists in rats with unilateral 6-hydroxydopamine lesions. Eur J Pharmacol 102:349–354
Arnt J, Hyttel J, Sanchez C (1992) Partial and full dopamine D1 receptor agonists in mice and rats: relation between behavioural effects and stimulation of adenylate cyclase activity in vitro. Eur J Pharmacol 213:259–267
Battaglia G, Norman AB, Hess EJ, Creese I (1986) Functional recovery of D1 dopamine receptor mediated stimulation of rat striatal adenylate cyclase activity following irreversible modification byN-ethoxycarbonyl-2-ethoxy-1,2-dihydroquinoline (EEDQ): evidence for spare receptors. Neurosci Lett 69:290–295
Bedard PJ, Boucher R (1989) Effect of D1 receptor stimulation in normal and MPTP monkeys. Neurosci Lett 104:223–228
Boyce S, Rupniak NMJ, Steventon MJ, Iversen SD (1990) Differential effects of D1 and D2 agonists in MPTP-treated primates: functional implications for Parkinson's disease. Neurology 40:927–933
Breese GR, Mueller RA (1985) SCH 23390 antagonism of a D2 dopamine agonist depends upon catecholaminergic neurones. Eur J Pharmacol 113:109–114
Burns RS, Chiueh CC, Parisi J, Markey SP, Ebert MH, Jacobowitz DM and Kopin IJ (1983) A primate model of parkinsonism: selective destruction of dopaminergic neurones in the pars compacta of the substantia nigra byN-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 80:4546–4550
Clark D, White FJ (1987) Review: D1 dopamine receptor — the search for a function: a critical evaluation of the D1/D2 dopamine receptor classification and its functional implications. Synapse 1:347–388
Close SP, Marriott AS, Pay S (1985) Failure of SKF 38393-A to relieve parkinsonian symptoms induced by 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine in the marmoset. Br J Pharmacol 85:320–322
Close SP, Elliott PJ, Hayes AG, Marriott AS (1990) Effects of classical and novel agents in a MPTP-induced reversible model of Parkinson's disease. Psychopharmacology 102:295–300
Collins P, Broekkamp CLE, Jenner P, Marsden CD (1991) Drugs acting at D1 and D2 dopamine receptors induce identical purposeless chewing in rats which can be differentiated by cholinergic manipulation. Psychopharmacology 103:503–512
Daly SA, Waddington JL (1992a) Two directions of dopamine D1/D2 receptor interaction in studies of behavioural regulation: a finding generic to four new, selective dopamine D1 receptor antagonists. Eur J Pharmacol 213:251–258
Daly SA, Waddington JL (1992b) D-1 dopamine receptors and the topography of unconditioned motor behaviour: studies with the selective, “full efficacy” benzazepine D1 agonist SKF 83189. J Psychopharmacol 6:50–60
Daly SA, Waddington JL (1993) Behavioural responses to the new, full efficacy isochroman selective D1 agonist A68930: differential sensitivity to the new isoquinoline selective D1 antagonist BW 737C in comparison with the benzazepines SCH 23390 and NNC-756? Psychopharmacology 113:45–50
Downes RP, Waddington JL (1993) Grooming and vacuous chewing induced by SKF 83959 and agonist of dopamine “D1 like” receptors that inhibits dopamine sensitive adenylyl cyclase. Eur J Pharmacol 234:135–136
Elliott PJ, Walsh DM, Close SP (1992) Dopamine D1 and D2 receptor interactions in the MPTP-treated marmoset. Neurosci Lett 142:1–4
Falardeau P, Bedard PJ, DiPaolo T (1988) Relation between brain dopamine loss and D2 dopamine receptor density in MPTP monkeys. Neurosci Lett 86:225–229
Gnanalingham KK, Erol DD, Hunter AJ, Smith LA, Jenner P, Marsden CD (1994a) The differential antiparkinsonian effects of benzazepine D1 dopamine agonists with varying efficacies in the MPTP-treated common marmoset. Psychopharmacology (in press)
