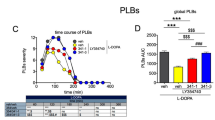
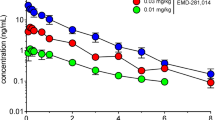
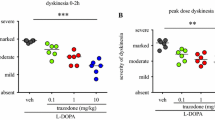
Abstract
A modified primate model of Parkinson's disease was developed to assess the effectiveness of various agents that act via dopamine, acetylcholine, serotonin or glutamate systems. Using a MPTP dosing regimen a reversible parkinsonian-like syndrome was produced in the marmoset. An obvious advantage of such a protocol is that it allows multiple drug studies to be undertaken in animals, without the need for prolonged anti-parkinsonian therapy to maintain their health. Results show that dopamine D2 agonists (bromocriptine, quinpirole, N,N-dipropyl,A,5,6-DTN, (+)3PPP and PHNO), anti-muscarinics (atropine, scopolamine and benztropine), in addition tol-DOPA and nomifensine, all reduced the bradykinesia induced by MPTP. The D1 agonist SKF-38393 and the partial dopamine agonist (−)3PPP were both ineffective. Finally, agents with potential therapeutic use in Parkinson's disease were also tested. However, a glutamate antagonist (MK801) and three serotonin antagonists (ritanserin, ketanserin and ICI 170,809) were all unable to alter the MPTP effects, at the doses used in our study.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen JM, Cross AJ, Yeats JC, Ghatei MA, McGregor GP, Close SP, Pay S, Marriott AS, Tyers MB, Crow TJ, Bloom SR (1986) Neuropeptides and dopamine in the marmoset. Effect of treatment with 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP): an animal model for Parkinson's disease? Brain 109:143–157
Ballard PA, Tetrud JW, Langston JW (1985) Permanent human parkinsonism due to 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP): seven cases. Neurology 35:949–956
Barone P, Bankiewicz KS, Corsini GU, Kopin IJ, Chase TN (1987) Dopaminergic mechanisms in hemiparkinsonian monkeys. Neurology 37:1592–1595
Bedard PJ, Di Paolo T, Falardeau P, Boucher R (1986) Chronic treatment with levodopa, but not bromocriptine induces dyskinesia in MPTP-parkinsonian monkeys. Correlation with 3H-spiperone binding. Brain Res 379:294–299
Braun A, Fabbrini G, Mouradian MM, Serrati C, Barone P, Chase TN (1986) Selective D-1 dopamine receptor agonist treatment of Parkinson's disease. J Neural Transm 68:41–50
Burns RS, Chiueh CC, Markey SP, Ebert MH, Jacobowitz DM, Kopin IJ (1983) A primate model of parkinsonism: selective destruction of dopaminergic neurons in the pars compacta of the substantia nigra by N-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 80:4546–4550
Clarke CE, Boyce S, Sambrook MA, Stahl SM, Crossman AR (1988) Behavioural effects of (+)-4-propyl-9-hydroxynaphthoxazine in primates rendered parkinsonian with 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine. Naunyn-Schmiedberg's Arch Pharmacol 338:35–38
Close SP, Elliott PE (1990) Haloperidol-induced gradykinesia in the marmoset. Br J Pharmacol 99:262
Close SP, Marriott AS, Pay S (1985) Failure of SKF 38393-A to relieve parkinsonian symptoms induced by 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine in the marmoset. Br J Pharmacol 85:320–322
Cohen G, Pasik P, Cohen B, Leist A, Mytilineou C, Yahr MD (1984) Pargyline and deprenyl prevent the neurotoxicity of 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) in monkeys. Eur J Pharmacol 106:209–210
Conrad LCA, Leonard CM, Pfaff DW (1974) Connections of the median and dorsal raphe nuclei in the rat: an autoradiographic and degeneration study. J Comp Neurol 156:179–206
Davis GC, Williams AC, Markey SP, Ebert MH, Caine ED, Reichert CM, Kopin IJ (1979) Chronic parkinsonism secondary to intravenous injection of meperidine analogues. Psychiatry Res 1:249–254
De Smet Y, Ruberg M, Serdaru M, Dubois B, Lhermitte F, Agid Y (1982) Confusion, dementia and anticholinergics in Parkinson's disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 45:1161–1164
Deutch AY, Elsworth JD, Goldstein M, Fuxe K, Redmond DE, Sladeck JR, Roth RH (1986) Preferential vulnerability of A8 dopamine neurons in the primate to the neurotoxin 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetra hydropyridine. Neurosci Lett 68:51–56
