Summary
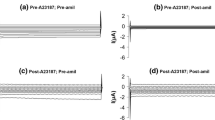
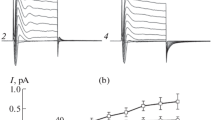
Ca2+-activated K+ channels were studied in cultured medullary thick ascending limb cells (MTAL) using the patch-clamp technique. The purpose was to determine the effect of acidic pH on channel properties in excised patches of apical cell membrane. At pH 7.4, increasing Ca2+ on the intracellular side or applying positive voltages increases channel open probability. Reducing pH to 5.8 on the intracellular face of the channel decreases channel open probability at each voltage and Ca2+ concentration. Channel mean open times display two distributions and mean closed times display three distributions. Increasing Ca2+ or applying depolarizing voltages lengthens each of the mean open times and shortens each of the closed times. Lowering pH to 5.8 decreases the mean open times and increases mean closed times at each Ca2+ and voltage with the greatest effect on the mean closed times. In contrast, both single-channel conductance and channel kinetics are unaffected when pH is reduced to 5.8 on the extracellular face of the membrane. We conclude that protons interfere with Ca2+ binding to the gate of Ca2+-activated K+ channels reducing the probability of channel opening.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berman, M., Shahn, E., Weiss, M. F. 1962. The routine fitting of kinetic data to models: A mathematical formalism for digital computers.Biophys. J. 2:275–287
Berman, M., Weiss, M. F. 1978. SAAM Manual US DHEW Publication No. (NIH) 78-180
Blair, L. A. C., Dionne, V. E. 1985. Developmental acquisition of Ca2+ sensitivity by K+ channels in spinal nerves.Nature (London) 315:329–331
Blatz, A. L., Magleby, K. L. 1987. Calcium-activated potassium channels.Trends Neurosci. 10(11):463–467
Bolivar, J. J., Cereijido, M. 1987. Voltage and Ca2+-activated K+ channel in cultured epithelial cells (MDCK).J. Membrane Biol. 97:43–51
Boundry, J. F., Stoner, L. C., Burg, M. B. 1976. The effects of lumen pH on potassium transport in renal cortical collecting tubules.Am. J. Physiol. 230:239–244
Burnham, C., Braw, R., Karlish, S. J. D. 1986. A Ca-dependent K channel in “luminal” membranes from the renal outer medulla.J. Membrane Biol. 93:177–186
Christensen, O., Zeuthen, T. 1987. Maxi K+ channels in leaky epithelia are regulated by intracellular Ca2+, pH and membrane potential.Pfluegers Arch. 408:249–259
Cook, D. L., Ikeuchi, M., Fijimodo, W. Y. 1984. Lowering pHi inhibits Ca2+-activated K+ channels in pancreatic B-cells.Nature (London) 311:269–273
Cornejo, M., Guggino, S. E., Guggino, W. B. 1987. Modification of Ca2+-activated K+ channels in cultured medullary thick ascending limb cells by N-bromoacetamide.J. Membrane Biol. 99:147–155
Frindt, G., Palmer, L. 1987. Ca2+-activated K+ channels in the apical membrane of the mammalian cortical collecting tubule and their role in K+ secretion.Am. J. Physiol. 252:F458-F467
Goligorsky, M. S., Hruska, K. A., Loftus, D. J., Elson, E. L. 1986. Alpha1-adrenergic stimulation and cytoplasmic free calcium concentration in cultured renal proximal tubular cells: Evidence for compartmentalization of Quin-2 and Fura-2.J. Cell. Physiol. 128:466–474
Golowasch, J., Kirkwood, H., Miller, C. 1986. Allosteric effects of Mg2+ on the gating of Ca2+-activated K+ channels from mammalian skeletal muscle.J. Exp. Biol. 124:5–13
Green, N., Algren, A., Hoyer, J., Triche, T., Burg, M. 1985. Differentiated lines of cells from rabbit renal medullary thick ascending limb grown on amnion.Am. J. Physiol. 249(18):97–104
Guggino, S. E., Guggino, W. B., Green, N., Sacktor, B. 1987a. Blocking agents of Ca2+-activated K+ channels in cultured medullary thick ascending limb cells.Am. J. Physiol. 252(21):C128-C137
Guggino, S. E., Guggino, W. B., Green, N., Sacktor, B. 1987b. Ca2+-activated K+ channels in cultured medullary thick ascending limb cells.Am. J. Physiol. 252(21):C123-C129
Hamill, O. P., Marty, A., Neher, E., Sakmann, B., Sigworth, F. I. 1981. Improved patch clamp technique for high resolution current recordings from cells and cell free membrane patches.Pfluegers Arch. 391:85–100
Hunter, M., Kawahara, K., Giebisch, G. 1986. Potassium channels along the nephron.Fed. Proc. 45(12):2723–2726
Latorre, R., Miller, C. 1983. Conduction and selectivity in potassium channels.J. Membrane Biol. 71:11–30
Malnic, G., Mello-Aires, M. de, Giebisch, G. 1971. Potassium transport across renal distal tubule during acid base disturbances.Am. J. Physiol. 211:1192–1971
Oberleithner, H., Kersting, U., Hunter, M. 1988. Cytoplasmic pH determines K+ conductance in fused renal epithelial cells.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 85:8345–8349
O'Neil, R. G., Sansom, S. C. 1984. Characterization of apical cell membrane Na+ and K+ conductances of cortical collecting dust using microelectrode techniques.Am. J. Physiol. 247:F14-F24
Pallotta, B. S. 1985. N-bromoacetamide removes a calcium-dependent component of channel opening from calcium-activated potassium channels in rat skeletal muscle.J. Gen. Physiol. 86:601–611
Stanton, B., Guggino, W. B., Giebisch, G. 1982. Acidification of the basolateral solution reduces potassium conductance of the apical membrane.Fed. Proc. 41:1006
Taniguchi, J., Guggino, W. B. 1989. A physiological stimulator of Ca2+-activated K+ channels in medullary thick ascending limb cells.Am. J. Physiol. (in press).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cornejo, M., Guggino, S.E. & Guggino, W.B. Ca2+-activated K+ channels from cultured renal medullary thick ascending limb cells: Effects of pH. J. Membrain Biol. 110, 49–55 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01870992
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01870992