Gnanalingham KK, Hunter AJ, Jenner P, Marsden CD (1994b) The differential behavioural effects of benzazepine D-1 dopamine agonists with varying efficacies, co-administered with quinpirole in primate and rodent models of Parkinson's disease. Psychopharmacology (in press)
Gomez-Mancilla B, Bedard PJ (1991) Effect of D1 and D2 agonists and antagonists on dyskinesia produced byl-dopa in 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine-treated monkeys. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 259:409–413
Gower AJ, Marriott AS (1982) Pharmacological evidence for the subclassification of central dopamine receptors in the rat. Br J Pharmacol 77:185–194
Itoh Y, Beaulieu M, Kebabian JW (1984) The chemical basis for the blockade of the D1 dopamine receptor by SCH 23390. Eur J Pharmacol 100:119–122
Izenwasser S, Katz JL (1993) Differential efficacies of dopamine D1 receptor agonists for stimulating adenylyl cyclase in squirrel monkey and rat. Eur J Pharmacol [Mol Pharmacol] 246:39–44
Kebabian JW, Calne DB (1979) Multiple receptors for dopamine. Nature 277:93–96
Kebabian JW, Britton DR, DeNinno MP, Perner R, Smith L, Jenner P, Schoenleber R, Williams M (1992) A77636: a potent and selective dopamine D1 receptor agonist with antiparkinsonian activity in marmosets. Eur J Pharmacol 229:203–209
Kerkman DJ, Ackerman M, Artman LD, MacKenzie RG, Johnson MC, Bednarz L, Montana W, Asin KE, Stampfli H, Kebabian JW (1989) A-69024: a non-benzazepine antagonist with selectivity for the dopamine D-1 receptor. Eur J Pharmacol 166:481–491
Levy AD, See RE, Levin ED, Ellison GD (1987) Neuroleptic induced oral movements in rats: methodological issues. Life Sci 41:1499–1506
Loschmann PA, Smith LA, Lange KW, Jaehnig P, Jenner, P, Marsden CD (1991) Motor activity following the administration of selective D-1 and D-2 dopaminergic drugs to normal common marmosets. Psychopharmacology 105:303–309
Loschmann PA, Smith LA, Lange KW, Jaehnig P, Jenner P, Marsden CD (1992) Motor activity following the administration of selective D-1 and D-2 dopaminergic drugs to MPTP-treated common marmosets. Psychopharmacology 109:49–56
Madras BK, Fahey MA, Canfield DR, Spealman RD (1988) D1 and D2 dopamine receptors in caudate-putamen of non-human primates (Macaca fascicularis). J Neurochem 51:934–943
Molloy AG, Waddington JL (1984) Dopaminergic behaviour stereospecifically promoted by the D-1 agonist R-SK&F 38393 and selectively blocked by the D-1 antagonist SCH 23390. Psychopharmacology 82:409–410
Molloy AG, O'Boyle KM, Pugh MT, Waddington JL (1986) Locomotor behaviours in response to new selective D-1 and D-2 dopamine receptor agonists and the influence of selective antagonists. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 25:249–253
Murray AM, Waddington JL (1989) The induction of grooming and vacuous chewing by a series of selective D-1 dopamine agonists: two directions of D-1:D-2 interaction. Eur J Pharmacol 160:377–384
Murray AM, Waddington JL (1990) New putative selective agonists at the D-1 dopamine receptor: behavioural and neurochemical comparison of CY 208–243 with SK&F 101384 and SK&F 103243. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 35:105–110
Nomoto M, Jenner P, Marsden CD (1985) The dopamine D-2 agonist LY 141865, but not the D-1 agonist SKF 38393 reverses parkinsonism induced by 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetraphy-dropyridine (MPTP) in the common marmoset. Neurosci Lett 57:37–41
O'Boyle KM, Gaitanopoulos DE, Brenner M, Waddington JL (1989) Agonist and antagonist properties of benzazepine and thienopyridine derivatives at the D1 dopamine receptor. Neuropharmacol 28:401–405
Pellegrino LJ, Pellegrino AS, Cushman AJ (1979) A stereotaxic atlas of the rat brain. Plenum Press, New York and London