Elliott PJ, Close SP, Walsh DM, Hayes AG, Marriott AS (1990) Use of neuroleptic-induced catalepsy in the rat as a model of Parkinson's disease. II Reversal by glutamate antagonists. J Neural Transm (in press)
Grandas F, Quinn N, Critchley P, Rohan A, Marsden CD, Stahl SM (1987) Antiparkinsonian activity of a single oral dose of PHNO. Mov Disord 2:47–51
Hjorth S, Clark D, Svensson K, Carlsson A, Wikstrom H, Sanchez D, Lindberg P, Hacksell U, Arvidsson Le, Johansson A, Nilsson JLG (1984) Central dopamine receptor agonist and antagonist actions of the enantiomers of 3-PPP. Psychopharmacology 81:89–99
Horstink MWIM (1984) Problems of levodopa treatment. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 86:196–206
Jacobs BL, Foote SL, Bloom FE (1978) Differential projections of neurons within the dorsal raphe nucleus of the rat: a horseradish peroxidase (HRP) study. Brain Res 147:149–153
Jenner P, Rupniak NMJ, Rose S, Kelly E, Kilpatrick G, Lees A, Marsden CD (1984) 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine-induced parkinsonism in the common marmoset. Neurosci Lett 50:85–90
Jenner P, Marsden CD, Nomoto M, Stahl S (1986) Antiparkinsonian activity of (+)-PHNO in the MPTP-treated marmoset following subcutaneous infusion or skin application. Br J Pharmacol 89:626
Kulik AV, Wilbur R (1982) Delirium and stereotypy from anticholinergic anti-parkinsonian drugs. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol 6:75–82
Langston JW, Irwin I, Langston EB (1984a) Pargyline prevents MPTP-induced parkinsonism in primates. Science 225:1480–1482
Langston JW, Forno LS, Rebert CS, Irwin I (1984b) Selective nigral toxicity after administration of 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydro pyridine (MPTP) in the squirrel monkey. Brain Res 292:390–394
Lieberman A, Chin L, Baumann G (1988) MK 458, a selective and potent D2 receptor agonist in advanced Parkinson's disease. Clin Neuropharmacol 11:191–200
Maertens de Noordhout A, Delwaide PJ (1986) Open pilot trial of ritanserin in parkinsonism. Clin Neuropharmacol 9:480–484
Mulder AH, Stoof JC, Horn AS (1980) Activation of presynaptic alpha-noradrenaline receptors in rat brain by the potent dopamine-mimetic N,N-dipropyl-5,6-ADTN. Eur J Pharmacol 67:147–150
Nomoto N, Jenner P, Marsden CD (1985) The dopamine D2 agonist LY141865, but not the D1 agonist SKF 38393 reverses parkinsonism induced by 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,36-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) in the common marmoset. Neurosci Lett 57:37–41
Nomoto M, Jenner P, Marsden CD (1986) Alterations in motor behaviour produced by isomers of 3-PPP in the MPTP-treated marmoset. Eur J Pharmacol 21:123–128
Nomoto M, Stahl S, Jenner P, Marsden CD (1987) Antiparkinsonian activity of (+)-PHNO in the MPTP-treated common marmoset. Mov Disord 2:37–45
Nomoto M, Jenner P, Marsden CD (1988) The D1 agonist SKF 38393 inhibits the antiparkinsonian activity of the D2 agonist LY 171555 in the MPTP-treated marmoset. Neurosci Lett 93:275–280
Schultz W, Studer A, Jonsson G, Sundstrom E, Mefford I (1985) Deficits in behavioural initiation and execution processes in monkeys with 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine-induced parkinsonism. Neurosci Lett 59:225–232
Schultz W, Scarnati E, Sundstrom E, Tsutsumi T, Jonsson G (1986) The catecholamine uptake blocker nomifensine protects against MPTP-induced parkinsonism in monkeys. Exp Brain Res 63:216–220
Spencer H (1976) Antagonism of cortical excitation of striatal neurones by glutamate as an excitatory transmitter in the rat striatum. Brain Res 102:91–101
Witter A, Slangen JL, Terpstra GK (1973) Distribution of [3H]methyl-atropine in rat brain. Neuropharmacology 12:835–841
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Close, S.P., Elliott, P.J., Hayes, A.G. et al. Effects of classical and novel agents in a MPTP-induced reversible model of Parkinson's disease. Psychopharmacology 102, 295–300 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02244093
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02244093