Pifl C, Reither H, Hornykiewicz O (1991) Lower efficacy of the dopamine D-1 agonist, SKF 38393, to stimulate adenylyl cyclase activity in primate than in rodent striatum. Eur J Pharmacol 202:273–276
Rose S, Nomoto M, Kelly K, Kilpatrick G, Jenner P, Marsden CD (1989a) Increased caudate dopamine turnover may contribute to the recovery of motor function in marmosets treated with the dopaminergic neurotoxin MPTP. Neurosci Lett 101:305–310
Rose S, Nomoto M, Jenner P, Marsden CD (1989b) Transient depletion of nucleus accumbens dopamine content may contribute to initial akinesia induced by MPTP in common marmosets. Biochem Pharmacol 38:3677–3681
Rosengarten H, Schweitzer JW, Friedhoff AJ (1983) Induction of oral dyskinesias in naive rats by D1 stimulation. Life Sci 33:2479–2482
Rosengarten H, Schweitzer JW, Friedhoff AJ (1986) Selective dopamine D2 receptor reduction enhances a D1 mediated oral dyskinesia in rats. Life Sci 39:29–35
Rupniak NMJ, Tye SJ, Iversen SD (1990) Drug-induced purposeless chewing: animal model of dyskinesia or nausea? Psychopharmacology 102:325–328
Rupniak NMJ, Boyce S, Steventon M, Iversen SD (1992) Weak antiparkinsonian activity of the D1 agonist C-APB (SKF 82958) and lack of synergism with a D2 agonist in primates. Clin Neuropharmacol 15:307–309
Setler PE, Sarau HM, Zirkle CL, Saunders HL (1978) The central effects of a novel dopamine agonist. Eur J Pharmacol 50:419–430
Sibley DR, Monsma FJ (1992) Molecular biology of dopamine receptors. Trends Pharmacol Sci 13:61–69
Stoof JC, Kebabian JW (1981) Opposing roles for D-1 and D-2 dopamine receptors in efflux of cyclic AMP from rat neostriatum. Nature 294:366–368
Sunahara RK, Guan H-C, O'Dowd BF, Seeman P, Laurier LG, Ng G, George SR, Torchia J, Van Tol HHM, Niznik HB (1991) Cloning of the gene for a human dopamine D-5 receptor with high affinity for dopamine than D-1. Nature 350:614–619
Taylor JR, Lawrence MS, Redmond DE, Elsworth JD, Roth RH, Nichols DE, Mailman RB (1991) Dihydrexidine, a full dopamine D-1 agonist, reduces MPTP-induced parkinsonism in monkeys. Eur J Pharmacol 199:389–391
Temlett JA, Chong PN, Oertel WH, Jenner P, Marsden CD (1988) The D-1 dopamine receptor partial agonist, CY 208–243, exhibits antiparkinsonian activity in the MPTP-treated marmoset. Eur J Pharmacol 156:197–206
Wachtel SR, Brooderson RJ, White FJ (1992) Parametric and pharmacological analyses of the enhanced grooming response elicited by the D1 dopamine receptor agonist SKF 38393 in the rat. Psychopharmacology 109:41–48
Watts VJ, Lawler CP, Gilmore JH, Southerland SB, Nichols DE, Mailman RB (1993) Dopamine D1 receptors: efficacy of full (dihydrexidine) vs. partial (SKF 38393) agonists in primates vs. rodents. Eur J Pharmacol 24:165–172
Weinstock J, Hieble JP, Wilson JW (1985) The chemistry and pharmacology of 3-benzazepine derivatives. Drugs Future 10:645–696
Weinstock J, Ladd DL, Wilson JW, Brush CK, Yim NCF, Gallagher G, McCarthy ME, Silvestri J, Sarau HM, Flaim KE, Ackerman DM, Setler PE, Tobia AJ, Hahn RA (1986) Synthesis and renal vasodilator activity of some dopamine agonist 1-aryl-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-1H-3-benzazepine-7,8-diols: halogen and methyl analogues of fenoldopam. J Med Chem 29:2315–2325
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gnanalingham, K.K., Jenner, P., Jackie Hunter, A. et al. Selective dopamine antagonist pretreatment on the antiparkinsonian effects of benzazepine D1 dopamine agonists in rodent and primate models of parkinson's disease — the differential effects of D1 dopamine antagonists in the primate. Psychopharmacology 117, 403–412 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02246211
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02246211